Get Help Treating Osteoarthritis Or Rheumatoid Arthritis With Joint Academy
Todays technology-driven society has led to telehealth becoming a popular way for patients to receive medical guidance or treatments. Fortunately, Joint Academy is at the forefront of virtual physical therapy technology that can be used as a first line of defense for conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. With the Joint Academy app, licensed physical therapists can connect with patients digitally and provide them with personalized, evidence-based treatment programs to follow.
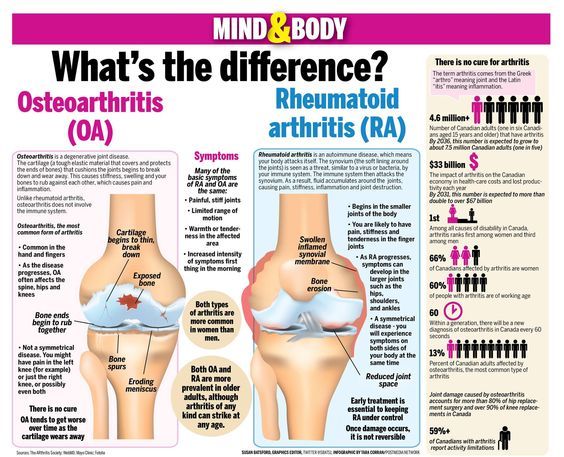
What Is The Difference Between Rheumatoid Arthritis And Osteoarthritis
Many people use the term arthritis interchangeably to describe the symptoms and causes of progressive joint deterioration and pain. However, there are several different forms of arthritis, which result in inflammation of the joints and results from a number of causes depending on the type. The most common form is osteoarthritis , and is generally caused by aging and the resulting wear and tear on the joints, most commonly those of the knees and hips. It can also result from a traumatic impact suffered from a car accident, a fall, or from an old sports injury. Arthritis treatment offered by Los Angeles rheumatologist Dr. Susan Baker can make a major difference in everyday life and comfort.
Another common form, known as rheumatoid arthritis , is actually an autoimmune disorder which occurs when the bodys own immune system targets healthy tissue. Both can lead to cartilage loss and permanent joint damage, which can cause chronic pain and affect proper function and mobility of the joint.
Characteristics Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis can happen at any point in a persons life and affects the entire body. With RA, patients typically experience a rapid onset of symptomsincluding painful, swollen, and stiff jointsin as little as a few weeks to a few months. Additionally, those living with RA experience morning stiffness that typically lasts longer than 1 hour, and fatigue and a feeling of being ill are commonly present. RA is often a symmetrical type of arthritis, which means it affects both small and large jointsincluding hands, wrists, elbows, or balls of the feeton both sides of the body simultaneously.
Anyone affected by rheumatoid arthritis has chronic inflammation in their joints, which means that the whole joint is breaking down. Therefore, rheumatoid arthritis does not only affect the cartilage. With RA, the joints then become swollen and tender, which is known as synovitis. The continuous pain, which is present both at rest and during exertion, may be so intense that anyone affected is prevented from carrying out simple everyday tasks. Anything from getting out of bed to brushing teeth can be difficult to do. Additionally, it is common for those living with RA to feel tired and depressed.
