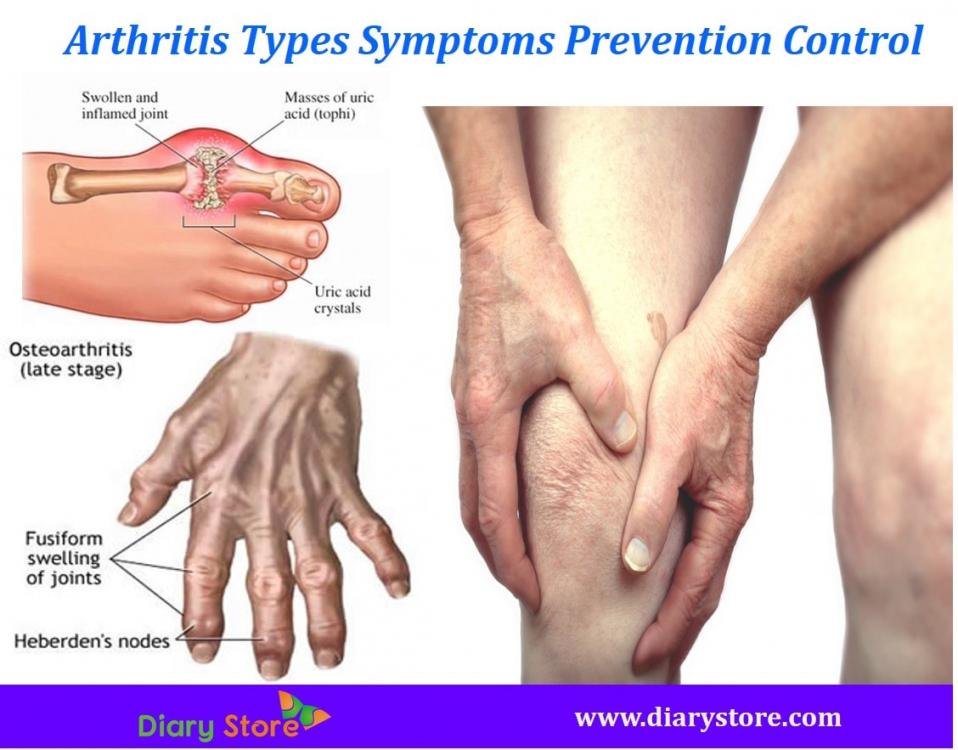
Types Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Seropositive Or Seronegative Ra
IBJI
February 11, 2016;|;Blog
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease wherein the immune system attacks parts of the body leading to inflammation of the joints.;While the exact cause of RA is still a mystery, it is believed that an infection can confuse the immune system causing it to start attacking the joints. Scientists think that two chemicals in our body, specifically the tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 trigger the immune system in rheumatoid arthritis. Symptoms such as pain, stiffness and swelling in multiple joints of the hands, wrists, knees, feet, shoulders, can develop gradually or come on suddenly.; RA symptoms are very similar to a number of other diseases, and therefore correct diagnosis even through clinical examination, x-rays, and lab tests can prove difficult. Without early treatment, the disease can damage the fibrous connective joints tissues, which eventually damages the bones.
Rheumatoid Factor Positive RA
Rheumatoid Factor Negative RA
People who test negative for the presence of antibodies or RF in the blood are referred to as seronegative. But they can still have RA. Diagnosis cannot be just based on this test, as clinical symptoms, X-rays, and other laboratory tests will be taken into account. While there is no certainty of this, people who test RF negative are likely to have a milder form of RA than those who test positive.
Overlapping Conditions
Related Services
Signs And Symptoms Of Rheumatic Diseases
Different types of rheumatic disease have different symptoms.
The following are some of the most common symptoms of arthritis and rheumatic diseases:
- Joint Pain
- Swelling of a joint or joints
- Joint stiffness that lasts for at least one hour in the early morning
- Chronic pain or tenderness in a joint or joints
- Warmth or redness in a joint area
- Limited movement in an affected joint or joints
In addition, some rheumatic diseases are characterized by specific symptoms. For example, the majority of lupus patients will experience some form of skin rash along with joint pain with inflammation and fatigue.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Arthritis: Whats The Difference
Arthritis is a general term used to describe joint disease. Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of arthritis in which the bodys immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing chronic inflammation.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the bodys immune system attacks the joint linings that produce fluid that lubricates the joints. This results in signs and symptoms of inflammation, swelling, and pain in and around the joints, and in some cases, a rash. Over time, if left untreated, RA damages cartilage and bone and causes permanent joint deformity.
