Ehealth And Mobile Health Interventions
A new emerging area of support for disease management is through digital technology using eHealth and mobile health interventions. These interventions have to potential to support the development of self-management skills, or assist the healthcare team to monitor symptoms. For JIA, current studies have focused on the health issues pain, health related quality of life, physical activity and disease management. Children and adolescents have used these interventions through a range of devices including computers, laptops, personal digital assistants, multimedia-players, and wearable accelerometers synchronised to smart phone. This allows access to these interventions from home. Early usability studies have been gaining positive feedback by children and adolescents. They are familiar with this type of technology and report liking these interventions. However further research is still needed to understand their full potential in supporting children and adolescents living with complex needs.
How Will Jia Affect Me
Many children who have JIA won’t have any symptoms when they’re adults, but its not possible to accurately predict this. In most cases, childhood arthritis has a good outcome. You should look forward to a future thats no different from those of your friends and classmates.
In at least 30% of cases, however, arthritis can remain active into adult life. Some young adults with JIA have joint damage that limits their daily activities to some extent and a few may need joint replacements. Other problems can sometimes occur. Some people are physically smaller than average or have osteoporosis as a result of their arthritis and/or treatment with steroids.
A successful outcome in JIA requires many things, including:
- a positive approach
- an experienced team working alongside your GP
- a caring, helpful environment with support from family, friends and teachers.
You also need to know how to get help that you can understand, know who to approach and be confident enough to ask for support and advice.
You can read more about JIA and how it will affect you in our Young people section of the website.
How Many Canadians Live With Jia And How Many Are Newly Diagnosed Each Year
Approximately 6,200 Canadians aged 15 years and younger live with diagnosed JIA and about 1,000 were newly diagnosed in 20162017. The prevalence and incidence of diagnosed JIA generally increase with age and are higher among females compared to males .
Figure 1: Prevalence of diagnosed juvenile idiopathic arthritis by sex and age group, CanadaFootnote a, 20162017
- Footnote a
| 17.1 |
Don’t Miss: Serum Negative Inflammatory Arthritis
How Can Parents Help
JIA is a lifelong disease, but treatments can help ease pain, keep kids active, and prevent long-term joint damage. To help your child:
- Make sure your child takes all medicines exactly as directed.
- Work with your childs physical therapist to develop a regular exercise program. This will help keep your childs muscles strong and flexible.
- Learn about JIA with your child. Your care team is a great resource. You can also find information and support online at:
What Are The Types Of Juvenile Arthritis
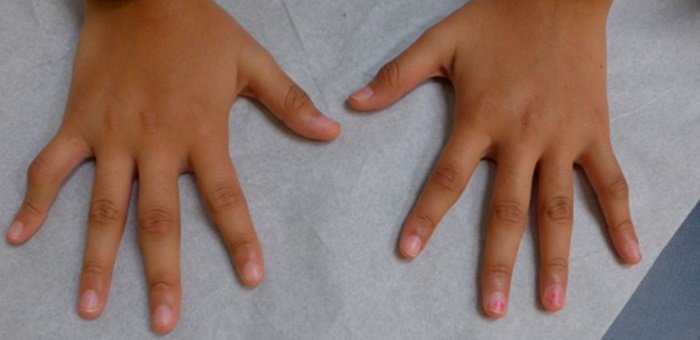
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is the umbrella term for several subtypes of arthritis seen in children and adolescents under the age of 16. JIA is arthritis with no known cause , to distinguish it from infectious forms of childhood arthritis. There are six main subtypes of JIA:
- Oligoarticular JIA: arthritis that involves four joints or fewer
- Polyarticular JIA: arthritis that involves five or more joints
- Systemic arthritis: begins with fevers, rashes, and inflammation in other parts of the body as well as the joints
- Psoriatic Arthritis: inflammation of the joints that occurs in some children with psoriasis
- Enthesitis-Related Arthritis: arthritis associated with enthesitis, which is inflammation of the entheses, the places where tendons and ligaments attach to bones
- Undifferentiated JIA: a type that doesnt fit into any one of the categories above
Other types of juvenile arthritis include:
- : arthritis caused by an infection of the joint
- lupus: a chronic autoimmune condition that can have arthritis as a feature
- juvenile dermatomyositis: a chronic autoimmune condition that can occasionally have arthritis as a feature
- enteropathic arthritis: a type of arthritis that can occur with inflammatory bowel disease
Don’t Miss: Ra Symptoms Hands
Are There Support Groups For Individuals With Jia
The Arthritis Foundation is a leading non-profit organization that is dedicated to addressing the needs of adults and children living with arthritis in the United States. There are more than one hundred local offices throughout the U.S. Many local and national events are organized to educate and connect patients and families. To learn more visit
Some information specific to children can be found at
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/01/2019.
