Question 3 Of : Symptoms
Blood Tests For Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is an autoimmune disease. Several blood tests can detect immune system changes or antibodies that may attack the joints and other organs. Other tests are used to measure the presence and degree of inflammation.
For blood tests, your doctor will draw a small sample from a vein. The sample is then sent to a lab for testing. Theres no single test to confirm RA, so your doctor may order multiple tests.
What Are The Four Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stage 1: In early stage rheumatoid arthritis, the tissue around your joint is inflamed. You may have some pain and stiffness. If your provider ordered X-rays, they wouldnt see destructive changes in your bones.
- Stage 2: The inflammation has begun to damage the cartilage in your joints. You might notice stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
- Stage 3: The inflammation is so severe that it damages your bones. Youll have more pain, stiffness and even less range of motion than in stage 2, and you may start to see physical changes.
- Stage 4: In this stage, the inflammation stops but your joints keep getting worse. Youll have severe pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of mobility.
Also Check: Does Sugar Cause Arthritis Flare Up
Learning When You’re Stiff
RA-related stiffness is usually worst in the morning and lasts about an hour, Dr. Khan says: The fingers are tight. They have a hard time movingthey feel like the Tin Manand then as they get moving, in half an hour to an hour, symptoms get better. Any extended period of sitting or just not moving can cause RA joints to stiffen up, too. Osteoarthritis stiffness typically happens for less time later in the day, after physical activity.
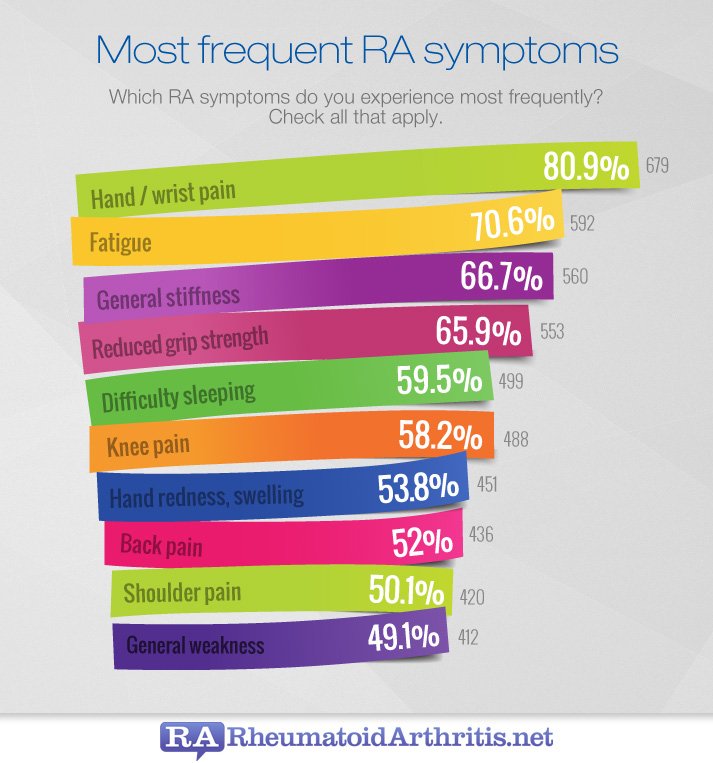
Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria

To help doctors make diagnoses, the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism collaborated to create the 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria.
These criteria set a minimum standard for what signs and symptoms must be noted before RA can be diagnosed.2 A total point score of 6 or more indicates rheumatoid arthritis.
| Joints Affected | |
|---|---|
| Normal C-reactive protein and normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate | |
| 1 point | Abnormal CRP or abnormal ESR |
Points may be added over time or retrospectively, meaning the signs and symptoms do not necessarily have to be recorded at the same doctors appointment.
Recommended Reading: What Do You Do For Arthritis In Your Back
What Is Involved In Reviewing Your Medical History And Your Current Symptoms
When reviewing your medical history, your healthcare provider may ask the following questions:
-
Have you had any illnesses or injuries that may explain the pain?
-
Is there a family history of arthritis or other rheumatic diseases?
-
What medication are you currently taking?
Your healthcare provider may also ask:
-
What symptoms are you having? For example, pain, stiffness, difficulty with movement, or swelling.
-
About your pain:
-
What makes it worse?
Question 1 Of : Background
You May Like: What Can Cure Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Is The Safest Drug For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The safest drug for rheumatoid arthritis is one that gives you the most benefit with the least amount of negative side effects. This varies depending on your health history and the severity of your RA symptoms. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a treatment program. The drugs your healthcare provider prescribes will match the seriousness of your condition.
