Ra Facts And Statistics About Diagnosis
In order to reach a RA diagnosis, doctors look at multiple criteria. Doctors must take into consideration the following:
- Clinical symptoms observed through physical examination
- Family and personal medical history
- Blood test results for rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies as well as inflammation levels
- Imaging tests detecting bone erosion and joint inflammation levels
Genetic Variants In Rheumatoid Arthritis
Furthermore, we evaluated the impact of genetic variants in selected pro- and anti-inflammatory genes in association with occurrence of RA. Significantly, more G allele carriers of rs1801275 in IL4R and of rs361525 in TNF were in the group of patients suffering from RA compared to the group of probands without RA .
Look Out For Signs Of Depression
People with chronic pain are four times more likely to experience depression than the general population. Symptoms of depression include:
People with depression may also have marked changes in their appetite and sleep habits.
If you have symptoms of depression along with fatigue, talk to your doctor. They can prescribe antidepressants or talk therapy, or both. Since fatigue is a symptom of depression, treating your depression may help relieve your fatigue too.
You May Like: How Do I Know What Type Of Arthritis I Have
Clinical Characteristics Of Ra And Psa
For RA, the American College of Rheumatology /European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria were designed for patient characterisation and use in clinical trials. The key clinical characteristic is the confirmation of definite, persistent, clinical synovitis in at least one joint. The criteria include the number of joints involved, duration of symptoms, and the demonstration of serological markers and an elevated acute-phase reactant. For PsA, the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis help categorise patients with inflammatory articular disease for clinical trials. Key clinical characteristics include a personal or family history of psoriasis, psoriatic nail dystrophy and dactylitis. Neither classification criteria should be confused as diagnostic criteria.
Joint involvement is predominantly symmetric in RA and often, but not always, asymmetric in PsA. In both RA and PsA, most patients have polyarthritis , although joint involvement can be oligoarticular or polyarticular. Monoarticular disease is less common in PsA however, 5%10% of patients may present with isolated distal joint involvement. In PsA, prognosis worsens and symmetry of joint involvement tends to increase as the number of affected joints increases.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Questions You Need To Ask Your Rheumatologist

RA has four progressive stages with varying symptoms and treatment at each stage. It may also enter remission, where you might not experience any symptoms for a few weeks or even months.
Asking about your current condition, how it may progress, indicators you need to be aware of, and how to manage it will help you deal with RA better.
RA has several treatment options:
- Diet and lifestyle changes: Nutritious diet, regular exercise, limiting alcohol, etc.
- Medications: Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Agents , Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs , corticosteroids, biological drugs, etc.
- Therapy: Physical and occupational therapy
- Surgery: Synovectomy, tendon repair, joint fusion, and total joint replacement
Your rheumatologist will create a personalized treatment plan that caters to your symptoms and condition. You can ask them about the side effects of medications or surgery and how to deal with them.
Every medicine works differently. Corticosteroids and NSAIDs work at a chemical level and reduce inflammation, providing faster pain relief.
On the other hand, DMARDs and biological drugs work towards treating the inflammation at its roots, taking a long time. You can ask your rheumatologist when youll start seeing results and what that might look like.
Don’t Miss: Is The Keto Diet Good For Arthritis
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Managed
You can manage rheumatoid arthritis by taking medicines as prescribed to treat pain and joint inflammation. You can also help reduce symptoms by exercising and maintaining a healthy weight. Aim to do 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This can be at one time or broken up into shorter sessions.
You may also need to make changes at home to help you manage daily tasks like cleaning or gardening. An occupational therapist can help you make adjustments if pain or joint stiffness makes certain tasks hard to complete. They can recommend tools to reduce strain on your joints, such as long-handled dustpans so you dont need to bend over, or book holders to reduce the strain on your hands and wrists.
You might find that rheumatoid arthritis makes you frustrated and upset. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause poor sleep, which can also make you feel down. Discus your feelings with friends and family and explain to them what they can do to support you. This may help you feel better and reassured that help is available, if needed. If you are struggling with a low mood or not managing to sleep, your doctor will be able to support you and work with you to build a plan to help.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Ra
With RA, there are times when symptoms get worse, known as flares, and times when symptoms get better, known as remission.
Signs and symptoms of RA include:
- Pain or aching in more than one joint
- Stiffness in more than one joint
- Tenderness and swelling in more than one joint
- The same symptoms on both sides of the body
Don’t Miss: Can Spinal Arthritis Be Cured
Epidemiological Characteristics Of Ra And Psa
RA is more common than PsA, affecting more than 1 million in the USA. PsA affects roughly half a million people in the USA and approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis. Worldwide prevalence estimates for RA and PsA are variable. In many populations, RA prevalence is estimated to be 0.5%1.0% however, prevalence is much higher in Native American Indian populations but lower in China and Japan . PsA prevalence estimates in the USA and Europe range from 0.1% to 0.4%, whereas in Japan, PsA prevalence is lower. This variability in prevalence suggests that both environmental and genetic factors affect risk for disease.
What Areas Of The Body Are Affected
Symptoms of joint inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis can occur throughout several areas of the body. The nature of autoimmune disease in RA leads to inflammation in multiple joints gradually wearing the bone and cartilage away.
The main areas affected by joint inflammation are:
RA symptoms can occur in either one or multiple locations. When symptoms occur in more than four different joints in the body, the condition is referred to as polyarthritis.
Don’t Miss: What Medication Works Best For Psoriatic Arthritis
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you think you have symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, so they can try to identify the underlying cause.
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis quickly is important, because early treatment can prevent it getting worse and reduce the risk of joint damage.
Find out more about diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis.
