Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Patterns: Everyone Is Different
RA symptoms typically develop slowly over weeks or months, starting intermittently and eventually becoming a daily occurrence.
Usually the small joints are the first to be targeted: those in the hands , or those connecting the feet to the toes. As the disease progresses, symptoms are likely to spread from the hands and feet to larger joints like the knees, ankles, elbows, hips, shoulders, and neck. The total number of joints affected varies, but RA almost always ends up being polyarticular, affecting more than four joints.
Still, its important to remember that RA symptoms, and the rate at which they progress, can be completely different for everyone. For one person, symptoms might come on suddenly within days, attacking several joints off the bat. Someone else, though, may have swelling in one or more joints that lasts days or weeks and then mysteriously disappears, only to return weeks or months later, sometimes in different joints. In either case, the more classic RA symptoms might not appear for months.
And while rare, some people experience RA onset as chronic pain in just one joint, known as monoarthritis. According to small studies, about 10% to 15% of patients with monoarthritis progress to a diagnosis of RA.
If you have joint pain that doesnt quite fit the classic pattern of RA, watch out for other clues:
-
morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
-
pain that decreases with activity
-
family history
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis
Many people confuse rheumatoid arthritis with osteoarthritis due to their similar symptoms, but the two diseases are caused by different factors.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Whereas rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes joint malfunction due to inflammation, osteoarthritis is a mechanical disease brought on by the destruction of joints through wear and tear.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, with approximately 27 million Americans over the age of 25 having been diagnosed with it. Osteoarthritis is also most commonly seen in people middle-aged to elderly and is the top cause of disability in those age groups, though it can also appear in younger people who have sustained joint injuries.
With osteoarthritis, the cartilage, joint lining, ligaments, and bone are all affected by deterioration and inflammation. When the cartilage begins to break down due to stress or changes in the body, the surrounding bones slowly get bigger and begin to fail.
Osteoarthritis is a slowly progressing disease and occurs in the joints of the hand, spine, hips, knees, and toes. Furthermore, risk factors of this disease most often stem from lifestyle or biological causes, such as:
- Obesity
Osteoarthritis sometimes occurs alongside rheumatoid arthritis or other disease, such as gout.
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of RA is not known. RA is an autoimmune disorder. This means the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy cells and tissues. This causes inflammation in and around the joints. This may damage the skeletal system. RA can also damage other organs, such as the heart and lungs. Researchers think certain factors, including heredity, may be a factor.
RA most often occurs in people from ages 30 to 50, but it can occur at any age. It happens more in women than in men.
Don’t Miss: Does Drinking Alcohol Make Arthritis Worse
Are People With Rheumatoid Arthritis At Greater Risk For Covid
Yes, but this is an ongoing area of research. Its believed that autoimmune and inflammatory rheumatic disease patients are at higher risk for being hospitalized due to COVID-19 and having worse outcomes compared to the general population, according to the ACR.
However, this is likely affected by factors such as age, other comorbidities such as heart or lung disease, which is common in RA, and taking steroid medications, rather than simply having RA alone.
The medical community does consider patients living with rheumatoid arthritis to be at a greater risk for COVID-19, based on their inflammatory response from their condition, says Dr. Cadet. The medications used to treat the disease can also suppress the immune system.
In other words, when your body is preoccupied by fighting its own cells, it doesnt attack invaders as well as it should. Medications that affect immune system function can also affect the bodys ability to fight off viruses like the coronavirus.
For more information, check out this summary of research on inflammatory arthritis and rheumatic disease patients and their risk for COVID-19 complications.
Causes And Risk Factors
The condition can develop at any age, though it is most likely to develop between the ages of 25 and 50 years. Rarely, children under the age of 16 years can develop a form of rheumatoid arthritis known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or Stills disease. Factors that increase your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Your genes – rheumatoid arthritis appears to run in families
- Hormones – changes or deficiencies in certain hormones may be involved in the development of rheumatoid arthritis
- Obesity – people who are overweight or obese appear to be at higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis
- Smoking – people who smoke are more likely to develop the condition.
Recommended Reading: Is Egg Bad For Arthritis
When To Seek Medical Assistance For Arthritis
It is important to take symptoms of arthritis seriously, no matter the type, as some forms require earlier intervention than others. In all cases, the risk for permanent damage or further complications to other bodily tissues increases over time. Arthritis should be diagnosed following a thorough medical evaluation by a doctor or specialist .
If any of the general arthritis symptoms are being experienced, especially when discomfort persists for at least 3 days or several episodes occur within a period of a month, it is best to see your doctor for an evaluation.
Arthritis in general terms is not considered a diagnosis, however, and it is best to keep this in mind. With there being so many different underlying causes of arthritic symptoms and various types and medical classifications of the condition , an evaluation done early enough can determine the exact variation for a diagnosis. A diagnosis is necessary in order to implement the correct, most beneficial treatment plan.
Infectious or septic arthritis, for instance, does require prompt action so as to avoid permanent damage and health further complications. In all instances where arthritis occurs rapidly, a quick diagnosis and implementation of treatment can help to better preserve joint function as well.
