Ra And The Ocular System
The inflammation caused by RA can affect your ocular system, a.k.a. your eyes. The most common symptom is dry eye. People with rheumatoid arthritis are also more likely to have Sjogrens syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that causes dry eye. Dry eye can be more than uncomfortable. Untreated, it may lead to infections and scarring on the outer layer of your eye, known as the cornea.
In up to about 5% of people with RA, inflammation can develop in or around the whites of the eyes, a condition called uveitis. This can cause pain, swelling, and sensitivity to light. should relieve eye symptoms. However, in rare cases, the damage may be permanent or result in blindness or the loss of the eye.
Stop Hand Cramps Before They Start
Better yet, aim to prevent muscle cramps in the first place. Keeping hand muscles strong will help prevent muscle fatigue, so exercises can decrease cramps long term, Weselman explains. Try repetitive finger tapping , or squeezing silly putty or a stress ball.
RELATED: 6 Exercises for Rheumatoid Arthritis Hand Pain Relief
If muscle cramps or hand pain persists, occurs often, or interferes with everyday activities, talk with your doctor, who can look for signs of underlying causes such as poor circulation, dehydration, poor nutrition, kidney disease, or electrolyte imbalances due to medication. In some cases, muscle atrophy could be related to injury, muscle abnormality, or a neurological condition.
Recommended Reading: Autoimmune Leg Pain
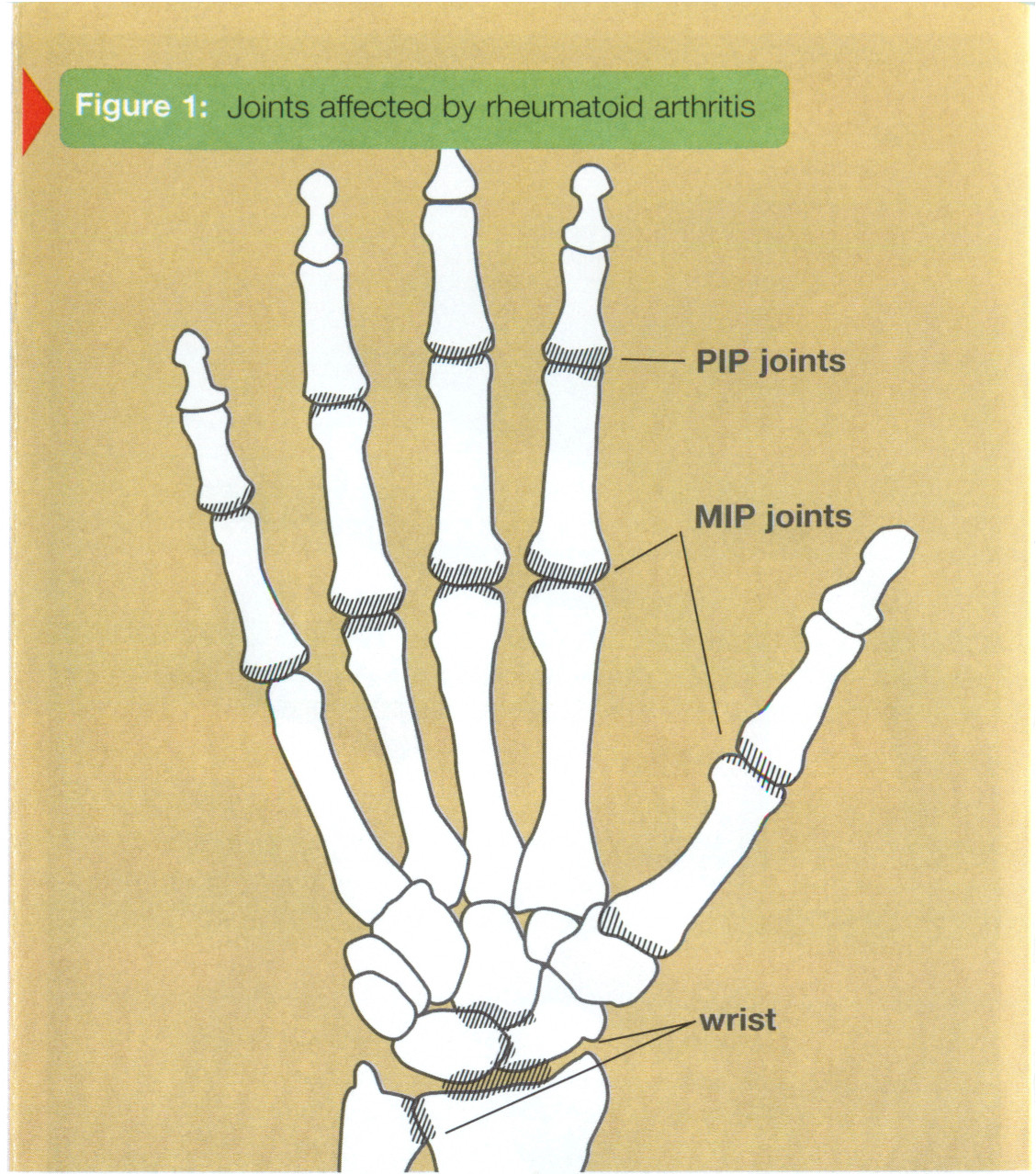
Symptoms Of Ra Can Occur In Any Of The Bodys Joints Including Your:
As the disease progresses, cartilage and bone are damaged and destroyed. Eventually, supporting tendons, ligaments, and muscles weaken. This can lead to a limited range of motion or difficulty moving the joints properly. In the long term, joints can become deformed.
Having RA also puts you at greater risk of developing osteoporosis, a weakening of the bones. This in turn can increase your risk of bone fractures and breaks.
Chronic inflammation of the wrists can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome, making it difficult to use your wrists and hands. Weakened or damaged bones in the neck or cervical spine can cause chronic pain.
Your doctor may order X-rays to investigate the extent of joint and bone damage from RA.
Recommended Reading: Why Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Fatigue
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis
Many people confuse rheumatoid arthritis with osteoarthritis due to their similar symptoms, but the two diseases are caused by different factors.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Whereas rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes joint malfunction due to inflammation, osteoarthritis is a mechanical disease brought on by the destruction of joints through wear and tear.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, with approximately 27 million Americans over the age of 25 having been diagnosed with it. Osteoarthritis is also most commonly seen in people middle-aged to elderly and is the top cause of disability in those age groups, though it can also appear in younger people who have sustained joint injuries.
With osteoarthritis, the cartilage, joint lining, ligaments, and bone are all affected by deterioration and inflammation. When the cartilage begins to break down due to stress or changes in the body, the surrounding bones slowly get bigger and begin to fail.
Osteoarthritis is a slowly progressing disease and occurs in the joints of the hand, spine, hips, knees, and toes. Furthermore, risk factors of this disease most often stem from lifestyle or biological causes, such as:
Osteoarthritis sometimes occurs alongside rheumatoid arthritis or other disease, such as gout.
Is There A Cure For Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no cure yet, however, we now know a great deal about what causes RA, and how to control it and prevent joint damage. This is achieved by the early implementation of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs . These are essential to gain rapid control of the disease, in order to avoid joint erosions and long-term limitation of function.
You May Like: What’s The Difference Between Gout And Arthritis
How Arthritis Can Affect The Spine And How It Is Treated
Arthritis is a painful condition affecting millions of people. When it hits the spine, the results can be debilitating and may even require surgery.
But the prognosis for arthritis of the spine is dependent on the way arthritis has manifested itself. Treatment may range from physical therapy and targeted mobility exercises to surgical intervention. Lets take a look at how arthritis can affect the spine and how it is treated.
Also Check: Peanuts And Arthritis
Arthritis In Certain Parts Of The Body Can Make It More Difficult To Walk Heres How To Deal With These Changes In Your Gait And Remain Mobile
Having arthritis in your hips, knees, ankles, or feet can making walking harder a side effect that can have consequences for your daily well-being and quality of life. I found myself limping to avoid pain, arthritis patient Lisa H. told us on Facebook. It got to the point where my daughter would imitate my walk, which made me realize I needed some help.
Managing the underlying disease, physical therapy to help correct your movements, and possibly using assistive devices or shoes can help you minimize changes to your gait and retain your independence and mobility.
