How Is Arthritis In The Hand Treated
Treatment options depend on the type of arthritis, stage of arthritis, how many joints are affected, your age, activity level, the hand affected and other existing medical conditions.
Goals of treatment are to:
- Improve mobility and function.
- Increase your quality of life.
- In the case of rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis, to slow the progression of the disease.
Treatment options include splinting/bracing, medications, injections, non-drug approaches and surgery.
Splinting/braces
Splits or braces support and protect the affected joint, reduce deformity, provide joint stability, lessen strain, and promote proper joint alignment. Your healthcare provider, occupational therapist or hand therapist will discuss splinting/bracing options, how and when to wear them and how long to wear them .
Medications
Steroid injections
Steroids reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Steroids are usually used if medications dont control inflammation or if the inflammation is limited to a few joints. Injections are administered directly into the affected joint. Because steroids can weaken tendons and ligaments, injections are repeated only a few times.
Other management strategies
A complete treatment plan for arthritis of the hand includes these additional approaches:
Surgery
If nonsurgical treatments no longer provide relief and the cartilage at the ends of your bones has worn away, surgery may be an option. There are several approaches:
Oxidative Stress And Muscle Weakness In Ra
RyR1 and its role in muscle weakness has gained a lot of interested over the years . For example, SNO modification of cysteines and carbonylation of RyR1 have been shown to make the channel less stable and thus lead to increased open probability of the channel, which have been observed in muscle dysfunction associated with, for example, malignant hyperthermia, bone metastases, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, heart failure and normal aging . Moreover, Yamada et al. showed that 3-NT modifications on the RyR1 macromolecular complex were associated with decreased muscle force in collagen-induced arthritis mice . However, the occurrence and relevance of specific oxPTMs on RyR1 in association with RA-induced muscle weakness is unknown.
Symptoms That Affect Your Skin
Some people with RA get rheumatoid nodules. These are bumps under the skin. Most of the time, they arenât painful, and they move easily when you touch them. About one in four people with RA get these skin bumps.
They usually happen on your elbows, but they might show up on other bony areas like:
You May Like: How To Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis In Hands
Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation And Your Body’s Systems
The central part of the disease is inflammation, says rheumatologist Cong-Qiu Chu, M.D., Ph.D., an associate professor of medicine and director of the Early Arthritis Clinic at Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, OR. While you may feel the effects of that inflammation most clearly in your joints, its impact goes much further. With RA, inflammation spreads throughout your body, putting your overall health at risk.
Before we take a look at the different systems of the body affected by RA, know this: For most people with rheumatoid arthritis, treatment today not only manages your joint pain, it also greatly reduces the risk of other damage to your body. When you treat the inflammation in the joints, you also suppress systemic inflammation in the rest of your body, says Dr. Chu.
Musculoskeletal Pain And Arthritis
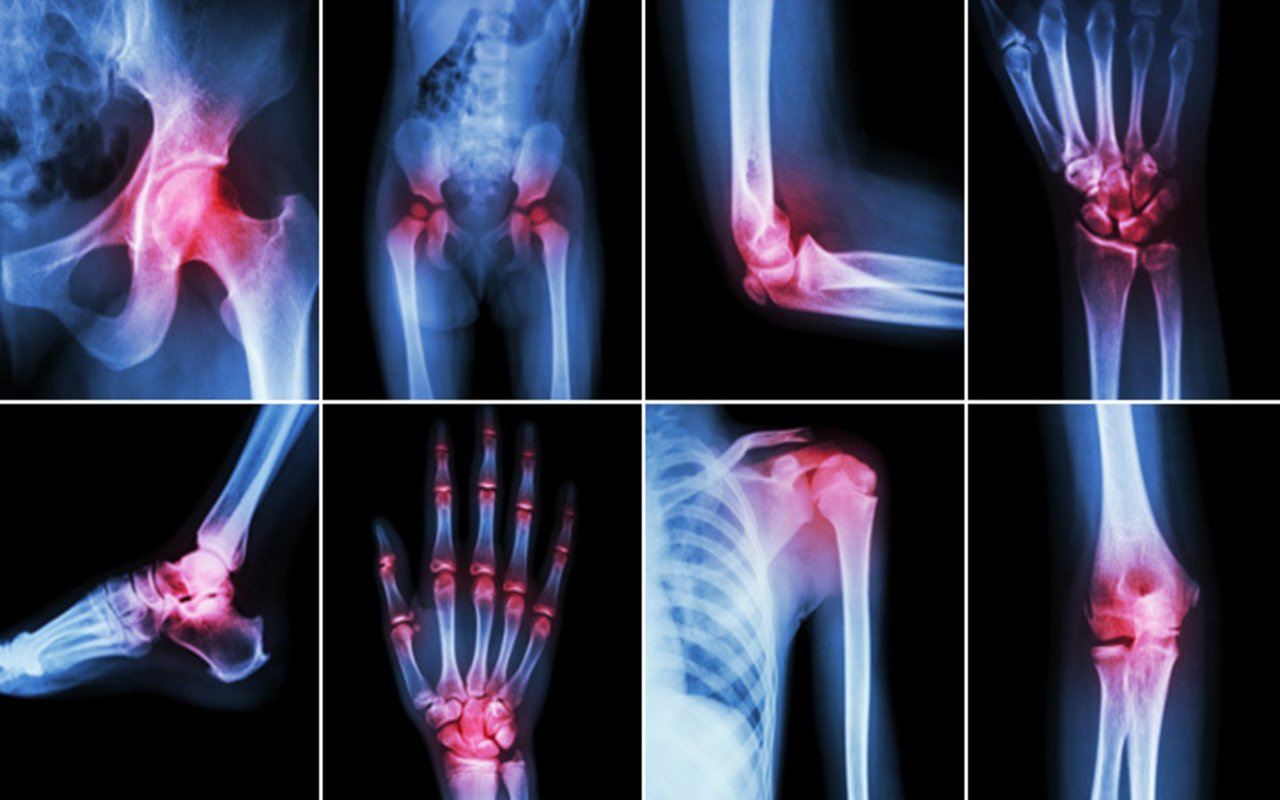