You May Like: How To Ease Arthritis Pain In Fingers
Main Differences Between Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis Causes Symptoms And Risk Factors
The bones in the various joints throughout the body are lined with a layer of cartilage, which prevents friction and allows the bones to glide freely to facilitate the motions that allow us to bend the knees, raise our arms above our shoulders, and sit and stand without experiencing pain and stiffness. Over time, the cartilage can wear out, leaving the ends of the bones exposed, which can result in pain and permanent damage to the joint if left untreated.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis in Los Angeles. The most common symptoms are:
- Pain, tenderness, and stiffness in the affected joints, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods of time
- Limited flexibility and range of motion
- Grating from friction between the ends of the bones
- Bone spurs
Anyone can develop and suffer from osteoarthritis, however, there are certain conditions and risk factors that can make the likelihood of developing the condition higher, including:
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Cream For Arthritis Pain
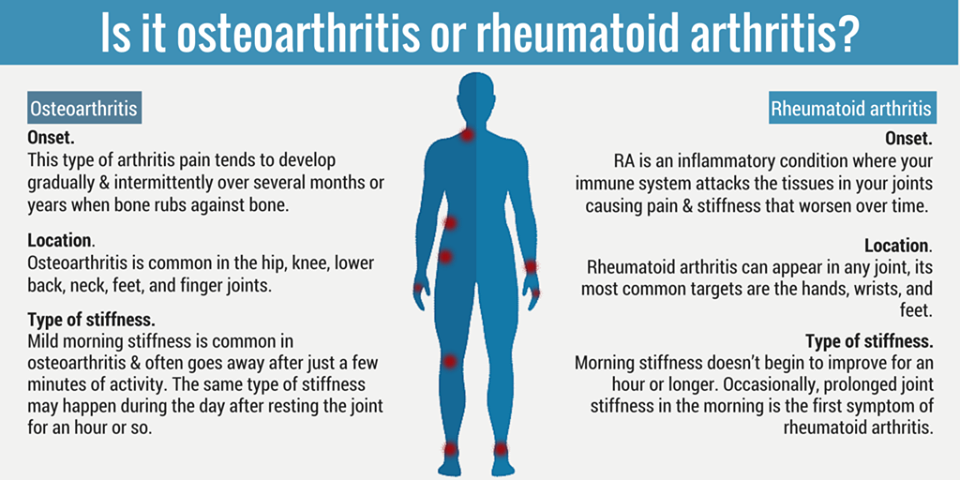
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis: Whats The Difference
- Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, affecting about 27 million people in the United States. Osteoarthritis is caused by degeneration of cartilage and is also known as degenerative arthritis.
- In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder caused by the immune system attacking the joints. This autoimmune process causes systemic inflammation, while in osteoarthritis, mechanical degeneration causes localized inflammation.
- Osteoarthritis commonly affects a single joint, such as one knee. Trauma, such as multiple injuries playing sports, is a risk factor for osteoarthritis.
- On the other hand, rheumatoid arthritis usually affects three or more joints, in a symmetric distribution . Rheumatoid arthritis frequently, but not always, causes elevation in blood levels of substances that are markers of systemic inflammation such as the ESR and CRP .
- In contrast, osteoarthritis does not cause abnormal blood test results. Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are hereditary. For example, if a woman has osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, her/his children are at increased risk of developing the same type of arthritis.
What Is The Treatment For Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis.
To date, the goal of treatment in rheumatoid arthritis is to reduce joint inflammation and pain, maximize joint function, and prevent joint destruction and deformity.
- Early medical intervention has been shown to be important in improving outcomes.
- Aggressive management can improve function, stop damage to joints as monitored on X-rays, and prevent work disability.
- Optimal RA treatment involves a combination of medicines, rest, joint-strengthening exercises, joint protection, and patient education.
- Treatment is customized according to many factors such as disease activity, types of joints involved, general health, age, and patient occupation.
- RA treatment is most successful when there is close cooperation between the doctor, patient, and family members.
- RA medications include NSAID and corticosteroids for pain and inflammation symptoms.
- Drugs that affect the progression of rheumatoid arthritis are called DMARDs
- These “second-line” or “slow-acting” medicines may take weeks to months to become effective. They are used for long periods, even years, at varying doses. If maximally effective, DMARDs can promote remission, thereby retarding the progression of joint destruction and deformity.
Arthritis
The treatment of arthritis is dependent on the precise type of arthritis present. An accurate diagnosis increases the chances for successful treatment.
Treatments available include
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Arthritis
Treatment Of Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
The good news is, there are some ways to treat both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. But, with that being said, there’s no cure for either type of arthritis and joint damage is irreversible. Instead, the treatment of both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis focuses on:
- Reducing pain in your joints
- Improving the function of your joints
- Minimising further damage to your joints
- Generally, anti-inflammatory medications and corticosteroids are used to help deal with the inflammation of your joints caused by arthritis. These should also help with the pain associated with both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
When it comes to osteoarthritis, other pain-relieving treatments are often used such as:
- Pain-reducing creams
- Pain-relievers like acetaminophen
As always, speak to your doctor before using any medications to treat your osteoarthritis.
Since rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, drugs that suppress your immune system can help with treatment. However, these treatment plans come with many caveats and require personalised care. Be sure to speak with your medical doctor about treating your rheumatoid arthritis.
