What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Inflammatory Arthritis
There are several common symptoms to be mindful of, including joint pain and stiffness. These symptoms may occur after a nights sleep or after being sedentary. You may also notice a warm sensation in your joints, and redness and swelling in the joint area. In addition, you may see inflammation on your skin. Still, your doctor may also discover that your inflammatory arthritis is causing inflammation in internal organs, such as your heart and lungs. Over time, this disease will cause the affected joints to become deformed, unstable and scarred. Sadly, this damage cannot be repaired.
The joints typically affected by inflammatory arthritis include hands, feet and knees. Some people with this condition have periods of respite, followed by what is known as painful flare-ups. In addition to joint pain, inflammatory arthritis may also cause muscle aches, fatigue and low fevers. If you begin to notice these symptoms, it is essential to discuss them with your healthcare team right away. On the other hand, osteoarthritis typically causes pain, stiffness and a reduced range of motion localized to the affected joints.
Are There Any Home Remedies For Rheumatoid Arthritis
If someone has joint pain or stiffness, he or she may think it is just a normal part of getting older and that there is nothing he or she can do. Nothing could be further from the truth. There are several options for medical treatment and even more to help prevent further joint damage and symptoms. Discuss these measures with a health-care professional to find ways to make them work.
- First of all, don’t delay diagnosis or treatment. Having a correct diagnosis allows a health-care professional to form a treatment plan. Delaying treatment increases the risk that the arthritis will get worse and that serious complications will develop.
- Learn everything about rheumatoid arthritis. If there are any questions, ask a health-care professional. If any questions remain, ask the health-care professional to provide reliable sources of information. Some resources are listed later in this article.
- Know the pros and cons of all of treatment options, and work with a health-care professional to decide on the best options. Understand the treatment plan and what benefits and side effects can be expected.
- Learn about the symptoms. If someone has rheumatoid arthritis, he or she probably has both general discomfort and pain in specific joints. Learn to tell the difference. Pain in a specific joint often results from overuse. Pain in a joint that lasts more than one hour after an activity probably means that that activity was too stressful and should be avoided.
Increase physical activity.
What Is Arthritis In Cats
Just as us humans, cats also develop arthritis as they age. Arthritis, also commonly referred to as osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease , occurs when the cartilage cushion between the bones deteriorates. The adjacent bones rub against each other, causing pain, a decrease in joint movement, and inflammation. Joints such as hips, shoulders, knees, elbows are commonly affected however any joint can be affected by arthritis. Although arthritis is a progressive bone disease commonly affecting older animals, it is important to remember that it is not just a normal part of ageing. If actively managed with proper treatment and care, the course of the disease can be slowed and remaining joint function may be preserved so your cat can enjoy its golden years in comfort.
Don’t Miss: Is Peanut Butter Bad For Arthritis
What Are Causes And Risk Factors Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not known. Many risk factors are involved in the abnormal activity of the immune system that characterizes rheumatoid arthritis. These risk factors include
- genetics ,
- hormones , and
- possibly infection by a bacterium or virus.
Other environmental factors known to increase the risk for developing rheumatoid arthritis include
- silica exposure, and
- periodontal disease.
Medical scientists have shown that alterations in the microbiome exist in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Emerging research shows that the microbiome has an enormous influence on our health, immune system, and many diseases, even those previously not directly linked to the gastrointestinal tract. Studies have shown different kinds of bacteria in the intestines of people with rheumatoid arthritis than in those who do not have rheumatoid arthritis. However, it remains unknown how this information can be used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment is probably not as simple as replacing missing bacteria, but this may explain why some individuals with rheumatoid arthritis feel better with various dietary modifications.
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is based on a combination of factors, including:
- Morning stiffness that lasts at least one hour and has been present for at least six weeks
- Swelling of three or more joints for at least six weeks
- Swelling of the wrist, hand, or finger joints for at least six weeks
- Swelling of the same joints on both sides of the body
- Changes in hand x-rays that are hallmarks of rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatoid nodules of the skin
- Blood test that is positive for rheumatoid factor* and/or anti-citrullinated peptide/protein antibodies
* The rheumatoid factor may be present in people who do not have rheumatoid arthritis. Other diseases can also cause the rheumatoid factor to be produced in the blood. A test called CCP antibody can sometimes help to determine whether the rheumatoid factor antibody is due to rheumatoid arthritis or some other disease. This is why the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is based on a combination of several factors and NOT just the presence of the rheumatoid factor in the blood.
