Causes And Risk Factors
Doctors donât know exactly what causes this disease. But they know these things could be risk factors for RA:
Age. RA can affect you at any age, but itâs most common between 40 and 60. It isnât a normal part of aging.
Family history. If someone in your family has it, you may be more likely to get it.
Environment. A toxic chemical or infection in your environment can up your odds.
Gender. RA is more common in women than men. Itâs more likely in women who’ve never been pregnant and those who’ve recently given birth.
Obesity. Extra weight, especially if youâre under 55.
Smoking. If your genes already make you more likely to get RA, lighting up can raise your odds even higher. And if you do get the disease, smoking can make it worse.
Your Ra Treatment Plan
As soon as youre diagnosed with RA, your doctor will likely prescribe disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs .
These drugs, which include newer biologic medications, can be extremely effective at slowing or even stopping the progression of RA.
In addition, another effective course of treatment developed in recent years can be antifibrotic agents such as nintedanib , especially if theres an impact on the lungs.
Your doctor may recommend additional prescription drugs, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen, and regular exercise or physical therapy.
Here youll find answers to additional questions about RA.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Ra
With RA, there are times when symptoms get worse, known as flares, and times when symptoms get better, known as remission.
Signs and symptoms of RA include:
- Pain or aching in more than one joint
- Stiffness in more than one joint
- Tenderness and swelling in more than one joint
- The same symptoms on both sides of the body
You May Like: What Is The Worst Vegetable For Arthritis
What Are The Four Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stage 1: In early stage rheumatoid arthritis, the tissue around your joint is inflamed. You may have some pain and stiffness. If your provider ordered X-rays, they wouldnt see destructive changes in your bones.
- Stage 2: The inflammation has begun to damage the cartilage in your joints. You might notice stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
- Stage 3: The inflammation is so severe that it damages your bones. Youll have more pain, stiffness and even less range of motion than in stage 2, and you may start to see physical changes.
- Stage 4: In this stage, the inflammation stops but your joints keep getting worse. Youll have severe pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of mobility.
What Is Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Arthritis doesn’t affect young people as much as it does adults, but lots of teens still get it. Arthritis is an of the synovial membrane, which lines the joints . When it becomes inflamed, fluid is produced. The joints can become stiff, swollen, painful, and warm to the touch. Over time, inflammation in a joint can damage the cartilage and bone.
“Idiopathic” is a medical word that doctors use to describe a disease that has no known cause. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is the most common kind of arthritis among kids and teens. Kids usually find out they have this disease between the ages of 6 months and 16 years.
You May Like: Is Cherries Good For Arthritis
Medical History And Physical Examination
After listening to your symptoms and discussing your general health and medical history, your doctor will examine your foot and ankle.
Skin. The location of callouses indicate areas of abnormal pressure on the foot. The most common location is on the ball of the foot . If the middle of the foot is involved, there may be a large prominence on the inside and bottom of the foot. This can cause callouses.
Foot shape. Your doctor will look for specific deformities, such as bunions, claw toes, and flat feet.
Flexibility. In the early stages of RA, the joints will typically still have movement. As arthritis progresses and there is a total loss of cartilage, the joints become very stiff. Whether there is motion within the joints will influence treatment options.
Tenderness to pressure. Although applying pressure to an already sensitive foot can be very uncomfortable, it is critical that your doctor identify the areas of the foot and ankle that are causing the pain. By applying gentle pressure at specific joints your doctor can determine which joints have symptoms and need treatment. The areas on the x-ray that look abnormal are not always the same ones that are causing the pain.