Also Check: Are Eggs Bad For Psoriatic Arthritis
Read Also: Is Tumeric Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Ra And The Musculoskeletal System
The primary way this disease affects your body is through whats known as the musculoskeletal system. This is basically what it sounds like: a system of muscles and skeletal structures like bones that give your body support and stability so that you can actually move. When rheumatoid arthritis attacks your musculoskeletal system, it makes it harder for you to perform even the most basic physical activities. The disease affects each part of the system in slightly different ways. Lets take a closer look.
Stage : Antibodies Develop And Swelling Worsens
In many cases, RA progresses to the second stage without being diagnosed. In the second stage the body makes the antibodies and the joints start swelling up, Dr. Bhatt says. It can affect other organ systems and cause inflammation there: the lungs, the eyes, a skin rash, and it can even affect the heart. Lumps on the elbows called rheumatoid nodules may also develop.
When it comes to imaging results, the second stage is more confirmative for the diagnosis, Dr. Bhatt says. It has kind of a moth-eaten, chipped off appearance on the X-rays. Ultrasound can also be done, and the most sensitive is an MRI, which would pick up if there are any problems even if the X-ray is normal.
You May Like: Is Garlic Good For Arthritis
Everyday Life With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis causes joint pain and swelling, reduced mobility and physical weakness. General tiredness, trouble sleeping and exhaustion are other common symptoms. All of these symptoms can greatly affect your everyday life and overall wellbeing.
Living with rheumatoid arthritis isn’t always easy. One reason is because it’s often difficult to predict the symptoms: They may get better or worse the next day it’s hard to know in advance. Having a “bad” day can be very difficult and make some people feel like they have fallen down into a deep dark hole. This can be made worse by worries about the future because it’s so difficult to predict how the condition might develop in each person. But various treatments can stop the condition from getting worse or slow it down.
Key Points About Rheumatoid Arthritis
- RA is a long-term that causes joint inflammation.
- RA can also affect many nonjoint areas such as the lungs, heart, skin, nerves, muscles, blood vessels, and kidneys.
- RA may cause deformities in the joints of the finger, making movement difficult.
- The joints most often affected by RA are in the hands, wrists, feet, ankles, knees, shoulders, and elbows.
- Symptoms may include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling decreased and painful movement bumps over small joints and fatigue or fever.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Arthritis In Your Fingers
What Are Complications Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Common complications of rheumatoid arthritis include the following:
Overall, the rate of premature death is higher in people with rheumatoid arthritis than in the general population. The most common causes of premature death in people with rheumatoid arthritis are infection, vasculitis, and poor nutrition. Fortunately, the manifestations of severe, long-standing disease, such as nodules, vasculitis, and deforming are becoming less common with optimal treatments.
Also Check: Rheumatoid Arthritis Leg Pain At Night
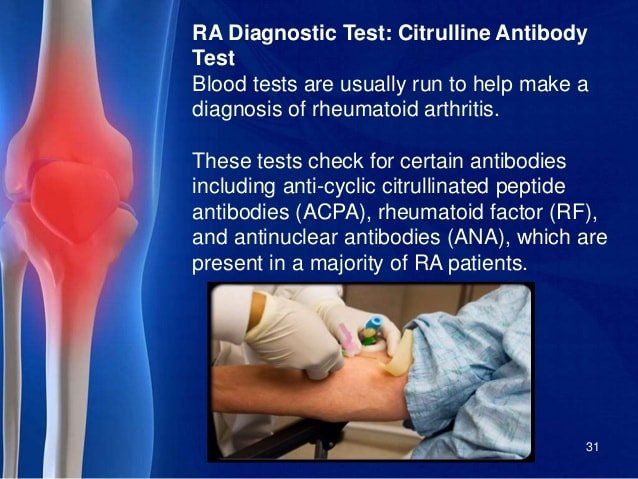
What Tests Are Done For Rheumatoid Arthritis
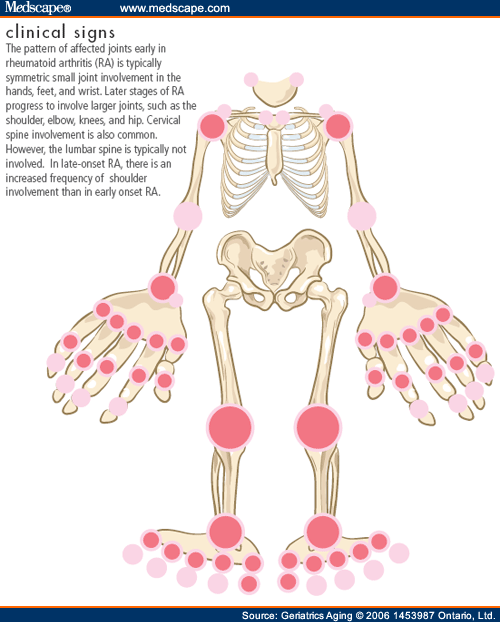
The diagnosis of RA is based on a person’s clinical signs and symptoms, but it is supported by laboratory tests, including X-rays and various blood tests, including but not exclusively the rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP.