RA affects joints on both sides of the body, typically the hands, feet, wrists, elbows, knees and ankles, although it can also affect other joints. It can also affect the cardiovascular or respiratory systems.
Different types of medications are used to treat RA, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs , and subsets of DMARDs . Rheumatoid arthritis is diagnosed with a physical exam and history, a blood test and sometimes xrays.
Other types of arthritis include:
- Osteoarthritis the most common type of arthritis, resulting from degeneration of cartilage
- frustration, and
- social withdrawal.
Rheumatoid arthritis usually inflames multiple joints and affects both sides of the body. In its most common form, therefore, it is referred to as a symmetric polyarthritis.
Arthritis
You May Like: What Can I Take Over The Counter For Arthritis Pain
What You Need To Know About Ra And Lung Disease
Learn more about how respiratory problems are one of the most serious and common complications of rheumatoid arthritis.
Besides the joints, the inflammatory process that underlies rheumatoid arthritis also affects other parts of the body, including the lungs, skin, eyes, digestive system, heart and blood vessels. RA-related lung complications are the most common extra-articular symptoms of RA and include pulmonary nodules ; pleural effusion ; bronchiectasis ; and interstitial lung disease .In fact, it is estimated that 1 in 10 people with rheumatoid arthritis will develop ILD over the course of their disease, making it as deadly among people with RA as congestive heart failure.
What Is Interstitial Lung Disease?
Interstitial lung disease refers to a group of disorders characterized by inflammation and scarring of the lung tissue. In the case of RA-associated ILD, the scarring is caused when the over-active immune system attacks the lungs. When the scarring builds up over time, breathing becomes difficult, and patients may need lung transplants to regain function.
Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease
The risk of developing lung disease is eight times higher in people with RA than in the general population. However, most people with RA are not affected. Risk factors for ILD include:
Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease
Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease
How Can You Protect Your Lungs?
Quick Links
What Are The Types Of Arthritis Medications
Arthritis medication regimens depend upon the diagnosis of the precise type of arthritis. Some types of medications that relieve pain and reduce inflammation are commonly used for all types of arthritis. These medications, however, do not alter the course of the disease.
Symptom-relief medications
Medications used for symptom relief from arthritis include the following:
- Analgesics
- Corticosteroids
Disease-specific medications
In addition to the pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications, the disease-specific medications that are prescribed include:
- Antimicrobial medications for infectious arthritis
- Medications for bone loss and joint lubrication in osteoarthritis
- Medications to lower uric acid in gout
- Medications for fibromyalgia
- Fostamatinib
Recommended Reading: What Does The Rash From Psoriatic Arthritis Look Like
Surgery For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Surgery is required only in severe cases of Rheumatoid Arthritis when conservative measures fail to work properly.
Given below are few of the different forms of surgeries performed to treat Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Joint Replacement: This surgical treatment procedure for Rheumatoid Arthritis is performed by removing the affected joint and replacing it with an artificial joint. The most frequently replaced joints are the knees and the hips.
- Joint Fusion: This surgical treatment procedure is more frequently performed for the small joints like as those in the fingers, wrist and ankle which are affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis . This is performed by placing the ends of the two bones of the infected joint locking them together and holding them until they unite and heal to form one single bone.
- Synovectomy: This surgery for rheumatoid arthritis is performed for removing the inflamed tissue of the joint i.e. synovium. Synovectomy is often performed by using arthroscopy.
Watch 3D Video of Knee Joint Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Measures To Reduce Bone Loss
Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can cause bone loss, which can lead to osteoporosis. The use of prednisone further increases the risk of bone loss, especially in postmenopausal women.
You can do the following to help minimize the bone loss associated with steroid therapy:
- Use the lowest possible dose of glucocorticoids for the shortest possible time, when possible, to minimize bone loss.