It is also important to note that not all of these features are present in people with early rheumatoid arthritis, and these problems may be present in some people with other rheumatic conditions.
In some cases, it may be necessary to monitor the condition over time before a definitive diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis can be made.
Don’t Miss: Best Thing For Arthritic Knees
Symptoms By Body Part
The most commonly affected areas during the onset of RA are the small joints in your hands and feet. This is where you may first feel stiffness and an ache.
Its also possible for RA inflammation to affect your knees and hips. Because the disease presents differently in different people, it can go on to affect almost any joint.
Your organs are another area that can be disrupted by RA inflammation:
- Your heart muscle can become damaged.
- Your lungs can become scarred.
- Blood vessel damage can lead to subsequent skin and nerve issues.
How Is Ra Treated
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs biological response modifiers are medications that are an effective second-line treatment. In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
Don’t Miss: Cure For Arthritis In Hands
What Is The Prognosis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
As a rule, the severity of rheumatoid arthritis waxes and wanes. Periods of active inflammation and tissue damage marked by worsening of symptoms are interspersed with periods of little or no activity, in which symptoms get better or go away altogether . The duration of these cycles varies widely among individuals.
Outcomes are also highly variable. Some people have a relatively mild condition, with little disability or loss of function. Others at the opposite end of the spectrum experience severe disability due to pain and loss of function. Disease that remains persistently active for more than a year is likely to lead to joint deformities and disability. Approximately 40% of people have some degree of disability 10 years after their diagnosis. For most, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic progressive illness, but about 5%-10% of people experience remission without treatment. This is uncommon, however, after the first three to six months.
Rheumatoid arthritis is not fatal, but complications of the disease shorten life span by a few years in some individuals. Although generally rheumatoid arthritis cannot be cured, the disease gradually becomes less aggressive and symptoms may even improve. However, any damage to joints and ligaments and any deformities that have occurred are permanent. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect parts of the body other than the joints.
What Are Medical Treatments For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a progressive inflammatory disease. This means that unless the inflammation is stopped or slowed, the condition will continue to worsen with joint destruction in most people. Although rheumatoid arthritis does occasionally go into remission without treatment, this is rare. Starting treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is strongly recommended. The best medical care combines medication and nondrug approaches.
Nondrug approaches include the following:
Drug approaches include a variety of medications used alone or in combinations.
Also Check: Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Curable
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
What Are The Different Types Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis usually begin gradually in several joints. Sometimes the symptoms begin only in one joint, and sometimes the symptoms begin initially in the whole body, with generalized stiffness and aching, and then localize to the joints.
- Typical “classic” rheumatoid arthritis is the most common type of rheumatoid arthritis. Classic rheumatoid arthritis involves three or more joints. Usually, people have a gradual onset of joint pain, stiffness, and joint swelling, usually in the fingers, wrists, and forefeet. Elbows, shoulders, hips, ankles and knees are also commonly affected.
- About 80% of people with rheumatoid arthritis are classified as “seropositive,” which simply means the rheumatoid factor blood test is abnormal. Some people with an abnormal rheumatoid factor also have an abnormal anti-CCP blood test. This is another blood test for rheumatoid arthritis.
- Approximately 20% of people with rheumatoid arthritis are classified as “seronegative,” which means the rheumatoid factor blood test is negative, or normal. In this case, the anti-CCP blood test may be abnormal or normal. Other blood tests, such as the ESR measure of inflammation, may be abnormal.
Palindromic rheumatism
Atypical presentations of RA
- Persistent arthritis of just one joint may be the first symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in some people.
- Some people experience generalized aching, stiffness, weight loss, and fatigue as their initial symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Recommended Reading: Vicks Vaporub For Joint Pain
In Summary If You Experience The Following Symptoms Its Time To Schedule An Appointment With Your Primary Care Provider:
- Symmetrical joint pain
- Swelling and tenderness in three or more joint areas for at least six weeks
- Stiffness that lasts more than an hour
- Subtle and general symptoms such as anorexia, fever, fatigue
Also, understand that these symptoms alone are not enough to diagnose inflammatory arthritis. Bone changes and the presence of auto-antibodies will need to be tested. The earlier you get diagnosed, the more likely you can improve your quality of life.