Learn more about the connection between musculoskeletal pain and arthritis and where you may experience this type of pain in your body.
Structures in the musculoskeletal system besides bones, cartilage and synovium can cause pain if you have arthritis.
Where you can experience musculoskeletal pain caused by arthritis:
-
Muscles.Muscle pain is a main symptom in some types of arthritis-related diseases, such as fibromyalgia, myositis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Your muscles may also ache if they are weakened due to lack of use or when trying to support joints with arthritis.
-
Ligaments.Joints are held together with tough bands of tissue connecting two bones. Ligaments can become torn, stretched or weakened when you have arthritis.
-
Tendons.These strong bands of tissue connect muscles to bone. Tendinitis occurs when the tendon becomes inflamed or irritated due to arthritis or overuse.
-
Bursae.These fluid-filled sacs pad the bones, tendons and muscles near your joints. Bursitis happens when bursae become inflamed or irritated due to arthritis or overuse.
Soft-tissue Musculoskeletal Damage
Athletes may have specific kinds of soft-tissue damage. Tennis elbow and golfers elbow are painful conditions that involve inflammation of the tendons holding the muscles of the elbow together. Runners may get a condition called plantar fasciitis when the thick band of tissue along the bottom of the foot becomes inflamed.
Neuropathic Musculoskeletal Pain
Recommended Reading: Rheumatoid Arthritis Edema Treatment
Key Points About Rheumatoid Arthritis
- RA is a long-term that causes joint inflammation.
- RA can also affect many nonjoint areas such as the lungs, heart, skin, nerves, muscles, blood vessels, and kidneys.
- RA may cause deformities in the joints of the finger, making movement difficult.
- The joints most often affected by RA are in the hands, wrists, feet, ankles, knees, shoulders, and elbows.
- Symptoms may include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling decreased and painful movement bumps over small joints and fatigue or fever.
What Causes Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain can be caused by a wide variety of conditions that cause inflammation, infection, nerve compression, or injury of the shoulder. Common causes of shoulder pain include arthritis and injury caused by excessive, repetitive, or overhead motions that involve the shoulder, such as occurs with baseball pitching or construction work.
A common cause of shoulder pain is a tear of the rotator cuff, the muscles and tendons that hold the arm bone in place in the shoulder joint. The rotator cuff also enables the arms range of motion. A torn rotator cuff results in shoulder pain or weakness when you move your arm.
Shoulder pain can also be caused by diseases or conditions of the body outside the shoulder area, such as heart attack or gallbladder disease. This is called referred shoulder pain.
Read Also: Can You Have Rheumatoid Arthritis In Your Back
Recommended Reading: What Really Causes Arthritis
Arthritic And Rheumatological Causes Of Chest Wall Pain
| Arthritic and Rheumatic diseases causes of chest wall pain | Less Common |
|---|---|
| Relapsing polychondritis | |
| Psoriatic arthritis |
Arthritis refers to joint inflammation, the most common is osteoarthritis. Related to arthritis are Rheumatic diseases that are characterized by inflammation that affects the connecting or supporting structures of the body most commonly the joints, but also sometimes the tendons, ligaments, bones, and muscles. Rheumatic diseases that primarily affect the spine are considered spondyloarthropathies such as ankylosing spondylitis. See .