References
Living With Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Whether your childs symptoms come and go or are long-lasting some things can help. This includes:
- Take a hot shower. Use a hot or cold pack or sleep in a warm bed to relieve stiffness.
- Stretching and do range-of-motion exercises. This reduces joint stiffness and improves flexibility. Exercise at the same time every day. Make it easy. Do it while watching TV or with family members.
- Take medicine at the right time and consistently. Have your child take his or her medicine at the same time as another activity. This makes it easy to remember.
Being active is important in managing the disease. Children who have the disease may need emotional support. This is important in managing the anger and sadness of having the disease.
Recommended Reading: Is Ra Painful
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Is An Autoimmune Disease
Polyarticular JIA affects 5 or more jointsoften the same joints on both sides of the body. Sometimes the neck, jaw joints, and small joints in the hands and feet are affected.
- JIA is the most common type of arthritis in children
- It occurs more often in girls
- It can cause inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and pain in the joints, as well as other symptoms, depending on the type of juvenile idiopathic arthritis a child has
Helping Your Child Live With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Help your child manage his or her symptoms by sticking to the treatment plan. This includes getting enough sleep. Encourage exercise and physical therapy and find ways to make it fun. Work with your child’s school to make sure your child has help as needed. Work with other caregivers to help your child take part as much possible in school, social, and physical activities. Your child may also qualify for special help under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. You can also help your child find a support group to be around with other children with JIA.
You May Like: Reduce Arthritis Swelling In Fingers
The Joints Are The Primary Jia Target
JIA kicks off a faulty immune response that causes the release of inflammatory chemicals that attack the synovia, which is the tissue that lines the joints and produces lubricating fluid, says. Dr. Oller. is the equivalent to grease or WD-40 that you put on hinges to make sure everything is moving smoothly and effectively. But with JIA, the inflamed synovia can cause joints to painfully swell and become stiff.
Types Of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Systemic arthritis: This type of JIA mainly affects all body systems and is widespread among both girls and boys.
- Oligoarthritis: Known by different names, as uveitis, iridocyclitis or iritis, this type of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis affects less than 5 joints in the body during the first 6 months and is more common in girls.
- Polyarthritis: This is a type of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis which involves five or more joints in the first 6 months.
- Psoriatic arthritis: This type of JIA occurs in children with arthritis and psoriasis.
- Enthesis related arthritis: Enthesis related arthritis is another type of JIA that affects the places where tendons attach to the bones. The condition also affects the spine, hips, and eyes and usually occurs in boys above the age of 8 years.
You May Like: Is Peanut Butter Bad For Arthritis
Jia Can Impact Liver Function
Patients who develop MAS are also more likely to experience severe liver inflammation, Dr. Kahn says. This can make a patient extraordinarily ill thanks to a rare cytokine storm happening in the body, he says. Cytokines are immune cells, but when too many are released too quickly the response can seriously harm healthy tissue. Research published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases found that early diagnosis of JIA may help halt autoimmune hepatitis as well as liver failure in these patients over time.