1 Firestein GS. Etiology and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Ruddy S, Harris E, Sledge C : Kellys Textbook of Rheumatology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 2001, 921-966.
2 Scott D, Kingsley G, Scott D. Inflammatory Arthritis in Clinical Practice. London: Springer 2008.
3 Gonzalez-Lopez L, Gamez-Nava JI, Jhangri G, et al. Decreased progression to rheumatoid arthritis or other connective tissue diseases in patients with palindromic rheumatism treated with antimalarials. J Rheumatol 2000 27:41.
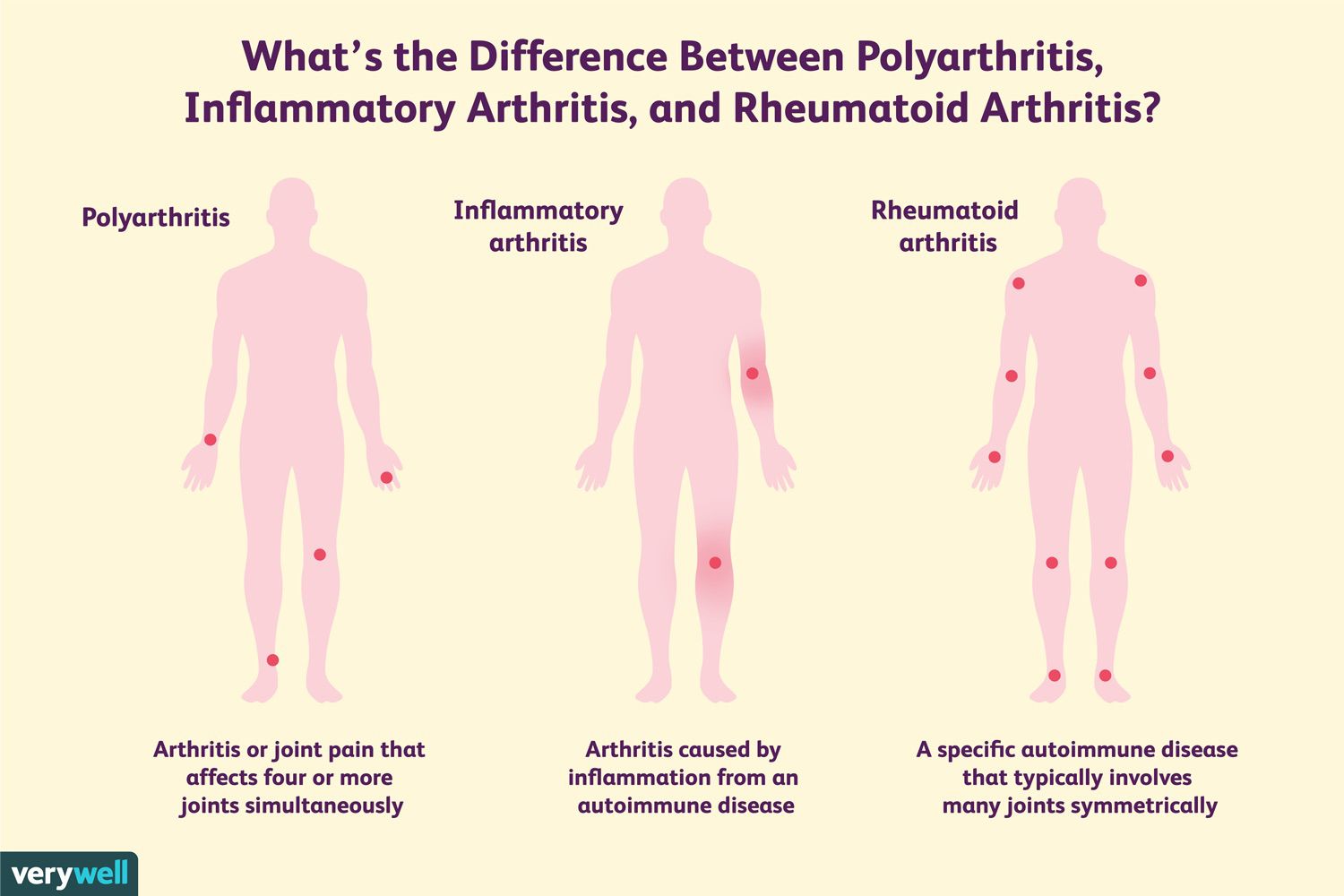
Types Of Inflammatory Arthritis
The three most common types of chronic inflammatory arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. But, there are others as well. In patients who exhibit musculoskeletal symptoms, inflammatory conditions that do not have joint involvement may include bursitis, tendinitis, or polymyalgia rheumatica. Patients who have one to three joints involved may have an acute inflammatory condition such as infectious arthritis, gout, pseudogout, Reactive arthritis, or Chlamydial arthritis or a chronic inflammatory condition such as psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, pauciarticular juvenile arthritis, or infectious arthritis that is slow to heal. Patients who have four or more joints involved may have acute inflammatory conditions such as viral arthritis, drug-induced arthritis, early connective tissue disease, rheumatic fever, palindromic rheumatism, or remitting seronegative symmetrical synovitis with pitting edema or chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, undifferentiated polyarthritis, inflammatory osteoarthritis, mixed connective tissue disease, lupus, scleroderma, polyarticular juvenile arthritis, or adult Still’s disease.