What Is The Difference
Rheumatoid arthritis vs. osteoarthritis
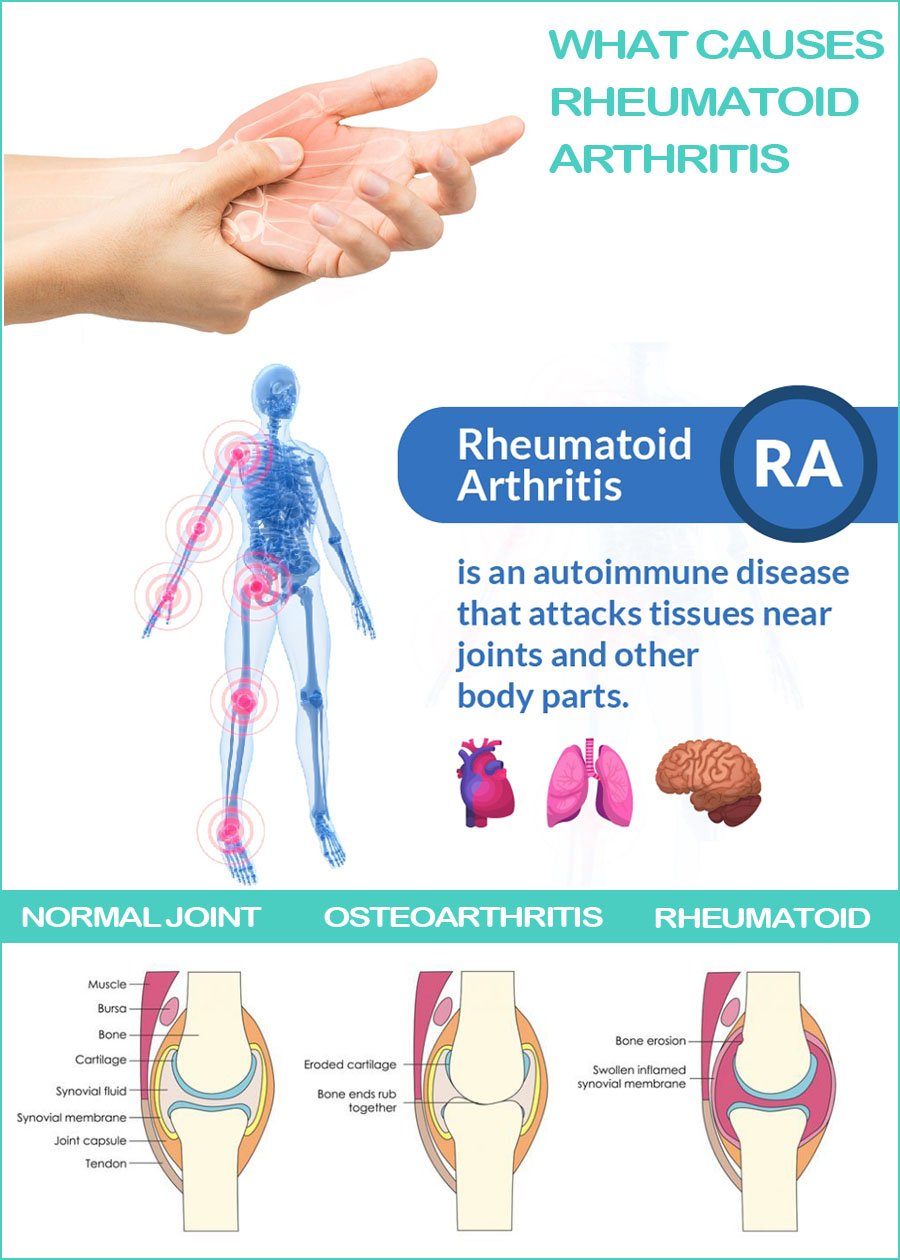
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are both common causes of pain and stiffness in joints. But they have different causes. In osteoarthritis, inflammation and injury break down your cartilage over time. In rheumatoid arthritis, your immune system attacks the lining of your joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis vs. gout
Rheumatoid arthritis and gout are both painful types of arthritis. Gout symptoms include intense pain, redness, stiffness, swelling and warmth in your big toe or other joints. In gout, uric acid crystals cause inflammation. In rheumatoid arthritis, its your immune system that causes joint damage.
Read Also: How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Different From Arthritis
Read Also: What Helps Arthritis In The Lower Back
Recognizing Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Jasmine was experiencing the onset of rheumatoid arthritis, says Anders Peck, M.D., a rheumatologist at The Seattle Arthritis Clinic at Northwest Outpatient Medical Center and Jasmines doctor.