- Get an adequate amount of calcium and vitamin D, either in the diet or by taking supplements.
- Use medications that can reduce bone loss, including that which is caused by glucocorticoids.
- Control rheumatoid arthritis itself with appropriate medications prescribed by your doctor.
Read Also: Is Bee Pollen Good For Arthritis
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease
Mixed connective tissue disease is an autoimmune disease with overlapping characteristics of three connective tissue diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and polymyositis. In addition to joint pain, symptoms include muscle pain or weakness, low-grade fever, fatigue, and Raynaud’s syndrome.
The cause of MCTD isn’t known, but there may be a genetic component. It’s much more prevalent in women than in men, especially young women.
This disease is very difficult to diagnose because its symptoms overlap with other diseases, and the symptoms don’t occur all at the same time. The distinguishing point with MCTD is the high concentrations of anti-U1 RNP in the blood.
Treatment involves managing symptoms with anti-inflammatory medications, pain relievers, and other drugs as needed. Treatment is dependent on the severity of the symptoms.
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood.; For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
Also Check: How To Stop Arthritis From Progressing
Medications To Manage Symptoms
Some drugs can help to relieve symptoms and slow disease progression.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are available over the counter from pharmacies. Examples include Advil, Motrin, and Aleve. Long-term use and high doses can lead to side effects, such as bruising, gastric ulcers, high blood pressure, and kidney and liver problems.
Corticosteroids reduce pain and inflammation and may help slow joint damage, but they cannot cure RA. If NSAIDs do not work, a doctor may inject a steroid into the joint. Relief is usually rapid, but the effect is variable. It can last a few weeks or months, depending on the severity of symptoms.
Corticosteroids can help with acute symptoms or short-term flareups. Long-term use of corticosteroids can have serious side effects, such as cataracts, osteoporosis, glaucoma, diabetes mellitus, and obesity. For this reason, a doctor will limit the number of times a person can receive these injections.
Diseases That Are Related To Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease that is characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints. Here is some information on diseases that are related to rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease that is characterized by chronic inflammation of the joints. Here is some information on diseases that are related to rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory autoimmune disorder wherein the immune cells and antibodies that normally defend the body against pathogens or disease-causing agents attack the membrane that lines the joints. Such an immune response occurs due to the bodys inability to differentiate between the bodys own tissues and the foreign invaders. When the joints get inflamed due to the attack by antibodies, it gives rise to symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, fatigue, malaise and reduced mobility.
Since rheumatoid arthritis is a serious disease, one must watch out for the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Though there can be flare-ups, the symptoms can be managed with medical treatment. If drug therapy is administered in the initial stages, the disease can go into remission and the patient would definitely have a better chance of living a normal life.
Recommended Reading: How To Ease Arthritis Pain In Fingers
What Is The Treatment For Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis.
To date, the goal of treatment in rheumatoid arthritis is to reduce joint inflammation and pain, maximize joint function, and prevent joint destruction and deformity.
- Early medical intervention has been shown to be important in improving outcomes.
- Aggressive management can improve function, stop damage to joints as monitored on X-rays, and prevent work disability.
- Optimal RA treatment involves a combination of medicines, rest, joint-strengthening exercises, joint protection, and patient education.
- Treatment is customized according to many factors such as disease activity, types of joints involved, general health, age, and patient occupation.
- RA treatment is most successful when there is close cooperation between the doctor, patient, and family members.
- RA medications include NSAID and corticosteroids for pain and inflammation symptoms.
- Drugs that affect the progression of rheumatoid arthritis are called DMARDs
- These “second-line” or “slow-acting” medicines may take weeks to months to become effective. They are used for long periods, even years, at varying doses. If maximally effective, DMARDs can promote remission, thereby retarding the progression of joint destruction and deformity.
Arthritis
The treatment of arthritis is dependent on the precise type of arthritis present. An accurate diagnosis increases the chances for successful treatment.
Treatments available include
Prevention Of Rheumatic Diseases
There are no known ways to prevent certain rheumatic diseases, including ankylosing spondylitis, fibromyalgia, gout, infectious arthritis, Lyme disease, lupus, psoriatic arthritis, and rheumatic arthritis.