If a person exhibits a clinical pattern of symptoms and signs that suggestive they have rheumatoid arthritis, a variety X-rays and blood tests will be performed. Certain blood tests can help to confirm the diagnosis, but a negative test does not necessarily mean a person does not have RA.
Approximately half of people developing rheumatoid arthritis will have blood test results that demonstrate inflammation. These tests are called acute phase reactants. Examples of these are an erythrocyte sedimentation rate and a C-reactive protein . These tests are performed to assess the activity of the disease in combination with an assessment of the patients symptoms and physical findings.
Read Also: What Is Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
How Rheumatoid Arthritis Threatens Bone Health
RA can increase your risk of osteoporosis, a disease in which bones become less dense and more fragile, increasing the likelihood they will break.
The reason: The inflammation of RA accelerates the normal bone resorption when bone tissue is broken down to release minerals into the blood that leads to osteoporosis. Normally, the bone tissue thats broken down gets replaced, but as we age, the rate of resorption exceeds the rate of new bone growth, reducing bone mass and setting the stage for osteoporosis. RA makes it even harder for bones to keep pace. The hip, forearm and pelvis are typical sites where breaks can occur, although breaks are more likely near the joints where the RA is active.
Steroids, which are sometimes used to control RA, can especially speed bone loss.
The best way to protect bones: Eat calcium-rich and vitamin Drich foods like eggs and fish, as well as D-fortified foods do weight-bearing exercises that your doctor approves if you smoke, quit and get a bone mineral density test so your doctor can consider whether you need medication.
Ra Progression Isnt Inevitable
Thanks to the newer treatments available and more on the horizon RA doesnt have to mean a life of eventual disability or even limited mobility. Its not an inevitable thing nowadays, says Dr. Bhatt. People can have a normal life.
But patients do have to be sure to follow their treatment plan and doctors recommendations. Routine follow-up with a rheumatologist who performs joint exams, follows levels of systemic inflammation in the blood and can assess function is the best way to ensure RA is being controlled and is not progressing, Dr. Lally says.
Read Also: Which Body System Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Affect
What Are The Complications Of Ra
Rheumatoid arthritis has many physical and social consequences and can lower quality of life. It can cause pain, disability, and premature death.
- Premature heart disease. People with RA are also at a higher risk for developing other chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. To prevent people with RA from developing heart disease, treatment of RA also focuses on reducing heart disease risk factors. For example, doctors will advise patients with RA to stop smoking and lose weight.
- Obesity. People with RA who are obese have an increased risk of developing heart disease risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Being obese also increases risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. Finally, people with RA who are obese experience fewer benefits from their medical treatment compared with those with RA who are not obese.
- Employment. RA can make work difficult. Adults with RA are less likely to be employed than those who do not have RA. As the disease gets worse, many people with RA find they cannot do as much as they used to. Work loss among people with RA is highest among people whose jobs are physically demanding. Work loss is lower among those in jobs with few physical demands, or in jobs where they have influence over the job pace and activities.
How Is Ra Diagnosed
RA is diagnosed by reviewing symptoms, conducting a physical examination, and doing X-rays and lab tests. Its best to diagnose RA earlywithin 6 months of the onset of symptomsso that people with the disease can begin treatment to slow or stop disease progression . Diagnosis and effective treatments, particularly treatment to suppress or control inflammation, can help reduce the damaging effects of RA.