Its not like one day you wake up and everything is terrible, but severe pain and stiffness can start and worsen over a course of several days to a week. People might notice significant stiffness in the morning and swollen joints without any mechanical trigger. They may find that they have difficulties doing simple things such as lifting a coffee cup, writing or buttoning a shirt, says Peck.
Symmetrical joint swelling is also an identifying characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis. The pain and inflammation that started in Jasmines right elbow joint and then affected her left elbow is a classic manifestation.
Its best to go to a doctor on the early side of recognizing symptoms such as these.
Its important to treat rheumatoid arthritis early after it starts. It is an autoimmune disease and may be easier to treat before the immune system becomes established in an abnormal pattern. Early treatment also helps to prevent the likelihood of severe damage to the joints in the future, says Peck.
But it can sometimes be challenging for young women who are otherwise healthy to recognize what theyre experiencing as symptoms of a disease.
I would take a lot of really long, hot showers. And I would sleep, says Jasmine.
Recommended Reading: Does Ilumya Treat Psoriatic Arthritis
Ra Progression Isnt Inevitable
Thanks to the newer treatments available and more on the horizon RA doesnt have to mean a life of eventual disability or even limited mobility. Its not an inevitable thing nowadays, says Dr. Bhatt. People can have a normal life.
But patients do have to be sure to follow their treatment plan and doctors recommendations. Routine follow-up with a rheumatologist who performs joint exams, follows levels of systemic inflammation in the blood and can assess function is the best way to ensure RA is being controlled and is not progressing, Dr. Lally says.
Recommended Reading: What Arthritis Feels Like In Hands
Read Also: Is Honey Good For Arthritis Pain
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
What It Feels Like To Have Ra + Oa
Although everyone is different, a typical day with both forms of arthritis might look like this: You wake up with the morning joint stiffness and pain characteristic of RA, says Dr. Bhatt. Those symptoms ease up after a few hours and with activity. Later in the day and after more activity, the pain and stiffness come roaring back, the classic end-of-day MO of OA. The pain with RA tends to occur when youre at rest, while OA aches are more likely to happen with movement. In addition to those OA aches, you might also notice a grating sensation or sound of bone on bone when you use a particular joint.
You May Like: Can You Have Psoriatic Arthritis And Not Have Psoriasis
What Are The Goals Of Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
The most important goal of treating rheumatoid arthritis is to reduce joint pain and swelling. Doing so should help maintain or improve joint function. The long-term goal of treatment is to slow or stop joint damage. Controlling joint inflammation reduces your pain and improves your quality of life.
How Your Ra Treatment Plan Prevents Disease Progression
Perhaps the biggest factor that affects how RA progresses is if youre in treatment with a specialist who can put you on medications to slow the disease. Being on a DMARD or biologic therapy for RA is the best way to prevent progression, Dr. Lally says.
Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs are usually the first line in medication. Methotrexate is the anchor drug for rheumatoid arthritis, Dr. Bhatt says. Some patients are scared because methotrexate is also used for cancer chemotherapy so they dont want to take a chemo pill, but those we use for RA are a very small dose with lesser chance of side effects. Your doctor will reassess in a month or so and see if its necessary to add in other drugs.
If after three to six months they have still not responded then we progress to medications called biologics, Dr. Bhatt says. These genetically engineered drugs target the inflammation process specifically, and are usually self-injected or infused via IV in your doctors office or a medical center. There are sub-classes and different types, Dr. Bhatt says. Your doctor will try various medications to see which you respond best to.
Recommended Reading: Which Is Better For Arthritis Heat Or Ice
How To Avoid Complications Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis can also affect the nerves in the body which is why a lot of patients experience numbness and sharp pain in affected areas. The condition is definitely alarming. It affects more parts of the body than you think. And does not just affect your joints as bones like most of the people say. It can also affect vital organs and affect your vision as well as your nerves. So, is vital to treat this condition as soon as possible to avoid complications of rheumatoid arthritis.
Dont Miss: Whats Bad For Arthritis
Can I Do Anything To Prevent Ra
Thereâs no way to prevent RA, but you can lower your chances if you:
Quit smoking. Itâs the one sure thing besides your genes that boosts your odds of getting RA. Some studies show it also can make the disease get worse faster and lead to more joint damage, especially if youâre ages 55 or younger. If youâre overweight and a smoker, your chances of developing RA go up.