You May Like: Is Arthritis Acute Or Chronic
Can I Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis
You cannot prevent rheumatoid arthritis because the cause of the disease is not known.
Quitting smoking, or never smoking, will reduce your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. You are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis if someone in your close family has it, but unfortunately there is no way to reduce this risk.
People who have rheumatoid arthritis often experience flare ups, which are times when their joints are particularly sore. Learning what triggers your flare ups can help reduce or prevent them.
For some people, stress can trigger a flare up, so can being run down or pushing yourself beyond your limits. Having an infection, missing a dose of your medicine or changing your treatment plan can also cause a flare up.
Keeping a food and activity diary may help work out your personal triggers but keep in mind that sometimes flare ups happen without any obvious cause.
What Are The Best Foods For Arthritis
There is no strict diet to cure arthritis. There are certain food products, which have a number of health benefits and can also reduce inflammation in the body. These foods include fish, carrot, oranges, berries, grapes, green leafy vegetables, olives, and other food products rich in omega-3 fatty acids, calcium and vitamin C.
You May Like: Finger Joint Swelling Treatment
What Symptoms Look And Feel Like And What To Do If You Can’t Shake The Ache
by Michelle Crouch, AARP, Updated December 20, 2021
En español |It’s not unusual to experience pain in your joints on occasion, especially if you’re active and participate in high-impact activities such as running. That unwanted ouch can be caused by injured muscles, tendons and ligaments around the joint or by tendonitis, a sprain or a strain.
But if you start experiencing aching, pain and stiffness on a routine basis and particularly if the pain is right at the joint you may be developing arthritis, says rheumatologist Uzma Haque, M.D., codirector of clinical operations at the Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center in Baltimore.
Your risk of arthritis increases as you age, and its a leading cause of disability in the U.S., affecting around 58.5 million people, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Managed
You can manage rheumatoid arthritis by taking medicines as prescribed to treat pain and joint inflammation. You can also help reduce symptoms by exercising and maintaining a healthy weight. Aim to do 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This can be at one time or broken up into shorter sessions.
You may also need to make changes at home to help you manage daily tasks like cleaning or gardening. An occupational therapist can help you make adjustments if pain or joint stiffness makes certain tasks hard to complete. They can recommend tools to reduce strain on your joints, such as long-handled dustpans so you dont need to bend over, or book holders to reduce the strain on your hands and wrists.
You might find that rheumatoid arthritis makes you frustrated and upset. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause poor sleep, which can also make you feel down. Discus your feelings with friends and family and explain to them what they can do to support you. This may help you feel better and reassured that help is available, if needed. If you are struggling with a low mood or not managing to sleep, your doctor will be able to support you and work with you to build a plan to help.
Don’t Miss: Can Osteoarthritis Turn Into Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Do Doctors Diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no single test that shows whether you have RA. Your doctor will give you a checkup, ask you about your symptoms, and possibly perform X-rays and blood tests.
Rheumatoid arthritis is diagnosed from a combination of things, including:
- The location and symmetry of painful joints, especially the hand joints
- Joint stiffness in the morning
- Bumps and nodules under the skin
- Results of X-rays and blood tests