Its important to meet with your healthcare provider regularly. Theyll watch for any side effects and change your treatment, if necessary. Your healthcare provider may order tests to determine how effective your treatment is and if you have any side effects.
What Should Be Done If Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Suspected
Any person who is suspected of having RA should be referred to a specialist rheumatologist. Early referral is important so that disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs may be prescribed as soon as possible so as to slow or halt the disease process. Delay in referral or receiving a definitive diagnosis and treatment can result in significant costs to the individual, particularly those who are employed. This is because joint damage occurs most rapidly in the early stages of the disease, and often the treatment drugs can take several months to work.
Investigations can be normal in rheumatoid arthritis, particularly early in the disease, and therefore there is no need to wait for results before the referral. In cases where it is felt that the most likely diagnosis is one of the conditions mentioned above then it is probable that you would be reviewed with the results of your investigations as these do not require an urgent referral. The Scottish equivalent of NICE also advises early referral. Both guidelines emphasise the importance of the history of what has been happening. As there is a strong genetic element to rheumatoid arthritis, it is very helpful to let your GP know if other members of your family are also affected by RA or another auto-immune condition.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know You Have Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis Blood Tests
The rheumatoid arthritis blood tests that doctors perform to help diagnose the disease include:
- Rheumatoid factor
- C-Reactive Protein
- Antinuclear Antibody
None of these tests can singularly conclude that a patient has rheumatoid arthritis. Rather, doctors look at the combined results from all, alongside a number of other criteria including physical symptoms and genetics, in order to reach a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
Getting Tested For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Testing for rheumatoid arthritis is ordered by a doctor or specialist if indicated by a patients symptoms. Blood and urine samples used for testing can be obtained in a doctors office or other medical setting.
Synovial fluid is a liquid that is located in spaces between a persons joints, helping to cushion ends of bones and reduce friction during movement. For a synovial fluid analysis, a sample of synovial fluid is obtained during a procedure called a joint aspiration or arthrocentesis. During a joint aspiration, a doctor uses a needle to withdraw a sample of synovial fluid from a joint.
Read Also: What Are The 4 Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Managed
You can manage rheumatoid arthritis by taking medicines as prescribed to treat pain and joint inflammation. You can also help reduce symptoms by exercising and maintaining a healthy weight. Aim to do 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This can be at one time or broken up into shorter sessions.
You may also need to make changes at home to help you manage daily tasks like cleaning or gardening. An occupational therapist can help you make adjustments if pain or joint stiffness makes certain tasks hard to complete. They can recommend tools to reduce strain on your joints, such as long-handled dustpans so you dont need to bend over, or book holders to reduce the strain on your hands and wrists.
You might find that rheumatoid arthritis makes you frustrated and upset. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause poor sleep, which can also make you feel down. Discus your feelings with friends and family and explain to them what they can do to support you. This may help you feel better and reassured that help is available, if needed. If you are struggling with a low mood or not managing to sleep, your doctor will be able to support you and work with you to build a plan to help.
Routine Monitoring And Ongoing Care
Regular medical care is important because your doctor can:
- Monitor how the disease is progressing.
- Determine how well the medications are working.
- Talk to you about any side the effects from the medications.
- Adjust your treatment as needed.
Monitoring typically includes regular visits to the doctor. It also may include blood and urine tests, and xrays. Having rheumatoid arthritis increases your risk of developing osteoporosis, particularly if you take corticosteroids. Osteoporosis is a bone disease that causes the bones to weaken and easily break. Talk to your doctor about your risk for the disease and the potential benefits of calcium and vitamin D supplements or other osteoporosis treatments.
Read Also: How Does Arthritis In The Knee Feel
How Is Ra Treated
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs biological response modifiers are medications that are an effective second-line treatment. In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
Family & Personal Medical History
The patients medical history and family history are important factors in helping to reach a RA diagnosis. Studies have shown that the average risk of someone in the general population developing RA is about 1%. However, if there is a family history of the disease, the risk of another family member developing RA increases.
When diagnosing RA doctors ask about the following:
- Patients family members who have or had RA
- Patients existing or past autoimmune disorders
- Patients family members with other autoimmune disorders
- Other medical conditions, illnesses or complications
Depending on each patients unique set of answers, it can help doctors identify factors that lead to a RA diagnosis.