Take care of your gums: New research shows a link between RA and periodontal disease. Brush, floss, and see your dentist for regular checkups.
Even though thereâs nothing you can do to ensure you wonât get it, keep in mind that early treatment can make your symptoms less painful and save your joints from damage. Ideally, you should begin treatment within 3 to 6 months of your first symptoms.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: What Supplements Good For Arthritis
Helping Your Child Live With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Help your child manage his or her symptoms by sticking to the treatment plan. This includes getting enough sleep. Encourage exercise and physical therapy and find ways to make it fun. Work with your childâs school to make sure your child has help as needed. Work with other caregivers to help your child take part as much possible in school, social, and physical activities. Your child may also qualify for special help under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. You can also help your child find a support group to be around with other children with JIA.
What Are The Early Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early signs of rheumatoid arthritis include tenderness or pain in small joints like those in your fingers or toes. Or you might notice pain in a larger joint like your knee or shoulder. These early signs of RA are like an alarm clock set to vibrate. It might not always been enough to get your attention. But the early signs are important because the sooner youre diagnosed with RA, the sooner your treatment can begin. And prompt treatment may mean you are less likely to have permanent, painful joint damage.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Pain Medication For Psoriatic Arthritis
Gout And Calcium Crystal Diseases
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that can cause painful swelling in joints. It typically affects the big toe, but it can also affect other joints in the body.
Joints affected by gout can become red and hot. The skin may also look shiny and can peel.
Its caused by having too much urate, otherwise known as uric acid, in the body. We all have a certain amount of urate in our body.
However, being overweight or eating and drinking too much of certain types of food and alcoholic drinks can cause some people to have more urate in their bodies. The genes you inherit can make you more likely to develop gout.
If it reaches a high level, urate can form into crystals that remain in and around the joint. They can be there for a while without causing any problems and even without the person realising they are there.
A knock to a part of the body or having a fever can lead to the crystals falling into the soft part of the joint. This will cause pain and swelling.
There are drugs that can reduce the amount of urate in the body and prevent gout attacks. Examples are allopurinol and . If youre having a gout attack, youll also need short-term pain relief. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as well as paracetamol can be good drugs to try first.
Men can get gout from their mid-20s, and in women its more common after the menopause. Taking water tablets can increase the risk of gout.
There are also conditions that cause calcium crystals to form in and around joints.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis
Many people confuse rheumatoid arthritis with osteoarthritis due to their similar symptoms, but the two diseases are caused by different factors.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Whereas rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes joint malfunction due to inflammation, osteoarthritis is a mechanical disease brought on by the destruction of joints through wear and tear.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, with approximately 27 million Americans over the age of 25 having been diagnosed with it. Osteoarthritis is also most commonly seen in people middle-aged to elderly and is the top cause of disability in those age groups, though it can also appear in younger people who have sustained joint injuries.
With osteoarthritis, the cartilage, joint lining, ligaments, and bone are all affected by deterioration and inflammation. When the cartilage begins to break down due to stress or changes in the body, the surrounding bones slowly get bigger and begin to fail.
Osteoarthritis is a slowly progressing disease and occurs in the joints of the hand, spine, hips, knees, and toes. Furthermore, risk factors of this disease most often stem from lifestyle or biological causes, such as:
Osteoarthritis sometimes occurs alongside rheumatoid arthritis or other disease, such as gout.