Different Types Of Arthritis Very Different Treatments
The goal of treatment for both is to improve movement, reduce pain, and minimize joint damage, but the way to that is different for each disease, says Dr. Rackoff. Here’s what to expect:
RA The first line of defense is using disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs to reverse chronic inflammation. Anti-inflammatories, pain meds, and physical therapy are also used. It may take some time to determine which medication works optimally for your specific circumstances. A person may even need to try a few different types of medicine or a combination of medications. No two people, even with the same diagnoses, are alike in how they respond to various treatments. Its a puzzle that has to be put together by you and your doctor, says Dr. Wilmarth. Its very important to keep an open and honest dialogue with your doctor and healthcare team in general and especially in order to ideally reach and maintain remission with RA.
The goal with RA and other autoimmune illnesses is to treat to target . This sets remission or low disease activity as a goal. Patients are monitored frequently with their rheumatologist and adjustments to their treatment protocol are made as necessary.
RELATED: Your Rheumatoid Arthritis Plan: When Remission Is the Target
Read Also: What Does The Rash From Psoriatic Arthritis Look Like
What Characterizes Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is far more commonand generally less debilitatingthan rheumatoid arthritis. Whereas RA typically affects the cervical spine, OA may affect all regions of the spinecervical, thoracic , and lumbar .
Unlike RA, osteoarthritis is not really a disease. It is caused by the natural aging process, and you may have heard it called degenerative joint disease or spondylosis.
In essence, OA is caused by aging. For instance, when an elderly patient develops a swollen, painful joint that causes compression on the spinal cord, we call that osteoarthritis. But some people have osteoarthritis to a more accelerated degree than others. That’s natural, really, because we all age at different rates.
There are a number of specific age-related conditions that can cause osteoarthritis. These include herniated discs and lumbar or cervical spinal stenosis.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, which cushions your joints. When your cartilage begins to wear away, you lose that barrier between the bones of your joints. So your bones then can rub onto one another, which can be very painful.
Treatment Of Oa And Ra
How Osteoarthritis is Treated
Unfortunately, osteoarthritis cannot be reversed or treated. We offer various treatments and pain relievers to help patients with OA manage unpleasant symptoms.
- Intra-articular injections: Injections of corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, BOTOX® or platelet-rich plasma in the joints can help to relieve pain in the joints. These injections can provide the missing cushion or padding that the cartilage once provided before it degenerated.
- Physical therapy: Because OA weakens the joints and muscles, physical therapy can help to strengthen the affected joints. Similarly, pain management classes can help patients to minimize the symptoms of OA.
- Pain-relieving medications: Various medications can be taken to relieve the symptoms of OA, dull the pain and discomfort, and reduce swelling. These medications include Tylenol® and NSAIDs .
How Rheumatoid Arthritis is Treated
There is unfortunately no treatment to reverse rheumatoid arthritis either. We can provide various medications along with therapy to help patients manage the symptoms of RA.
- Disease-modifying medications: Various medications, known as DMARDs , can be taken to either slow the progression of RA or stop the progression entirely. These treatments can save the joints from further damage.
Also Check: Is Banana Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Ra Vs Oa: Which Is Worse Rheumatoid Arthritis Or Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disease with fluctuating symptoms and resultant complications that create a unique pattern in each patient. Often times, RA symptoms are confused with osteoarthritis symptoms. This confusion happens commonly during the initial stages of arthritic symptoms.
Despite the fact that both types of arthritis cause joint pain, the two diseases have different diagnostic criteria. Both are considered to be chronic and non-curable diseases, however, they have entirely different causes, symptoms, prognoses, and treatments.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition which is characterized by pain, tenderness, swelling and stiffness in the affected joints including hands, feet, and wrists, in a symmetrical manner. This can also result in extra-articular manifestations involving skin, eyes, lungs, blood and nerves.
Even though the exact etiology of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is an autoimmune condition where the body produces antibodies against its own cells. Some scientists suggest that microorganisms such as virus and bacteria play a major role in pathophysiology where smoking is thought to be another.
Accounting for a significant female predominance, Rheumatoid Arthritis usually affects young people around the age of 20. The majority of the patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis experience an acute onset of joint pain, tenderness, swelling and limping in joints all over the body which will gradually progress over weeks. Other extra-articular symptoms can include fever, loss of appetite and weight, generalized body aches, red eyes, rheumatoid nodules over the skin, anemia, etc. Patients can also experience aggravated joint pains in the morning which usually improves within 30 minutes in contrast to osteoarthritis pain.