Fibromyalgia is a long-term condition that causes pain and tenderness all over your body. When it extends to the chest, the pain feels like an intense stabbing sensation primarily in the centre of the chest, around the breastbone and rib cage. Its thought to be caused by your nervous system not being able to control or process pain signals from other parts of your body. The condition is also linked to increased sensitivity to pain, headaches. extreme tiredness , muscle stiffness, difficulty sleeping problems with mental processes such as problems with memory and concentration. There is no specific diagnostic test.
Fibromyalgia and the associated paired tender points
Osteophyte of the sternum . It was excised with relieve of pain
What Type Of Doctors Treat Arthritis
Part of your treatment plan may involve working with different health-care specialists. Some common health-care professionals and their role in your treatment are described below. Most doctors make referrals to one of a group of health professionals with whom they work. But you too can ask your doctor to request medical services you think might help you.
Your family doctor may be an excellent source of medical care for your arthritis. Besides having your medication records, your family doctor already has your medical history, is familiar with your general physical health and knows of any past illnesses or injuries. All these facts will give your family doctor a head start in prescribing a treatment plan most suited to your needs.
If your arthritis affects many joints or other parts of the body or seems resistant to treatment, you may benefit from seeing a rheumatologist. This is a doctor with special training and experience in the field of arthritis. Your family doctor, the local chapter of the Arthritis Foundation or the county medical society can refer you to a rheumatologist. You can also search for a rheumatologist on the American College of Rheumatology web site.
Recommended Reading: Ra Symptoms In Knees
Ra And The Musculoskeletal System
The primary way this disease affects your body is through whats known as the musculoskeletal system. This is basically what it sounds like: a system of muscles and skeletal structures like bones that give your body support and stability so that you can actually move. When rheumatoid arthritis attacks your musculoskeletal system, it makes it harder for you to perform even the most basic physical activities. The disease affects each part of the system in slightly different ways. Lets take a closer look.
What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The joints most often affected by RA are in the hands, wrists, feet, ankles, knees, shoulders, and elbows. The disease often causes inflammation in the same areas on both sides of the body. Symptoms may begin suddenly or slowly over time. Each persons symptoms may vary, and may include:
- Pain
These symptoms can seem like other health conditions. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Rheumatoid Arthritis In Hands
Costochondritis And Arthritis: Whats The Link
Costochondritis is not as common as inflammation in the joints of the hands, elbows, knees, or feet, but if you have inflammatory arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, or psoriatic arthritis, you may also be more likely to get costochondritis.
When you have a condition that predisposes you to inflammation over multiple joints, you have increased susceptibility to developing it, says Vinicius Domingues, MD, a rheumatologist in Daytona Beach, Florida, and medical advisor for CreakyJoints.
Though costochondritis can happen at any age, it is more common in people over 40 and, like inflammatory arthritis, it affects women more than men 70 percent versus 30 percent.
Stop Hand Cramps Before They Start
Better yet, aim to prevent muscle cramps in the first place. Keeping hand muscles strong will help prevent muscle fatigue, so exercises can decrease cramps long term, Weselman explains. Try repetitive finger tapping , or squeezing silly putty or a stress ball.
RELATED: 6 Exercises for Rheumatoid Arthritis Hand Pain Relief
If muscle cramps or hand pain persists, occurs often, or interferes with everyday activities, talk with your doctor, who can look for signs of underlying causes such as poor circulation, dehydration, poor nutrition, kidney disease, or electrolyte imbalances due to medication. In some cases, muscle atrophy could be related to injury, muscle abnormality, or a neurological condition.
Additional reporting by Jessica Firger.
Recommended Reading: Autoimmune Leg Pain
Other Body Parts Ra Can Affect
- Bones. The chemicals that cause inflammation can also take a bite out of your bones. It often affects your hips and spine. Sometimes, itâs a byproduct of years of treating RA with steroids.
- Liver and kidneys. Itâs rare for RA to affect these organs. But the drugs that treat it can. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be bad for both. Cyclosporine may cause kidney disease. Methotrexate can damage your liver.
- Immune system. The medications you take can slow it down. This makes you more likely to get infections.
- Mucous membranes. You might be more likely to get a condition called Sjogrenâs syndrome that dries out moist places in your body like your eyes, your mouth, and inside your nose.
- Muscles. When inflammation stops you from moving your joints, the attached muscles can get weak. Or you could get a condition called myositis that weakens them. The medications you take for RA can also be to blame.
- Nerves. RA causes symptoms that range from numbness and tingling to paralysis. It can result from joint damage that RA causes, the disease process itself, or medications that treat it.