What Are The Different Types Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis usually begin gradually in several joints. Sometimes the symptoms begin only in one joint, and sometimes the symptoms begin initially in the whole body, with generalized stiffness and aching, and then localize to the joints.
- Typical “classic” rheumatoid arthritis is the most common type of rheumatoid arthritis. Classic rheumatoid arthritis involves three or more joints. Usually, people have a gradual onset of joint pain, stiffness, and joint swelling, usually in the fingers, wrists, and forefeet. Elbows, shoulders, hips, ankles and knees are also commonly affected.
- About 80% of people with rheumatoid arthritis are classified as “seropositive,” which simply means the rheumatoid factor blood test is abnormal. Some people with an abnormal rheumatoid factor also have an abnormal anti-CCP blood test. This is another blood test for rheumatoid arthritis.
- Approximately 20% of people with rheumatoid arthritis are classified as “seronegative,” which means the rheumatoid factor blood test is negative, or normal. In this case, the anti-CCP blood test may be abnormal or normal. Other blood tests, such as the ESR measure of inflammation, may be abnormal.
Palindromic rheumatism
Atypical presentations of RA
- Persistent arthritis of just one joint may be the first symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in some people.
- Some people experience generalized aching, stiffness, weight loss, and fatigue as their initial symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Arthritis Pain In Hands
How Is Ra Diagnosed
RA is diagnosed by reviewing symptoms, conducting a physical examination, and doing X-rays and lab tests. Its best to diagnose RA earlywithin 6 months of the onset of symptomsso that people with the disease can begin treatment to slow or stop disease progression . Diagnosis and effective treatments, particularly treatment to suppress or control inflammation, can help reduce the damaging effects of RA.
What Are The Symptoms
The important signs and symptoms to be aware of are:
- pain, swelling and possibly redness around your joints. Hands and feet are often affected first, though RA can start in any joint
- stiffness in your joints when you get up in the morning or after sitting for a while, which lasts for more than 30 minutes and has no other obvious cause
- fatigue thats more than just normal tiredness
Theres more information about signs and symptoms here –Have you got the S-factor
If you have any of these symptoms, go and see your GP. The sooner RA isdiagnosedand treated, the better the long-term outcomes are likely to be.
Painis a significant symptom for most people. At first, it is caused by the inflammation in the joints, and later on pain can be as a result of damage to the joints. Pain levels can also vary from day to day.
Stiffnessis most marked/severe first thing in the morning and it can last several hours if youre not taking effective medication. Theres agellingof the joints, meaning that they become difficult to move from a position after youve rested them. This also happens when you have been sitting for any length of time.
Fatiguecan be due to anaemia but it can also be due to the inflammation. It has been linked to a number of things including pain levels.
Some people getflu-like symptomswith fever and muscle pains as well as being tired, especially in the early days before or during diagnosis.
You May Like: Does Psoriatic Arthritis Cause Hair Loss
What Is The Treatment
NICE guidelines for the management of RA and the RA Quality Standard recommend that a Treat to Target approach should be adopted which should include,frequent reviewof your RA,formal assessmentof your joints to see if there is still inflammation and anescalationof therapy until good control of joint inflammation is achieved. Taking medication is necessary in RA as this is the only way you are likely to be able to adequately reduce inflammation and get your disease under control. This table shows the different types of drugs used to treat RA.
When youre first diagnosed, your consultant will want to get you started straight away on Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs orDMARDs. These can be very effective in slowing down or even halting the progress of the disease, and preventing the severe damage to joints that people with RA used to suffer.
Disease modifying treatment might be one drug or a combination of drugs. It usually includes methotrexate. This is often used as theanchor drugin treating RA, meaning a drug that others are added to, in order to get the best effect. Not all drugs work equally well for everyone, so it may take time to find the right drug or combination for you: namely, what is most effective and has the least side effects for you.
General Signs And Symptoms Of Arthritis
Symptoms as related to direct causes vary. The type of arthritis is directly related to the pattern and location of arthritic symptoms.
The general signs and symptoms associated with all variations of arthritis include:
- Joint pain, swelling and stiffness
- Joint tenderness and inflammation
- Redness of the skin surround affected joints
- Loss of hand grip or grip strength
These symptoms may be at the worst first thing in the morning. Symptoms may develop suddenly or over a period of time . Symptoms can also occur in flares and as damage worsens, may begin to persist for longer periods.
Pain in the joints can fluctuate in varying degrees or be constant. It may be isolated to one specific area of the body or in multiple parts, depending on the number of affected joints. Stiffness is more often a problem first thing in the morning once awake, but can also be problematic after sitting for long periods of time, and even after exercise.
As some types of arthritis are closely associated with other types of conditions, a range of related symptoms over and above those which affect the joints can be experienced as well. Types of symptoms in this regard include fatigue, fever, swollen lymph nodes, weight loss, general malaise, as well as a range of others showing problems with the heart, lungs and kidneys.
Don’t Miss: Does Arthritis Pain Cause Fatigue
Ra In The Muscular System
When inflammation makes it harder to move your joints, the attached joints will get weak. According to a 2017 report in the journal EBioMedicine, a 2575% reduction in muscle strength has been observed in people with RA when compared to others without RA of the same ages.