How Is Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed
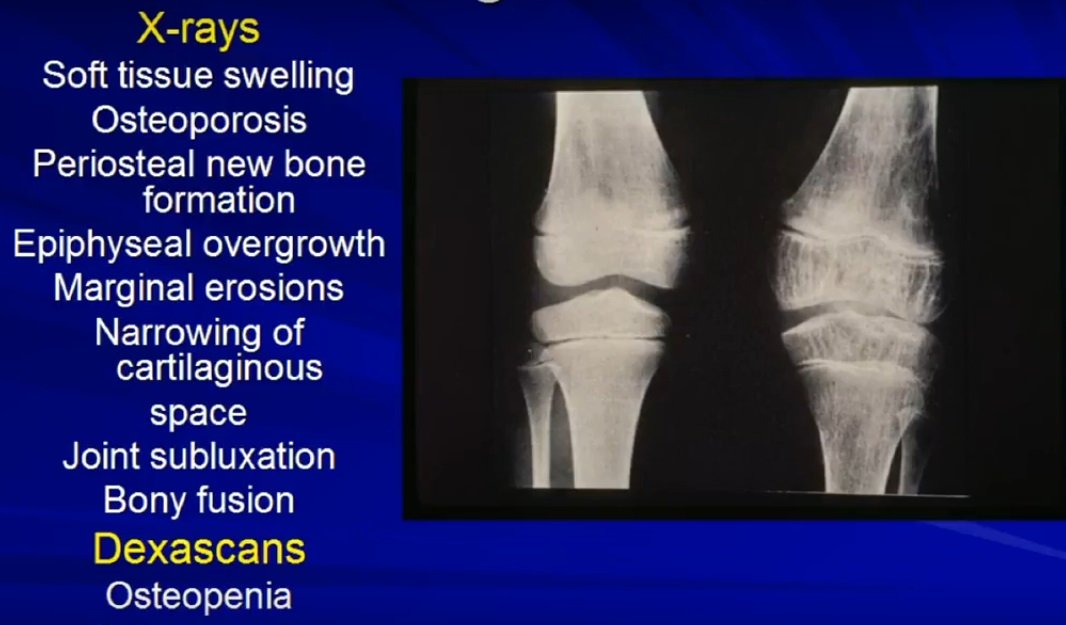
Your childs doctor will ask about your childs symptoms and do a physical exam. It can be hard to diagnose. You doctor may do an X-ray or blood test to rule out other illnesses. X-rays also can show more severe damage or deformities. Your childs doctor may want to take a sample of fluid from an actively inflamed joint or spinal fluid. It may take a few months before your doctor makes a diagnosis. This is so he or she can watch your childs symptoms over time.
Read Also: Symptom Of Arthritis
Points To Remember About Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- JIA is a type of arthritis that affects children. It causes joint pain, swelling, warmth, stiffness, and loss of motion.
- JIA begins when the immune system, which normally helps to fight off infections and heal cuts and wounds, becomes overactive and creates inflammation.
- Treatment depends on the type of JIA and how bad the symptoms are, but usually includes a mix of medications, physical therapy, and regular doctor visits. Treatments can help children with the disease participate in activities.
- There are many things you can do at home to help your child live with JIA, such as taking care of painful joints, balancing rest and exercise, working with their school, and coping with stress.
What Are The Symptoms
Children can have one or many symptoms, such as:
- Joint pain.
- Fever.
- Rash.
In some cases these symptoms can be mild and hard for you to see. A young child may be more cranky than normal. Or a child may go back to crawling after he or she has started walking. Your child’s joints may feel stiff in the morning. Or your child may have trouble walking.
Children with this disease can also get inflammatory eye disease. This can lead to permanent vision problems or blindness if it’s not treated. Eye disease often has no symptoms before vision loss occurs.
Also Check: Over The Counter Medicine For Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Can Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Be Managed
As with many autoimmune diseases, the cause of juvenile idiopathic arthritis is not well understood. However, it is likely related to a combination of genetic factors, environmental exposures, and other factors.Footnote 5 While there is no cure for juvenile idiopathic arthritis, early diagnosis followed by an effective management strategy can help improve an individual’s functional ability and productivity in daily life. Medication treatment plans aimed at reducing pain and inflammation are key to controlling the disease and improving function. The treatment plan also often includes physiotherapy and occupational therapy along with regular exercise. Children diagnosed with juvenile idiopathic arthritis benefit from a multidisciplinary team, including paediatric rheumatologists, rheumatology nurses, pharmacists, physiotherapists and occupational therapists, optometrists and ophthalmologists, in addition to their primary care physician. Dieticians and social workers may also be part of the team.Footnote 4
What Is Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Understanding The Basics
It is well known that arthritis is usually associated with older people. However, pain is not only limited to older folks or adults. Surprisingly, kids can experience arthritis, too. As per the Arthritis Foundation, juvenile arthritis is a term that encompasses all forms of arthritis of unknown etiology lasting for at least 6 weeks and with onset before the age of 16 years. There are many types of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, the most common of which is Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis .
JIA, which was previously known as Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and frequently referred by doctors in the present day, is the most common type of arthritis in children.
In this article, we will let you know the basics of this type of arthritis in detail.
