Where Is Eczema On Babies
In babies, eczema is often found on the scalp and face, particularly the cheeks. It’s most often found on the head, but it can be found anywhere. It is not typically in the diaper area.
A baby may rub their face or head on the carpet or their sheets to scratch the itchy skin. This can further irritate the skin and lead to infection.
As they start to crawl, eczema may be more frequently seen on their elbows or knees. This is because these are areas that are prone to rubbing as they crawl.
In toddlers, eczema may often be seen on their face, around their mouth, or on their eyelids. It may also be on wrists, elbow creases, and knees.
The Role Of Blood Tests
Blood tests dont provide a simple yes-or-no answer to whether you have RA. But they can help your doctor steer toward a diagnosis. Blood tests narrow down options and suggest how your disease might progress.
After you receive a diagnosis of RA, continued blood tests will monitor the side effects of drugs used in treatment. They can also help track the progression of the disorder.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Initial Diagnosis
There is no single test that can definitively diagnose RA.
As with other illnesses, diagnosis of RA typically begins with your doctor getting your medical history and conducting a physical exam.
You doctor will begin by asking questions about the symptoms you’re experiencing, including when and how they occur and how they’ve changed over time . One specific symptom they will ask about is morning joint stiffness that lasts for at least 30 minutes and occurs in the peripheral joints rather than the lower back a common RA symptom.
The other main symptom is swelling of the joints that lasts for at least six weeks, particularly if the swelling occurs on the same joints on both sides of the body. Swelling that occurs for less than six weeks could be a sign of multiple different things an example is acute viral polyarthritis, an inflammation of the joints caused by a virus.
Arthritis Care & ResearchAutoimmunity Reviews