People with RA can develop a condition called rheumatoid myositis that causes weakness, swelling, and pain. While rheumatoid myositis is poorly understood, researchers speculate a number of causes, including inflammation, the medications used to treat RA, impaired joint flexibility, and reduced activity levels.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Doctor Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next doctor’s appointment to help you ask the right questions.
What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
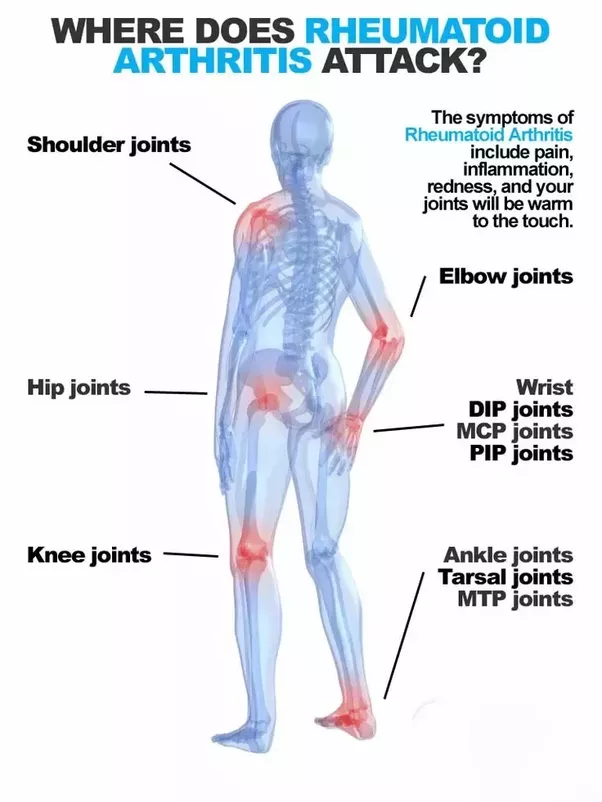
The joints most often affected by RA are in the hands, wrists, feet, ankles, knees, shoulders, and elbows. The disease often causes inflammation in the same areas on both sides of the body. Symptoms may begin suddenly or slowly over time. Each persons symptoms may vary, and may include:
- Pain
These symptoms can seem like other health conditions. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
You May Like: What Are The Three Types Of Arthritis
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
What Does Ra Feel Like
- The usual symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are stiff and painful joints, muscle pain, and fatigue.
- The experience of rheumatoid arthritis is different for each person.
- Some people have more severe pain than others.
- Most people with rheumatoid arthritis feel very stiff and achy in their joints, and frequently in their entire bodies, when they wake up in the morning.
- Joints may be swollen, and fatigue is very common.
- It is frequently difficult to perform daily activities that require use of the hands, such as opening a door or tying one’s shoes.
- Since fatigue is a common symptom of rheumatoid arthritis, it is important for people with rheumatoid arthritis to rest when necessary and get a good night’s sleep.
- Systemic inflammation is very draining for the body.
Read Also: How Quickly Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Spread
What’s The Difference Between Seropositive Vs Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
In RA, there are two classic auto-antibodies:
-
rheumatoid factor
-
anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide
RA patients who test positive for auto-antibodies have whats known as seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. About 70% to 80% of RA patients have this form of the disease.
On the other hand, patients who have RA symptoms but test negative for these auto-antibodies are diagnosed with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis.
Why does it matter? Symptoms are similar between the two groups of patients, though some evidence suggests that seronegative patients have a lower risk of joint damage and experience fewer extra-articular symptoms. What are extra-articular symptoms? Glad you asked…
What Are Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments
Despite significant advances in treatment over the past decades, rheumatoid arthritis continues to be an incurable disease. While there is no cure, the goal of disease remission is frequently attainable. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis has two major components:
Don’t Miss: Does Psoriatic Arthritis Cause Swelling
What Are Common Arthritis Treatments
There are many things that help reduce pain, relieve stiffness and keep you moving. Your care may involve more than one kind of treatment. Your doctor may recommend medications but there are many things you can do on your own to help manage pain and fatigue and move easier.
Finding the right treatment takes time. It can involve trial and error until you and your healthcare team or therapist find what works best. Be sure to let your doctor know if a treatment is not working. Your treatment may also change as your arthritis changes.
Treatments for arthritis can be divided into several categories: medication, exercise, heat/cold, pacing, joint protection, surgery and self-help skills. You can do things in each of these areas to help yourself feel better and move easier.
How Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Progress Over Time
Regardless of whether symptoms appear gradually over several months or rapidly over weeks, the disease follows the same progression:
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Arthritis In Lumbar Spine
Who Should Diagnose And Treat Ra
A doctor or a team of doctors who specialize in care of RA patients should diagnose and treat RA. This is especially important because the signs and symptoms of RA are not specific and can look like signs and symptoms of other inflammatory joint diseases. Doctors who specialize in arthritis are called rheumatologists, and they can make the correct diagnosis. To find a provider near you, visit the database of rheumatologistsexternal icon on the American College of Rheumatology website.