However, in some cases, avoiding or reducing certain triggers can help prevent flares. For lupus, this means avoiding common triggers, such as stress, infections, certain medications, or sunlight, per the Lupus Foundation of America.
For gout, it may help to avoid diuretics , drinking alcohol, or consuming foods or drinks high in fructose or too many purine-rich foods , notes the CDC.
Recommended Reading: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Swollen Lymph Nodes
Symptoms And Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Onset of rheumatoid arthritis is usually insidious, often beginning with systemic and joint symptoms. Systemic symptoms include early morning stiffness of affected joints, generalized afternoon fatigue and malaise, anorexia, generalized weakness, and occasionally low-grade fever. Joint symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness. Occasionally, the disease begins abruptly, mimicking an acute viral syndrome.
The disease progresses most rapidly during the first 6 years, particularly the first year; 80% of patients develop some permanent joint abnormalities within 10 years. The course is unpredictable in individual patients.
Joint symptoms are characteristically symmetric. Typically, stiffness lasts > 60 minutes after rising in the morning but may occur after any prolonged inactivity . Involved joints become tender, with erythema, warmth, swelling, and limitation of motion. The joints primarily involved include the following:
-
Wrists and the index and middle metacarpophalangeal joints
-
Proximal interphalangeal joints
Alternative And Complementary Therapies For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Certain;lifestyle changes and home remedies;may be beneficial in addition to the conventional treatment of medication, physical therapy, and surgery if needed.
Relaxation techniques, visualization exercises, group counseling, and psychotherapy can help reduce the stress of living with RA.;Sleeping well;is also an important part of managing symptoms.
You should always check with your medical provider before trying any complementary or alternative therapies.
Don’t Miss: How To Ease Arthritis Pain In Lower Back
Signs And Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis equally affects the joints on both sides of the body. The joints which often get affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis may include knees, feet, wrists, ankles and fingers. Rheumatoid arthritis usually starts slowly with fatigue, stiffness and minor joint pains.
Some of the common symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis may include:
- Stiffness is the most common symptom of rheumatoid arthritis, which is often experienced in the morning hours which may continue up to an hour.
- Warmth, tenderness and stiffness over the joints when not in use for an hour is also a symptom of Rheumatoid arthritis .
- Pain in the joints on both sides of the body may also be experienced.
- Range of motion of the joints may reduce over time.
- Dryness in the mouth and eyes may also be experienced.
- Discharge from the eyes with itching and burning.
- Development of nodules under the skin could also be noted.
- Another notable symptom of Rheumatoid arthritis is burning, numbness and tingling in the feet and hands.
- Difficulties with sleep.
How Is Ra Treated
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs ; biological response modifiers are medications that are an effective second-line treatment.; In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
Read Also: How To Keep Arthritis From Spreading
Related Conditions And Causes Of Rheumatic Diseases
About 10 percent of people with ankylosing spondylitis also have a form of inflammatory bowel disease, according to the Spondylitis Association of America. Inflammatory bowel disease includes both Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis.
Lupus typically occurs alone. However, according to the Lupus Foundation of America, some people with lupus experience symptoms typical of one or more other connective tissue diseases such as celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune thyroid disease.
According to the Arthritis Foundation, 20 to 30 percent of rheumatoid arthritis patients will eventually develop an RA-related lung disease, such as interstitial lung disease , chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , or asthma.
In addition, osteoporosis, anxiety, and depression are common in people with RA, notes the Mayo Clinic.
Can I Do Anything To Prevent Ra
Thereâs no way to prevent RA, but you can lower your chances if you:
Quit smoking. Itâs the one sure thing besides your genes that boosts your odds of getting RA. Some studies show it also can make the disease get worse faster and lead to more joint damage, especially if youâre ages 55 or younger. If youâre overweight and a smoker, your chances of developing RA go up.
Take care of your gums: New research shows a link between RA and periodontal disease. Brush, floss, and see your dentist for regular checkups.
Even though thereâs nothing you can do to ensure you wonât get it, keep in mind that early treatment can make your symptoms less painful and save your joints from damage. Ideally, you should begin treatment within 3 to 6 months of your first symptoms.
You May Like: How To Treat Arthritis In Knee At Home