You May Like: How To Diagnose Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
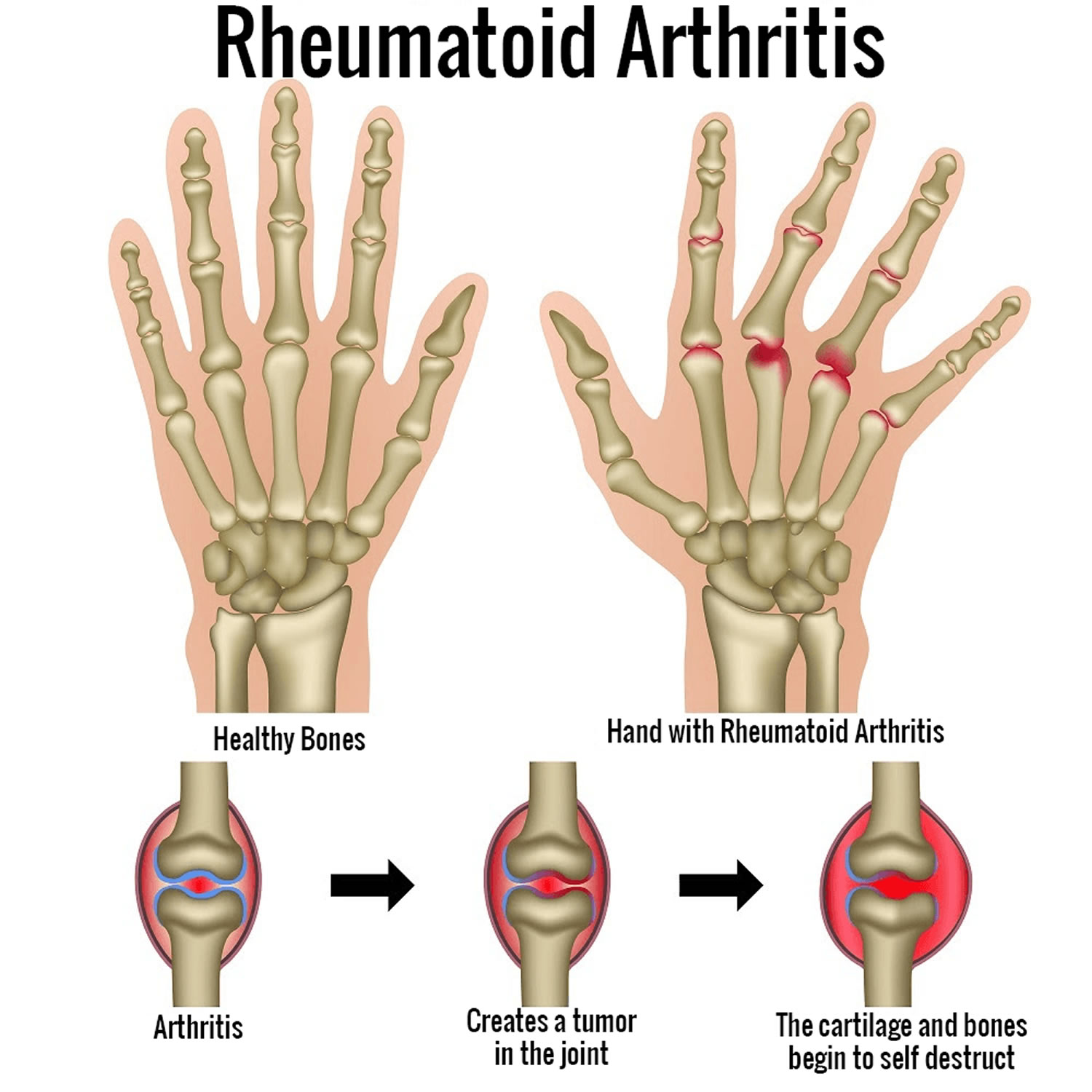
What Happens In Rheumatoid Arthritis
Doctors do not know why the immune system attacks joint tissues. However, they do know that when a series of events occurs, rheumatoid arthritis can develop. This series of events includes:
- A combination of genes and exposure to environmental factors starts the development of RA.
- The immune system may be activated years before symptoms appear.
- The start of the autoimmune process may happen in other areas of the body, but the impact of the immune malfunction settles in the joints.
- Immune cells cause inflammation in the inner lining of the joint, called the synovium.
- This inflammation becomes chronic, and the synovium thickens due to an increase of cells, production of proteins, and other factors in the joint, which can lead to pain, redness, and warmth.
- As RA progresses, the thickened and inflamed synovium pushes further into the joint and destroys the cartilage and bone within the joint.
- As the joint capsule stretches, the forces cause changes within the joint structure.
- The surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tendons that support and stabilize the joint become weak over time and do not work as well. This can lead to more pain and joint damage, and problems using the affected joint.