The treatment plan for Rheumatoid arthritis mainly includes lifestyle modifications and pharmacological interventions.
Even though there is no lifelong cure for Rheumatoid Arthritis, timely interventions can definitely prevent disability.
Also Check: Is Banana Good For Arthritis
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Rheumatoid And Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although rheumatoid arthritis can have many different symptoms, joints are always affected. Rheumatoid arthritis almost always affects the joints of the hands , wrists, elbows, knees, ankles, and/or feet. The larger joints, such as the shoulders, hips, and jaw, may be affected. The vertebrae of the neck are sometimes involved in people who have had the disease for many years. Usually at least two or three different joints are involved on both sides of the body, often in a symmetrical pattern. The usual joint symptoms include the following:
- Stiffness: The joint does not move as well as it once did. Its range of motion may be reduced. Typically, stiffness is most noticeable in the morning and improves later in the day.
- Inflammation: Red, tender, and warm joints are the hallmarks of inflammation. Many joints are typically inflamed .
- Swelling: The area around the affected joint is swollen and puffy.
- Nodules: These are hard bumps that appear on or near the joint. They often are found near the elbows. They are most noticeable on the part of the joint that juts out when the joint is flexed.
- Pain: Pain in rheumatoid arthritis has several sources. Pain can come from inflammation or swelling of the joint and surrounding tissues or from working the joint too hard. The intensity of the pain varies among individuals.
These symptoms may keep someone from being able to carry out normal activities. General symptoms include the following:
Osteoarthritis
Oa And Ra: Key Comparisons
More than 30 million people in the United States are believed to have osteoarthritis, which is a degenerative joint disease. It’s often called wear-and-tear arthritis and is caused by the breakdown of joint cartilagecushioning that sits between the bones that form your joints.
Cartilage loss can cause bones to rub together, which is extremely painful. Osteoarthritis typically begins in a single joint and is more common after age 65.
Rheumatoid arthritis is much less common, with an estimated 1.5 people in the U.S. diagnosed with it. RA is a chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease that primarily targets the lining of the joint , but it can also affect the organs throughout your body. Multiple joints are usually involved, as well.
RA disease onset is most common in people between 30 and 60. Women are two to three times more likely than men to have the disease, and men tend to get it later in life.
| OA vs. RA: At a Glance |
|---|
You May Like: How To Deal With Arthritis
What Is Osteoarthritis
Also known as Arthrosis, osteoarthritis is a degenerative type of disorder which is known to be the commonest form of arthritis seen in the community.
It occurs as a result of wearing off of the protective cartilage at the end of joints over time. This cartilage acts a friction absorbing cushion, and the absence of it can lead to a continuous friction generated on rubbing the bones with one another, ultimately ending up with a worn-off joint. Even though this condition can damage any joint in the body, most commonly affected joints include hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Advanced age, obesity, trauma to the joints, genetics, bone deformities , long-term weight bearing and heavy weight lifting can be risk factors for osteoarthritis females are at a higher risk than males. More often, this affects people over 40 years of age but it can also be seen in youngsters following accidents and trauma.
Patients with osteoarthritis usually experience pain around the affected joints, difficulty in moving them due to stiffness pain and stiffness are aggravated more towards the morning just after waking up which usually lasts for more than 30 minutes. In addition, these people will also complain of loss of flexibility, limited range of movements, loss of muscle bulk, a grating sensation on moving joints and spurs which present as hard bony-like structures over the skin around the affected joints.
Ra Vs Oa Epidemiology
The primary difference between RA and OA is the underlying nature of the disease. RA is an autoimmune disorder that produces inflammatory joint symptoms throughout the body. OA is a degenerative condition that is the result of increased wear and tear on joints. OA may produce inflammatory symptoms as well, but it primarily destroys joint cartilage over time.
OA affects an estimated 27 million Americans while only 1.3 million Americans have RA. Both RA and OA are more prevalent in women than in men. RA can develop in patients anytime between the ages of 30 and 60 years old. OA generally develops later in life.
Also Check: Rheumatoid Arthritis Drug Side Effects