- Blood vessels. RA can cause inflammation of your blood vessels. It can show up as spots on the skin or can cause ulcers in more severe cases.
Ra In The Muscular System
When inflammation makes it harder to move your joints, the attached joints will get weak. According to a 2017 report in the journal EBioMedicine, a 2575% reduction in muscle strength has been observed in people with RA when compared to others without RA of the same ages.
People with RA can develop a condition called rheumatoid myositis that causes weakness, swelling, and pain. While rheumatoid myositis is poorly understood, researchers speculate a number of causes, including inflammation, the medications used to treat RA, impaired joint flexibility, and reduced activity levels.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Doctor Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next doctor’s appointment to help you ask the right questions.
You May Like: Arthritis And Skin Rash
Ra Affects Your Body Systematically
This inflammatory disease can be both a debilitating and disfiguring condition. Its effect to the joints can be significant enough to make your daily activities extremely difficult.
Typically, it initially tires your daily tasks. And then eventually, you will not able to do them at all .
Some common complications caused by RA that affect your bone and joint include:
The good news, new treatments are more effective to control the disease. With prompt treatment, RA is not the end of everything and you can have an average expected lifespan .
The bad news, however its not always easy to cope with the disease. Although RA mainly affects your joints, again it can affect the entire body.
Ra Symptoms In Your Joints
RA almost always affects your joints. It may take a few weeks or months for the first signs to show. The inflammation it causes often leads to these three hallmark symptoms:
- Pain.Inflammation inside a joint makes it hurt whether youâre moving it or not. Over time, it causes damage and pain.
- Swelling. Fluid in the joint makes it puffy and tender.
- Tenderness. It hurts when you move or push on a joint.
Other RA symptoms include:
- Stiffness. The joint is harder to use and doesn’t move as well as it should. Itâs especially common in the morning. Although many people with other forms of arthritis have stiff joints in the morning, it takes people with rheumatoid arthritis more than an hour before their joints feel loose.
- Redness and warmth. The joints may be warmer and have color changes related to the inflammation.
You May Like: Can You Stop Arthritis In Fingers
Novel Actions To Improve Muscle Function
Based on the scientific results discussed in this review, illustrates a tentative vicious cycle that may contribute to the arthritis-induced muscle weakness. This model show that nitrosative modifications of the RyR1 protein complex results in facilitated and increased Ca2 + release during muscle contractions, which further activates the Ca2 +-sensitive NOS1 that by itself can cause amplification of O2, NO and ONOO. This results in ONOO attacks of myofibrillar proteins and causes contractile dysfunction and muscle weakness. Thus, a novel action to counteract RA-associated muscle weakness could be to inhibit this viscous cycle by pharmacological intervention targeting RyR1 to stabilize SR Ca2 + release, hence counteract the facilitated Ca2 + release observed in arthritis . AICAR and S107 are known to stabilize RyR1 activity, normalize Ca2 + release and shown to reduce the ROS/RNS burden and improve muscle function in muscle dystrophy and cancer-related muscle weakness, respectively . Thus, AICAR and S107 could be potentially useful compounds to counteract RA-induced muscle weakness.
Joint Pain And Stiffness
Typically, your wrists, feet, and knuckles are most commonly affected. Some people show symptoms in their ankles, knees, elbows, and shoulders.
Joints become stiff, particularly in the morning or after long periods of rest. Joints are often described as tender or achy, and range of motion can be limited. Along with pain and stiffness, joints affected by RA are often warm to the touch. They also become swollen. Over time, the long-term damage to the joints can cause severe deformities, if inflammation isnt controlled.
Read Also: Does Arthritis Hurt All The Time
Functional Capacity And Knee Extensor Muscular Strength
The TUG test measures the time for an individual to rise from a chair, walk 3m to touch a marker on a wall, turn 180°, return to the chair and sit down . Time was recorded by a stopwatch, and participants were instructed not to use their hands when rising from or sitting back down on the chair.
Maximal knee-extensor muscle strength was measured with a Biodex System 3 dynamometer . Volunteers were positioned on the dynamometer according to the manufacturers recommendations for knee evaluations, with the hip angle fixed at 85°, knee flexed at 90° and the trunk, hips and thighs firmly strapped to the apparatus. Subjects performed a warm-up protocol consisting of 10 submaximal knee extension/flexion repetitions at an angular velocity of 90°.s1. Next, subjects were instructed to execute the test with the highest possible effort to develop maximal knee extension, and verbal encouragement was provided throughout the test. Three knee extensor isometric tests at 90° of knee flexion were executed, with a 2-min resting period between contractions . The peak torque obtained from these three contractions was normalized to body mass and used for analysis.