You May Like: What Tests Are Done To Diagnose Psoriatic Arthritis
How Does A Normal Joint Work
A joint is where two bones meet. Most of our joints are designed to allow the bones to move in certain directions and within certain limits.
For example, the knee is the largest joint in the body and one of the most complicated. It must be strong enough to take our weight and must lock into position, so we can stand upright.
It also has to act as a hinge, so we can walk, and needs to twist and turn when we run or play sports.
The end of each bone is covered with cartilage that has a very smooth, slippery surface. The cartilage allows the ends of the bones to move against each other, almost without rubbing.
The joint is held in place by the synovium, which contains thick fluid to protect the bones and joint.
The synovium has a tough outer layer that holds the joint in place and stops the bones moving too far.
Strong cords called tendons anchor the muscles to the bones.
Arthritic And Rheumatological Causes Of Chest Wall Pain
| Arthritic and Rheumatic diseases causes of chest wall pain | Less Common |
|---|---|
| Relapsing polychondritis | |
| Psoriatic arthritis |
Arthritis refers to joint inflammation, the most common is osteoarthritis. Related to arthritis are Rheumatic diseases that are characterized by inflammation that affects the connecting or supporting structures of the body most commonly the joints, but also sometimes the tendons, ligaments, bones, and muscles. Rheumatic diseases that primarily affect the spine are considered spondyloarthropathies such as ankylosing spondylitis. See .
Fibromyalgia is a long-term condition that causes pain and tenderness all over your body. When it extends to the chest, the pain feels like an intense stabbing sensation primarily in the centre of the chest, around the breastbone and rib cage. Its thought to be caused by your nervous system not being able to control or process pain signals from other parts of your body. The condition is also linked to increased sensitivity to pain, headaches. extreme tiredness , muscle stiffness, difficulty sleeping problems with mental processes such as problems with memory and concentration. There is no specific diagnostic test.
Fibromyalgia and the associated paired tender points
Osteophyte of the sternum . It was excised with relieve of pain
Also Check: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Tiredness
Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation And Your Bodys Systems
The central part of the disease is inflammation, says rheumatologist Cong-Qiu Chu, M.D., Ph.D., an associate professor of medicine and director of the Early Arthritis Clinic at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, OR. While you may feel the effects of that inflammation most clearly in your joints, its impact goes much further. With RA, inflammation spreads throughout your body, putting your overall health at risk.
Before we take a look at the different systems of the body affected by RA, know this: For most people with rheumatoid arthritis, treatment today not only manages your joint pain, it also greatly reduces the risk of other damage to your body. When you treat the inflammation in the joints, you also suppress systemic inflammation in the rest of your body, says Dr. Chu.
How Rheumatoid Arthritis May Affect Your Mouth
Research shows that people who have rheumatoid arthritis may be more likely to develop periodontal disease, which usually starts with a gum infection.
They are also more likely to have dry mouth, which can predispose them to tooth decay.
The flip side of this may be true too: Poor oral health may lead to the onset or worsening of RA. Experts believe that inflammation in the mouth may stimulate the immune system, and in a people predisposed to RA the inflammation may trigger the body to start making antibodies associated with the disease.
Researchers have been working to better understand the mechanism behind this, but the takeaway is that treating gum disease and preventing unnecessary gum infections is good for your RA, as well. Schedule frequent dental checkups to catch minor issues before they become major problems.
Read Also: What Helps Lower Back Arthritis
What Happens In A Joint Affected By Rheumatoid Arthritis
If you have rheumatoid arthritis, your immune system can cause inflammation inside a joint or a number of joints. Inflammation is normally an important part of how your immune system works. It allows the body to send extra fluid and blood to a part of the body under attack from an infection. For example, if you have a cut that gets infected, the skin around it can become swollen and a different colour.
However, in the case of rheumatoid arthritis, this inflammation in the joint is unnecessary and causes problems.
When the inflammation goes down, the capsule around the synovium remains stretched and cant hold the joint in its proper position. This can cause the joint to become unstable and move into unusual positions.
The following can play a part in why someone has rheumatoid arthritis: