Diagnosis And Management Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
AMY M. WASSERMAN, MD, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Dec 1 84:1245-1252.
Patient information: A handout on this topic is available at .
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common inflammatory arthritis, with a lifetime prevalence of up to 1 percent worldwide.1 Onset can occur at any age, but peaks between 30 and 50 years.2 Disability is common and significant. In a large U.S. cohort, 35 percent of patients with RA had work disability after 10 years.3
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Patients with inflammatory joint disease should be referred to a rheumatology subspecialist, especially if symptoms last more than six weeks.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
In persons with RA, combination therapy with two or more disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs is more effective than monotherapy. However, more than one biologic agent should not be used at one time because of the high risk of adverse effects. |
||
|
A guided exercise program can improve quality of life and muscle strength in patients with RA. |
||
|
Cardiovascular disease is the main cause of mortality in persons with RA therefore, risk factors for coronary artery disease should be addressed in these patients. |
RA = rheumatoid arthritis.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
RA = rheumatoid arthritis.
Other Connective Tissue Diseases
Diseases such as primary Sjögren’s syndrome, polymyositis-dermatomyositis, limited and diffuse scleroderma and mixed connective tissue disease may also manifest as polyarthritis. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome may be extremely difficult to differentiate from rheumatoid arthritis when the main feature is polyarthritis. Prominent muscle weakness is a clue to myositis, and patients with scleroderma almost always have sclerodactyly and Raynaud’s phenomenon. Mixed connective tissue disease may present with features of rheumatoid arthritis in conjunction with those of other connective tissue diseases.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis is a general term for inflammation in joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of chronic arthritis that occurs in joints on both sides of the body , which helps distinguish it from other types of arthritis.
In addition to affecting the joints, rheumatoid arthritis may occasionally affect other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, blood, nerves, or kidneys.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, meaning that patients immune system is overreacting against itself. The result can cause some or all of the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Read Also: Rheumatoid Arthritis Longterm Effects
Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria
To help doctors make diagnoses, the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism collaborated to create the 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria.
These criteria set a minimum standard for what signs and symptoms must be noted before RA can be diagnosed.2 A total point score of 6 or more indicates rheumatoid arthritis.
| Joints Affected | |
|---|---|
| Normal C-reactive protein and normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate | |
| 1 point | Abnormal CRP or abnormal ESR |
Points may be added over time or retrospectively, meaning the signs and symptoms do not necessarily have to be recorded at the same doctors appointment.
What Else Could It Be

When a doctor thinks about how likely you are to have one disease over another, or over several others, this is called a differential diagnosis. There are many conditions your doctor may consider besides RA, and besides other forms of autoimmune arthritis:
Viral arthritis: Rubella, parvovirus, and hepatitis B and C can lead to short-term arthritis symptoms that resemble RA.
Palindromic rheumatism: Periodic joint inflammation that may lead to RA, lupus, and similar diseases
Polymyalgia rheumatica: This is more common over age 50, generally less painful than RA, and associated more with shoulders and hips.
Also Check: How To Relieve Arthritis Pain In Hands
Physical Exam And Medical History
The appointment will likely begin with the physician taking a thorough medical history. This will include asking the patient several questions, such as:
- What joints are affected?
- How would you describe the pain?
- Do you have morning stiffness?
- Have you noticed increased fatigue or weight changes?
- Have you experienced other symptoms besides joint pain?
- When did symptoms begin?
- How have symptoms changed over time?
- What movements or activities make the patient feel better or worse?
The history will also include a review of the patients:
- Other medical problems
See Lifestyle Factors and Fatigue Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
During the physical exam, a doctor will evaluate the patients general health and then examine the joints, looking for signs of joint inflammation. For example, a doctor may measure a joints range of motion, press the skin over a joint to see if it causes pain, and test joint strength.
Exercise And Physical Therapy
Results of randomized controlled trials support physical exercise to improve quality of life and muscle strength in patients with RA.32,33 Exercise training programs have not been shown to have deleterious effects on RA disease activity, pain scores, or radiographic joint damage.34 Tai chi has been shown to improve ankle range of motion in persons with RA, although randomized trials are limited.35 Randomized controlled trials of Iyengar yoga in young adults with RA are underway.36
Don’t Miss: Can Arthritis Cause Burning Sensation
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
The Primary Care Physician’s Guide To Inflammatory Arthritis: Diagnosis
The Journal of Musculoskeletal Medicine
Inflammatory arthritis includes a variety of diseases the most common are rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis. A large proportion of patients seen in most rheumatology practices have inflammatory arthritis these patients also are seen in the primary care setting, where they present initially before a diagnosis has been made. The inflammatory arthritides are chronic progressive diseases that can cause irreversible joint damage even early in the disease course.
Significant improvements have been seen in the diagnosis and management of the inflammatory arthritides over the past 10 years, including new diagnostic tests and radiological studies with higher sensitivity and specificity and biologic therapies with various mechanisms of action and improved ease of administration. The most common inflammatory arthritides-rheumatoid arthritis , ankylosing spondylitis , and psoriatic arthritis -are chronic conditions with varying causes and clinical presentations. If not recognized and managed early in the disease course, these disorders may result in irreversible joint destruction, significant physical disability, and comorbidities.1,2
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Rheumatoid arthritis RA is the most common form of chronic systemic inflammatory disease it affects 0.5% to 1% of adults in the United States.4 Some data suggest that the incidence of RA is increasing.5
Read Also: Vicks Vapor Rub For Arthritis
Which Patients Should Be Referred
Early treatment of RA can be a realistic goal only if general practitioners and other non-rheumatologists recognize the clinical picture of early inflammatory arthritis and refer patients promptly for a specialist opinion. Patients with joint pains that have persisted for more than 68 weeks should be referred especially in the presence of the following features:
-
Joint swelling
What Imaging Techniques May Be Used To Diagnose Arthritis
Imaging techniques may give your healthcare provider a clearer picture of what is happening to your joint. Imaging techniques may include the following:
-
X-ray. X-rays may show joint changes and bone damage found in some types of arthritis. Other imaging tests may also be done.
-
Ultrasound. Ultrasound uses sound waves to see the quality of synovial tissue, tendons, ligaments, and bones.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . MRI images are more detailed than X-rays. They may show damage to joints, including muscles, ligaments, and cartilage.
-
Arthroscopy. This procedure uses a thin tube containing a light and camera to look inside the joint. The arthroscope is inserted into the joint through a small incision. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen. It is used to evaluate any degenerative and/or arthritic changes in the joint to detect bone diseases and tumors to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation, and to treat certain conditions.
You May Like: Arthritis Pain In Fingers Treatment
What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include the following:
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods
- Fatigue
Rheumatoid arthritis affects each person differently. In most people, joint symptoms may develop gradually over several years. In other people, rheumatoid arthritis may proceed rapidly. A few people may have rheumatoid arthritis for a limited period of time and then go into remission .
Cartilage normally acts as a shock absorber between the joints. Uncontrolled inflammation causes the destruction and wearing down of the cartilage, which leads to joint deformities. Eventually, the bone itself erodes, potentially leading to fusion of the joint . This process is aided by specific cells and substances of the immune system, which are produced in the joints but also circulate and cause symptoms throughout the body.
Who Gets Rheumatoid Arthritis

RA is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis as previously mentioned, it affects as high as 1% of the world’s population, occurs three times more often in women than in men, and in most cases, develops in adults between the ages of 25 and 50. However, children and the elderly are also at risk.
You May Like: What Can You Take For Arthritis In Your Fingers
Illustrative Case Of Polyarthritis
A woman schoolteacher, aged 30, has for twelve weeks been troubled by pain and swelling in the small joints of her hands and feet. She says that her hands are stiff in the early mornings for a couple of hours and then improve gradually in the course of the day. Her sleep is sometimes disturbed by pain, and she feels very tired during the day. Previously she was fit and well: there is no personal or family history of psoriasis or inflammatory bowel disease and she was not knowingly exposed to infections before the onset of this illness. She lives with her husband and two children, aged 6 and 4, and her symptoms interfere with some activities of daily living. On examination her metacarpophalangeal joints are swollen and tender bilaterally, as are a few of the proximal interphalangeal joints in both hands. Compression of metatarsophalangeal joints causes pain. All her other joints are clinically normal and the examination reveals nothing else of note. Blood investigations, including liver function tests, give normal results apart from an ESR of 28 mm/h. Antibodies to parvovirus are not found, and rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibody are likewise absent. On plain radiographs of the hands and feet the only abnormality is periarticular soft tissue swelling around a few PIP joints.
Box 1Features suggestive of inflammatory arthritis
Assessing Your Physical Ability
If you have been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, your specialist will do an assessment to see how well you’re coping with everyday tasks.
You may be asked to fill in a questionnaire on how well you can do things like dress, walk and eat, and how good your grip strength is.
This assessment may be repeated after your treatment, to see if you have made any improvements.
Further information
Recommended Reading: Best Thing For Arthritis In Knees
What Are The Benefits Of Discovering Inflammatory Arthritis Early
IA requires early diagnosis it can remit if left unchecked and undiagnosed in perhaps 5% of patients, but will much more likely evolve into a chronic inflammatory arthritis, most commonly RA. Conversely, early treatment can prevent future deformity and disability, and will likely help reduce collateral damage, such as atherosclerosis.
In early arthritis there is a “window of opportunity, during which the disease can be treated before irreversible joint erosions evolve. This window is usually open 3 to 6 months after the onset of the disease. For this reason, RA can be considered a “medical emergency.”
In a meta-analysis of 14 trials by the American College of Rheumatology , patients suffering from a shorter duration of their disease were more likely to show improvement than long-term sufferers when properly diagnosed and treated. This finding supports the concept of a window of opportunity, in that early treatment improves not only short-term but long-term outcome.
How Is Ra Treated
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs biological response modifiers are medications that are an effective second-line treatment. In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
Recommended Reading: Rheumatoid Arthritis Edema Treatment
The Importance Of Early Diagnosis Of Ra
Identification of RA at initial presentation and treatment at earlier stage can affect disease course, prevent the development of joint erosions or retard progression of erosive disease . Early diagnosis and treatment may affect disease outcomes even to a remission state . Recognizing early RA from non-RA at the onset of disease is not straightforward but there is limitation in the use of the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for early diagnosis. Since due to inadequate clinical or laboratory evidences at onset of arthritis, this criteria is not sensitive enough to identify early RA .
In a study of Frech cohort, only 50.9% of RA satisfied 1987 ACR revised criteria for diagnosis of RA in 1 year . However, in the absence of treatment inflammation will lead to articular damages and bone erosion particularly within the first two years of disease onset . Regarding the current concept of “window of opportunity”, early diagnosis of RA is essential for initiation of treatment, otherwise, disease will progress to more severe forms requiring more aggressive therapy .
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. However, it is believed to be caused by a combination the following factors:
- Genetics
- The environment
- Hormones
Normally, the immune system protects the body from disease. In people who have rheumatoid arthritis, somethingpossibly infections, cigarette smoking, and physical or emotional stress, among other causestriggers the immune system to attack the joints .
Gender, heredity, and genes largely determine a person’s risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. For example, women are about three times more likely than men to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
Read Also: Arthritis Itchy Skin
Other Tests For Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis
Blood tests are not only used to detect RF and anti-CCP antibodies. They’re also used to reveal if you have:
- Anemia, or low red blood cell count, which occurs in up to half of people with RA
- A high erythrocyte sedimentation rate, also known as a sed or ESR rate, a crude measure of inflammation in your body
- High C-reactive protein levels, another marker of inflammation
Aside from blood tests, an X-ray can help your doctor determine the degree of destruction in your joints, but may only be useful when RA has progressed to a later phase.
What Are The Phases Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
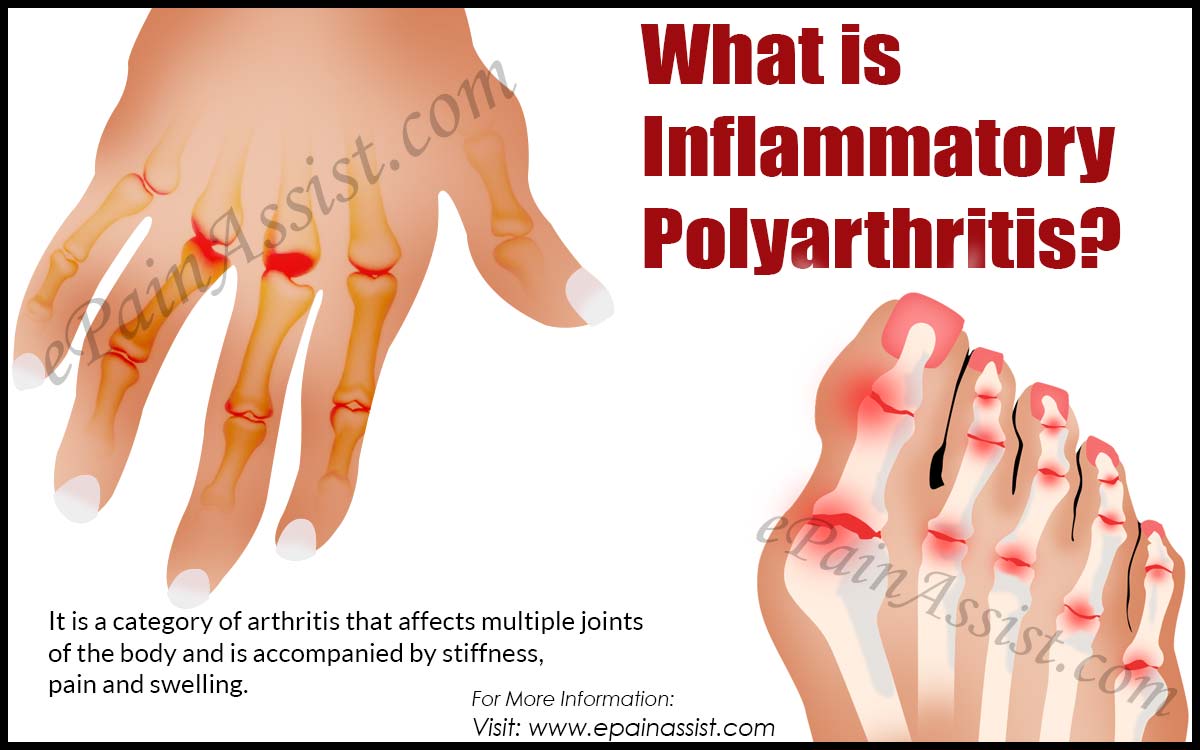
Early arthritis The term is generally applied to disease that is between a few weeks and one year in its progression. Some studies, however, consider “early arthritis” to be disease with six months of duration or less.
The turning point to chronic RA begins after 12 weeks. This is when the aforementioned window of opportunity enters its most critical stage.
Chronic RA sets in at more than one to two years, though some may consider any RA after six months to fall under this category.
Recommended Reading: I Think I Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Are The Warning Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Multiple tests can be administered to detect the warning signs of RA. The proper diagnosis of RA can include the following:
- Symmetrical inflammatory arthritis , especially in the small joints of the hands, associated with morning stiffness in the joints lasting over one half hour.
- Lab test results