You May Like: How To Beat Rheumatoid Arthritis Naturally
The Diagnostic Criteria For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis cant be established with just one test. Instead, rheumatologists rely on a combination of your medical history, a physical exam, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging tests to pinpoint the disease.
They also try to rule out the possibility of other conditions that may resemble RA, such as lupus, psoriatic arthritis, gout, or osteoarthritis. This is called a differential diagnosis.
To begin the diagnostic process, a rheumatologist will take your medical history, which includes asking questions about your current symptoms particularly pain, swelling, and stiffness and their location, duration, and severity.
Theyll also ask about your familys medical history as it pertains to RA and other autoimmune conditions. Conditions like RA can be more common in families with RA or other immune system-related health problems. For example, research recently published in the journal Arthritis Care & Research found that people who have a first-degree relative with RA are more than twice as likely as the general population to develop RA. A family history of lupus, scleroderma, thyroid disease, or inflammatory bowel disease also substantially increased the risk of RA.
Your rheumatologist will also perform a physical examination, testing each of your joints for things like swelling, tenderness, and limited range of motion. The location of affected joints is important to diagnosis.
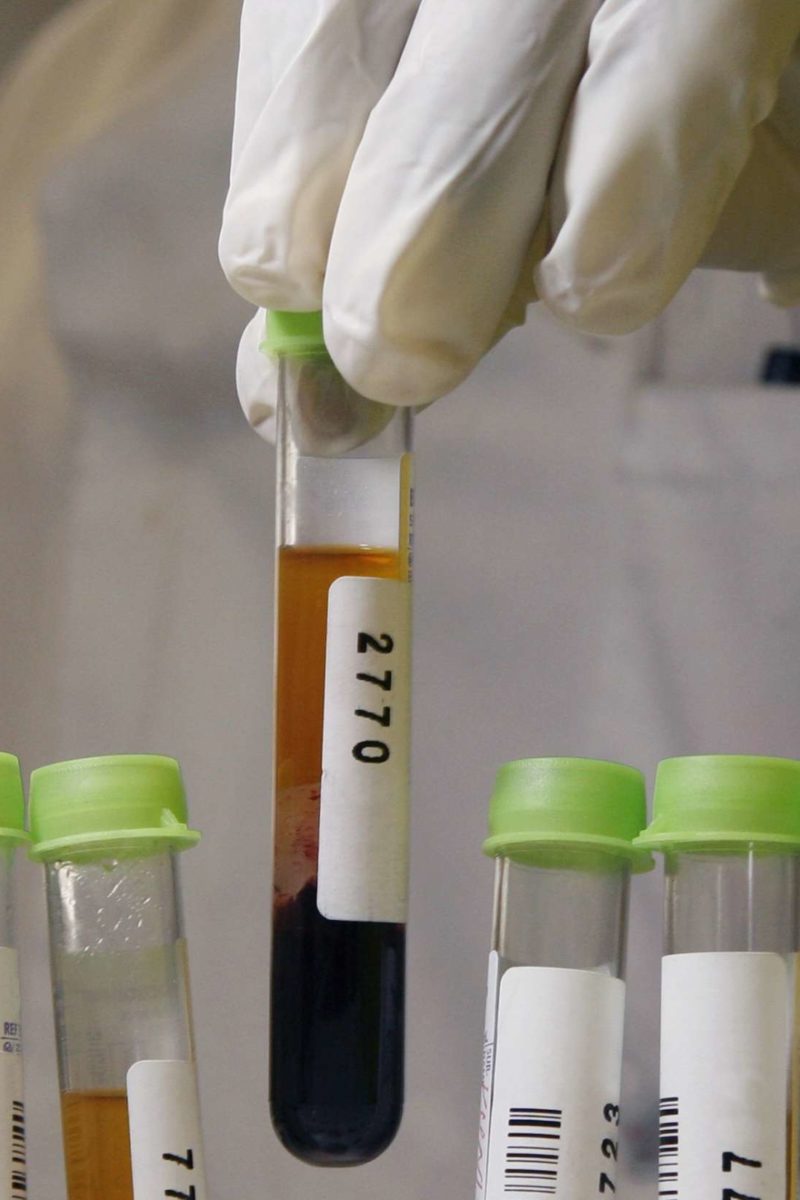
The Role Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Testing
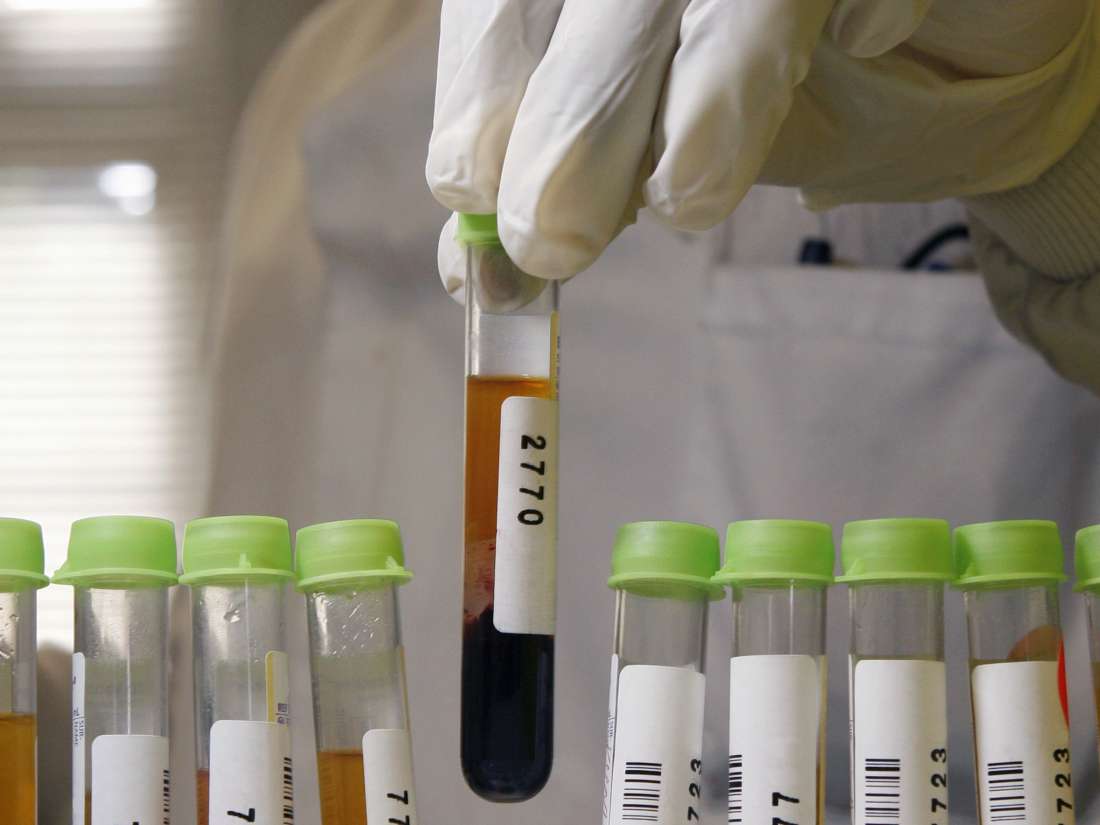
Rheumatoid arthritis testing is used to diagnose RA, evaluate the severity of a patients disease, monitor treatment, and detect potential side effects of treatment drugs:
- Diagnosis: Diagnostic testing helps determine the cause of a patients symptoms. If a doctor is concerned that a patients symptoms may be related to rheumatoid arthritis, testing can assist in diagnosing RA and ruling out other health conditions.
- Evaluating severity: The results of several laboratory tests can inform doctors about the severity of a patients RA, the amount of joint damage, and the prognosis or expected course of the disease.
- Treatment monitoring: Monitoring patients diagnosed with RA involves regular medical care, including doctors visits, laboratory testing, and imaging tests. Combining these strategies can assist doctors in tracking the progression of RA and understanding if treatment is effective.
- Detecting side effects: Testing may also be used to detect side effects caused by treatment drugs, as well as other health conditions that are more common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, including osteoporosis, heart disease, and diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Does Smoking Make Arthritis Worse
Assessing Your Physical Ability
If you have been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, your specialist will do an assessment to see how well you’re coping with everyday tasks.
You may be asked to fill in a questionnaire on how well you can do things like dress, walk and eat, and how good your grip strength is.
This assessment may be repeated after your treatment, to see if you have made any improvements.
Further information
Blood And Pathology Tests For Arthritis
Before any tests are done, the doctor will ask you about your symptoms and will often examine you for signs of arthritis or other autoimmune features. Then tests may be done.
Your symptoms and signs on physical examination are more important for making a diagnosis than the results of the tests.
What are blood tests and pathology tests used for?
- Confirming a diagnosis of arthritis or autoimmune disorder
- Monitoring disease activity and response to treatment
- Checking for side effects from medicines
Are all types of arthritis diagnosed by blood tests?
Most forms of arthritis can be diagnosed by blood tests. The doctor may use blood tests to provide support for the diagnosis made on the symptoms and signs, or to help rule out other types of arthritis or conditions that cause similar symptoms. No blood or pathology tests may be required to diagnose some conditions such as osteoarthritis or chronic back pain.
Recommended Reading: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Swelling In Legs
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate Test
An erythrocyte sedimentation rate test evaluates how much inflammation is present in your body. The test measures how quickly your red blood cells, called erythrocytes, separate from your other blood cells in a lab when they are treated with a substance that prevents clotting.
Red blood cells clump together when theres inflammation in your body, making them separate from your other blood cells much faster. Low ESR levels indicate low levels of inflammation while high ESR results indicate high levels of inflammation.
Doctors use this test to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis because this condition causes inflammation throughout your body. An ESR test on its own, however, is not enough to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.
Inflammation and a rise in ESR levels can be caused by other chronic conditions, and by infections or injuries. However, your ESR rate can help point doctors in the right direction. For example, very elevated ESR levels would likely indicate an infection and not rheumatoid arthritis.
Blood Fluid And Tissue Tests For Arthritis
Checking blood, tissues and various body fluids help doctors diagnose and monitor arthritis.
Blood and other lab tests play a critical role in diagnosing and monitoring arthritis. When your doctor needs to confirm an arthritis diagnosis, monitor disease progress, check medication effectiveness or determine if medications are causing potentially dangerous but not evident side effects, lab tests are ordered.
Most tests require drawing and testing the blood, but some may involve testing urine, joint fluid or even small pieces of skin or muscle.
Diagnosing and Monitoring Disease Activity
If your doctor suspects you have inflammatory arthritis, these are the most common tests used to diagnose as well as monitor the disease:
Blood Tests
Other Lab Tests
- Skin biopsy A small piece of skin is removed by a doctor. Its usually done under local anesthetic. The sample is tested in a lab and the results help determine the presence of lupus, vasculitis and psoriatic arthritis.
- Muscle biopsy A doctor takes the tissue sample from a muscle with a biopsy needle. The sample is reviewed for signs of damage to muscle fibers to help confirm a diagnosis of polymyositis or vasculitis.
- Joint fluid tests A doctor removes a small amount of fluid from a joint to determine the presence of uric acid and diagnose gout.
Monitoring Medication Response and Side Effects
Checking for Comorbidities
Quick Links
Recommended Reading: What To Do For Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Does A High Ccp Mean
Anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibody levels are characteristically elevated in rheumatoid arthritis, although they can be elevated in other rheumatologic conditions associated with inflammatory arthritis, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
What are the 4 stages of rheumatoid arthritis? Each stage of RA comes with different treatment goals. Stage 1. Stage 1 is early stage RA. Many people feel joint pain, stiffness, or swelling. Stage 2. Stage 2 is moderate stage RA. Stage 3. Once RA has progressed to Stage 3, it is considered severe. Stage 4. At Stage 4, there’s no longer inflammation in the joint.
What To Expect During The Tests
You usually do not need to do anything before a blood test for RA, fasting is not required. Tell your healthcare provider if you are taking any prescription or over-the-counter medications that may affect your tests.
Wear a garment that allows access to your elbow area for the blood draw. Bring your identification. The healthcare professional drawing the blood will ensure your identification and label the blood draw sample tubes.
A tourniquet will be placed on your arm, the vein area sanitized, and a needle will be used to collect the blood into one or more vials.
After drawing the blood, the site will be bandaged. You should not have any side effects and usually do not need to take any precautions after the test.
These tests are sent to the lab rather than being done in the clinic as a rapid test. Your results will not be available immediately but will be reported to your healthcare provider in hours to a day or more.
Recommended Reading: Does Cracking Your Knuckles Give You Arthritis
What Are The Blood Tests For Lupus And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Several autoimmune diseases affect the body. It is still unclear why these diseases occur. Again, most of them display similarities in their manifestation. Today we are looking at lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. In particular, we will dwell on the difference in blood tests for lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis

Similar to other autoimmune conditions, rheumatoid arthritis causes your immune system to attack the healthy tissues and cells in your body. Although RA usually damages the joints, it can affect other parts of the body, such as the eyes, heart, or lungs. RA can cause inflammation in joints located in the wrists, hands, knees, and ankles.
Symptoms can vary from person to person, but some early signs of RA include pain and tenderness in the joints. Over time, symptoms may get worse and progress to redness, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. Some people also have a low-grade fever and fatigue.
The exact cause of RA is not known, but several factors increase the risk of having this disease. It occurs more often in older adults and women. Smoking and being overweight also raise the risk of having RA. Certain genes have been linked to a higher chance of developing RA.
Illustration by Verywell
Also Check: Is Glucosamine And Chondroitin Good For Arthritis
Tests For Rheumatoid Arthritis
If your doctor suspects that your joint pain and tenderness could be signs of rheumatoid arthritis, hell most likely refer to you a rheumatologist for testing to confirm the diagnosis. Naturally, youll feel a little nervous as you wait to see this new doctor, and youll probably have a lot of questions, too including wondering what tests are done to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.
The good news is that rheumatoid arthritis tests are mostly non-invasive and not painful. However, you should prepare for a relatively long appointment. Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis requires a very comprehensive exam because there is no one specific test that tells us a patient has RA, says John Davis III, MD, a rheumatologist and internist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota. I set aside an hour to evaluate a new patient.
Is there a test for rheumatoid arthritis? Yes but its not just one test that can confirm the diagnosis. Here are the key components of tests for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis:
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
While the exact cause of RA is not known, various factors can increase the risk of developing RA, for example,
- Family history of RA
- Gender .
A few factors that may trigger the onset of RA include:
- Injury to bones or joints, such as a fracture, joint dislocation, or ligament tear
- Smoking
- History of viral infections, such as the Epstein-Barr virus.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Arthritis In The Knee
Diagnosing Ra In Outlier Patients
Some cases of RA may be different or more difficult to diagnose then others, and certain routine tests and exams might not be as helpful. These include patients with a very recent onset of disease, people whose RA is inactive, and those with seronegative RA.