Also Check: How To Stop Arthritis Inflammation
What Conditions May Be Confused With Ra
Fibromyalgia
People with this condition often feel pain all over, in all their muscles and joints, and have multiple tender points when examined. They will also often have a degree of early morning stiffness. Poor unrestorative sleep is often present, with associated fatigue and low mood, and often there are associated symptoms of headaches and irritable bowels and bladder. Investigations tend to be normal. It is important to distinguish this condition from rheumatoid arthritis as their management is very different, although sometimes both conditions are present.
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
This condition causes pain and stiffness of the shoulders and thighs and tends to occur in people over 65 years of age. It is more common in females. Sometimes elderly people with RA present with similar symptoms. PMR is treated by a course of steroid tablets where the dosage is gradually reduced over months and can generally be stopped after about 18 months 2 years. In people with RA presenting with PMR type symptoms, the correct diagnosis of RA usually becomes apparent when the patient is unable to reduce the steroid dosage below 10mg.
Post-viral arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Crystal Arthritis
Other types of inflammatory arthritis
Key Points: Diagnosis And Initial Management Decisions
There are 2 questions for the primary care physician when evaluating a patient with arthritis: Is the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis likely? Does the patient need early treatment or referral to a rheumatologist, or both? Findings making rheumatoid arthritis the likely diagnosis and prompting initiation of treatment are:
Joint swelling of 3 or more joints
-
Metacarpal or metatarsal joint involvement
Don’t Miss: Can Prednisone Help Arthritis Pain
How Else Can Your Gp Surgery Help
Your GP surgery can be involved in your RA care in many different ways. They continue to look after you in general and may want to keep a close eye on your blood pressure, cholesterol and blood glucose levels as there is a higher risk of heart disease in people affected by rheumatoid arthritis. This is often done as an annual review with one of the practice nurses. Many GP surgeries are involved in doing the blood monitoring for the specific drugs used in controlling and treating the joint inflammation , so you may get your regular blood tests performed by your surgery.
Rheumatoid arthritis, along with many of the treatments used affects the bodys immune response to infections. Your surgery may therefore contact you to offer you annual influenza jab and also a Pneumovax for pneumonia . With some of these treatments live vaccines should be avoided so please ensure you contact your Doctors surgery if you are planning to travel abroad.
Understand What Tests May Be Needed To Properly Diagnose This Chronic Inflammatory Condition
The early detection of rheumatoid arthritis is important to change the course of the disease. Unfortunately, no single test can adequately diagnose the condition, so individuals who suspect they may have RA may need to undergo a series of screenings and exams. Be sure to share with your doctor all of your symptoms, even if they do not seem related to the disease, advises Arthritis Research UK.
Don’t Miss: Does Psoriatic Arthritis Get Worse
What Imaging Techniques May Be Used To Diagnose Arthritis
Imaging techniques may give your healthcare provider a clearer picture of what is happening to your joint. Imaging techniques may include the following:
-
X-ray. X-rays may show joint changes and bone damage found in some types of arthritis. Other imaging tests may also be done.
-
Ultrasound. Ultrasound uses sound waves to see the quality of synovial tissue, tendons, ligaments, and bones.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . MRI images are more detailed than X-rays. They may show damage to joints, including muscles, ligaments, and cartilage.
-
Arthroscopy. This procedure uses a thin tube containing a light and camera to look inside the joint. The arthroscope is inserted into the joint through a small incision. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen. It is used to evaluate any degenerative and/or arthritic changes in the joint to detect bone diseases and tumors to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation, and to treat certain conditions.
Diagnosing Ra In Outlier Patients
Some cases of RA may be different or more difficult to diagnose then others, and certain routine tests and exams might not be as helpful. These include patients with a very recent onset of disease, people whose RA is inactive, and those with seronegative RA.
In these situations, making an RA diagnosis may take more time, or more weight may be given to certain factors, but RA can still be accurately established.
In people with inactive RA, for example, a rheumatologist may rely less on CRP and ESR tests and more on RF and anti-CCP tests, as well as evidence of characteristic joint erosions on imaging, if the disease has been present for long enough to develop erosions.
Don’t Miss: Can You Take Aleve Everyday For Arthritis
How Is Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed
Some patients still have RA but do not test positive for either anti-CCPs or RF they have seronegative RA.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
Your doctor may also conduct a synovial biopsy, which involves removing a small piece of the tissue lining one of your joints.
RELATED: Psoriatic vs Rheumatoid Arthritis: Whats The Difference?