Don’t Miss: Rheumatoid Arthritis And Itching
Sometimes A Fever Is The Main Jia Symptom
Heres where it gets murky with JIA: There are seven subtypes of the disease, and each comes with its own symptoms, says Philip J. Kahn, M.D., a pediatric rheumatologist at Hassenfeld Childrens Hospital in New York City. Many of these pertain to how many joints are affected during the first six months of diagnosis, but systemic-onset JIA comes with more vague side effects than the others. With systemic-onset JIA, the child almost always presents with a prolonged fever, says Dr. Kahn. They may not have swollen joints to start, but a fever that isnt infectious is the most florid symptom.
What Causes Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Like adult rheumatoid arthritis, JIA is an autoimmune disease. This means the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy cells and tissues. JIA is caused by several things. These include genes and the environment. This means the disease can run in families, but can also be triggered by exposure to certain things. JIA is linked to part of a gene called HLA antigen DR4. A person with this antigen may be more likely to have the disease.
Don’t Miss: Remedy For Arthritis Pain In Hands
Disease Course Quality Of Life And Functional Outcome
Substantial progress in JIA treatment has been made over the last three decades. Clinical outcomes have dramatically improved, with disease control and remission possible in most patients. Nevertheless, a significant proportion of patients have ongoing disease activity. In fact, about half of patients continue to require active treatment into adult life, whereas complete remission is achieved in only 2025% of patients .
Administration of biological agents has decreased the mortality rate of JIA from 1 to 4% in 1970s to 0.31% in 2016 . Improved clinical outcomes in physical disability are reflected in the Steinbrocker functional classification scale. Between 1976 and 1994, 15% of JIA patients were within Class III and Class IV , compared to 5% in 2002 . However, joint damage, occurring before treatment led to surgical intervention in 14% of patients, emphasising the importance of early aggressive treatment to achieve complete remission . The prominent factor influencing treatment outcome is presence of systemic manifestation. Multi-organ failure in patients with MAS is fatal in approximately 8% of cases .
Being the most frequent extraarticular manifestation JIA–associated uveitis became the main cause of vision loss in childhood, and furthermore about half of these patients suffer from active uveitis in adulthood . Additionally, a high risk of osteoporosis and consequently fractures in early adulthood remain higher in JIA patients even in remission .
How Common Is Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
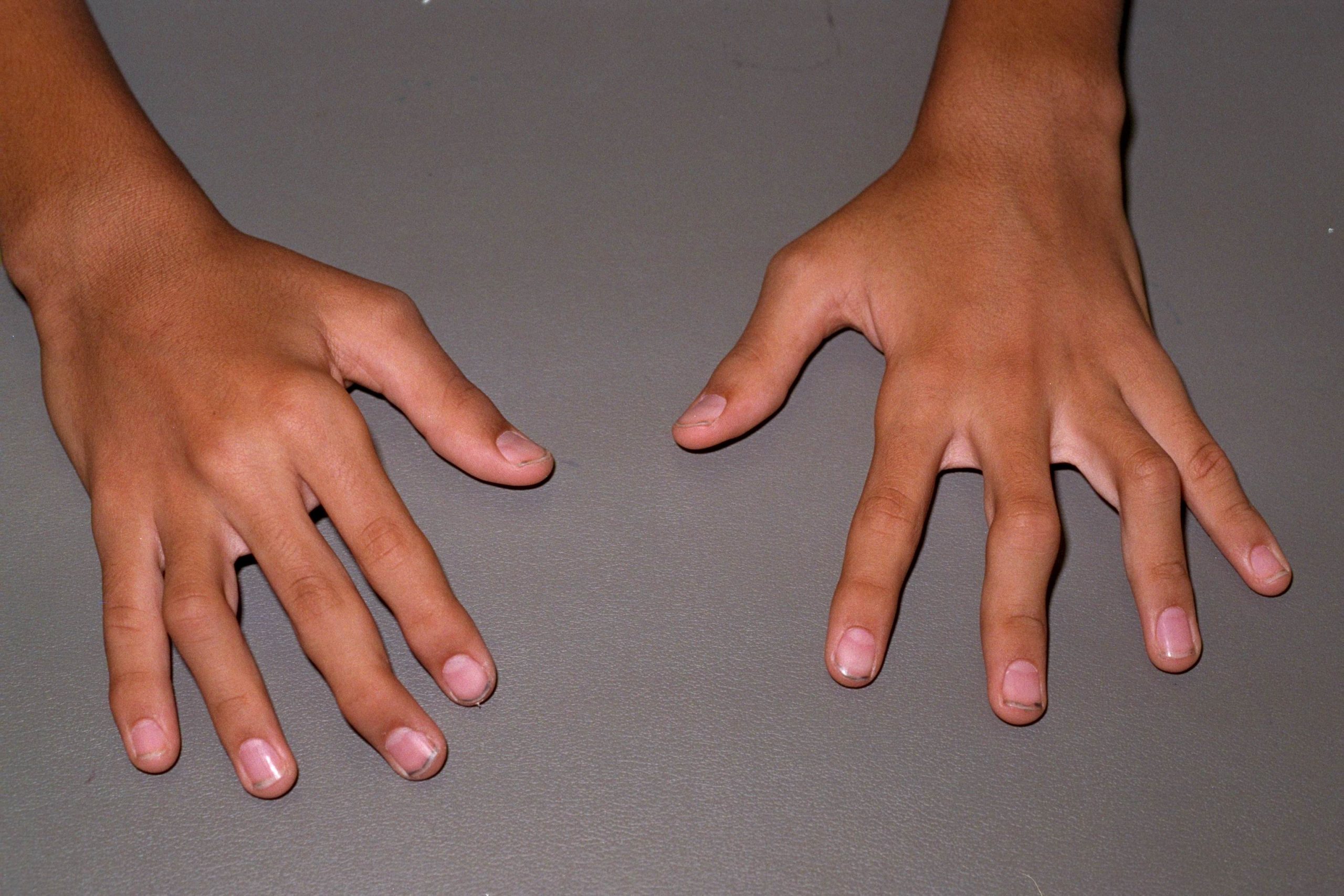
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is uncommon. Between 1 and 2 in every 1,000 children are affected at any one time. Between 1 and 2 in every 10,000 children develop JIA each year.