In these situations, making an RA diagnosis may take more time, or more weight may be given to certain factors, but RA can still be accurately established.
In people with inactive RA, for example, a rheumatologist may rely less on CRP and ESR tests and more on RF and anti-CCP tests, as well as evidence of characteristic joint erosions on imaging, if the disease has been present for long enough to develop erosions.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Blood Tests For Diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that mostly affects the joints. Obtaining an RA diagnosis can feel like putting together a puzzle because this disease has symptoms that are similar to other disorders. In addition to checking your medical history and doing a physical exam, your healthcare provider may order multiple tests before diagnosing RA.
There is not a test for RA that can definitively diagnose this condition, so you may have several imaging and blood tests. The blood tests can show if your body has inflammation and is making specific proteins that are common when you have RA.
The blood tests may include:
- Rheumatoid factor
Verywell / Joshua Seong
Don’t Miss: Is Salmon Good For Arthritis
What Else Could It Be
When a doctor thinks about how likely you are to have one disease over another, or over several others, this is called a differential diagnosis. There are many conditions your doctor may consider besides RA, and besides other forms of autoimmune arthritis:
Viral arthritis: Rubella, parvovirus, and hepatitis B and C can lead to short-term arthritis symptoms that resemble RA.
Palindromic rheumatism: Periodic joint inflammation that may lead to RA, lupus, and similar diseases
Polymyalgia rheumatica: This is more common over age 50, generally less painful than RA, and associated more with shoulders and hips.
What Is A Ccp Blood Test
AkashCCP testblood teststests
Can CCP levels change? This study aimed to investigate changes in anti-CCP serum levels in RA patients on biological drugs with different mechanism of action. CONCLUSIONS: Our study showed that anti-CCP levels may change during RA course, regardless of the biological drug used and the clinical response.
Read Also: What Can You Do For Arthritis In The Neck
Rheumatoid Factor And Anti
One blood test measures levels of rheumatoid factors in the blood. Rheumatoid factors are proteins that the immune system produces when it attacks health tissue.
About half of all people with rheumatoid arthritis have high levels of rheumatoid factors in their blood when the disease starts, but about 1 in 20 people without rheumatoid arthritis also test positive.
A related blood test known as anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide test is also available. Anti-CCPs are antibodies also produced by the immune system.
People who test positive for anti-CCP are very likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis, but not everybody with rheumatoid arthritis has this antibody.
Those who test positive for both rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP may be more likely to have severe rheumatoid arthritis requiring higher levels of treatment.
What Can I Do To Prevent This In The Future
If you are on a personal connection, like at home, you can run an anti-virus scan on your device to make sure it is not infected with malware.
If you are at an office or shared network, you can ask the network administrator to run a scan across the network looking for misconfigured or infected devices.
Another way to prevent getting this page in the future is to use Privacy Pass. You may need to download version 2.0 now from the Chrome Web Store.
Cloudflare Ray ID: 6a56d9b8cf4d5a16Your IP: 3.87.240.148Performance & security byCloudflare
Recommended Reading: What Tests Diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis
Eczema Symptoms: How To Spot Them
- Get link
Eczema is a term for multiple conditions that cause itching, inflammation, or a rash-like occurrence on the skin. It is a common disorder, with over 31 million Americans experiencing it, according to the National Eczema Association .
The symptoms of eczema can vary and may not be the same for everyone. There can even be different kinds of eczema on different parts of your body at various times.
Much of the information available about eczema is about how the symptoms appear on light skin. But eczema on dark skin can look different.
In people with black or brown skin, scratching the itchy skin can also lead to hyperpigmentation in affected areas. Hyperpigmentation is when the skin becomes darker than usual.
Other the other hand, inflammation can sometimes cause depigmentation on dark skin. This is when the skin loses color and becomes lighter than usual.
Being aware of the symptoms can help you determine if you need to see a doctor for a definitive diagnosis and any treatment.
The hallmark of eczema is itchy and inflamed skin. Several different skin conditions fall under the category of eczema, so other symptoms may be present as well.
These symptoms can include:
- oozing or crusting
- swelling
Eczema looks different in babies and toddlers than in older children and adults. In babies 6 months and younger, the skin with eczema will look red and a little wet or oozy.