How common each type is varies in different parts of the world. For example, in the UK, oligoarticular JIA is the most common type. Polyarticular JIA is more common in countries such as India, New Zealand and South Africa. Systemic arthritis is more common in Asia than it is in Europe.
Also Check: Over The Counter Drugs For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Complementary Medicine Therapies For Pain Management
- Massage is used to promote relaxation, relieve pain, and restore normal joint movement.
- Guided imagery may be used to promote relaxation and manage pain.
- Acupuncture is mildly effective in relieving pain in adults who have rheumatoid arthritis. It may help relieve pain in children who have JIA, but this has not been proved.
Enthesopathies Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Arthritis associated with enthesopathies mainly affects boys after the age of 7-8 years. The most common manifestation is oligoarthritis which mainly affects the large joints of the lower limbs associated with enthesitis. Enthesitis is an inflammation of the enthesis, where tendons are inserted into the bones. The evolution of this form is variable.
Also Check: Triggers For Arthritis
What Are The Types Of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The types of JIA and their symptoms are:
Systemic JIA
Children with systemic JIA have arthritis in 1 or more joints. They also have a fever and rash that come and go. They may have swollen and problems with the heart, lungs, and blood.
Polyarticular JIA
A child with polyarticular JIA has arthritis is in 5 or more joints in the first 6 months of disease. They also might have inflammation inside the eye and other problems.
Oligoarticular JIA
Children with oligoarticular JIA have arthritis is in fewer than 5 joints in the first 6 months of the disease. In some children, more joints become affected after that. They may also have uveitis.
Enthesitis-Related JIA
Children with enthesitis-related JIA have enthenitis and arthritis. They may also have uveitis and inflammatory bowel disease .
Psoriatic JIA
Psoriatic JIA affects children who also have psoriasis or a close relative with psoriasis. They may also have uveitis, swelling of fingers and toes, and changes in their nails.
Undifferentiated JIA
Undifferentiated JIA is when someone’s symptoms dont fit into any of the above types or fall into more than one of those types.
What Causes Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis?
JIA is an autoimmune disease. This means that the bodys immune system, which normally attacks germs, mistakenly attacks the joints. This causes inflammation in the joints and other problems.
- genetic causes
- the way the immune system responds to infection and illness
- a trigger such as an infection
What Are The Complications Of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Nearly half of all children with JIA recover fully. Others may have symptoms for years. Some will have rashes and fever. Others may have arthritis that gets worse. Problems may include slow growth and thinning bones . In rare cases, there may be problems with the kidneys, heart, or endocrine system.
Also Check: What Does Arthritis In The Back Feel Like