What Are The Diagnostic Criteria For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnostic criteria are a set of signs, symptoms and test results your provider looks for before telling you that youve got rheumatoid arthritis. Theyre based on years of research and clinical practice. Some people with RA dont have all the criteria. Generally, though, the diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Inflammatory arthritis in two or more large joints .
- Inflammatory arthritis in smaller joints.
- Positive biomarker tests like rheumatoid factor or CCP antibodies.
- Elevated levels of CRP or an elevated sed rate.
- Your symptoms have lasted more than six weeks.
You May Like: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Headaches
Ra Facts: What Are The Latest Statistics On Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex disease that affects each patient differently. People from all ethnic backgrounds are at risk of developing RA. It is the third most common type of arthritis behind osteoarthritis and gout.
Below are some RA facts and statistics provided by ongoing disease research.
Living With Rheumatoid Arthritis

There is no cure for RA. But it is important to help keep your joints working well by reducing pain and inflammation. Work on a treatment plan with your healthcare provider that includes medicine and physical therapy. Work on lifestyle changes that can improve your quality of life. Lifestyle changes include:
- Activity and rest. To reduce stress on your joints, switch between activity and rest. This can help protect your joints and lessen your symptoms.
- Using assistive devices. Canes, crutches, and walkers can help to keep stress off certain joints and to improve balance.
- Using adaptive equipment. Reachers and grabbers let you extend your reach and reduce straining. Dressing aids help you get dressed more easily.
- Managing the use of medicines. Medicines for this condition have some risks. Work with your healthcare provider to create a plan to reduce this risk.
- Seeking support. Find a support group that can help you deal with the effects of RA.
Don’t Miss: What Oil Is Good For Arthritis
Common Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Symptoms experienced by rheumatoid arthritis patients are a direct result of the inflammation of joint tissue and/or accumulation of synovial fluid caused by this autoimmune disorder.
An autoimmune disorder is a disease in which the bodys immune system attacks healthy tissue, mistaking it for foreign or damaged tissue. Though there are many types of autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis is one that afflicts roughly 1.5 million Americans.
Symptoms of RA can range from mild to debilitating, and every level in between. However, there are some common overall symptoms to be aware of should you suspect that you or someone you know is suffering from rheumatoid arthritis.
Below are the most commonly reported rheumatoid arthritis symptoms:
Who Should Diagnose And Treat Ra
A doctor or a team of doctors who specialize in care of RA patients should diagnose and treat RA. This is especially important because the signs and symptoms of RA are not specific and can look like signs and symptoms of other inflammatory joint diseases. Doctors who specialize in arthritis are called rheumatologists, and they can make the correct diagnosis. To find a provider near you, visit the database of rheumatologistsexternal icon on the American College of Rheumatology website.
Don’t Miss: How To Relieve Arthritis Pain In Jaw
Comorbidities Occurring In Ra And Psa
Differences in patient comorbidities may help clinicians differentiate between RA and PsA . Overall, comorbidity burden may be higher in RA than in PsA, but both diseases are similarly associated with increased risk for comorbidities linked to systemic inflammation . Han and colleagues found that patients with RA and PsA had similarly increased prevalence ratios of ischaemic heart disease, atherosclerosis, peripheral vascular disease, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, hyperlipidaemia and hypertension compared with healthy controls. However, registry data suggest that the rates of obesity, diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome are significantly higher in patients with PsA compared with those with RA. Notably, most patients with PsA are overweight or obese. Cardiometabolic comorbidities of PsA are associated with higher levels of systemic inflammation and increased disease severity. In addition, psoriatic skin lesions are associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease and mortality. Of interest, PsA is an independent predictor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with psoriasis, while in patients with RA, the rates of NAFLD are similar to those observed in the general population.
Summary of differences in common comorbidities associated with PsA and RA
Differences Of Ra And Psa
RA is an autoimmune systemic inflammatory disease characterised by synovitis, bony erosions and cartilage damage. PsA is a heterogeneous autoimmune systemic disease with diverse clinical and radiographic manifestations. The presence of psoriasis precedes the development of PsA in 85% of patients, and PsA typically develops about 10 years after the onset of psoriasis. Other common clinical features of PsA include synovitis with subsequent osteolysis and/or joint fusion of peripheral joints, axial involvement, sacroiliitis, and extra-articular manifestations, including nail dystrophy, enthesitis and dactylitis not all are present in every patient. Key clinical, serological and radiographic differences between RA and PsA are summarised in .
Clinical, serological and radiographic characteristics of PsA and RA
Read Also: Does Taking Calcium Help Arthritis
What Are The Common Symptoms Of Ra
It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of RA early on, as left undiagnosed and untreated, this form of arthritis can become a severe and disabling disease. Treating early and appropriately will get you back on track, and your chances at a better, if not normal, life are so much higher than if your diagnosis is delayed. Here is video that you can watch on my Youtube Channel.
Lifestyle Changes To Cope With Fatigue And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Even with the best treatment, many people with RA still experience some fatigue. This fatigue may hit every few days, weeks, or months. Some people with RA may experience a bout of fatigue almost every day, often at the same time each day.
You may not be able to eliminate fatigue in your life, but you may be able to decrease the impact that fatigue has on your day-to-day life with these steps.
It can take time for medication and lifestyle changes to make a difference in how you feel day to day. In the meantime, go easy on yourself, and remember that fatigue often comes and goes in RA.
Learn more about the UPMC Rheumatoid Arthritis Center and call 1-800-533-8762 to schedule an appointment.
Don’t Miss: Is Walking Good For Hip Arthritis
Center On Aging Care Sheets
Adam J. Berlinberg, MD Jaren R. Trost, MD and Jawad Bilal, MD, Department of Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine
TIPS ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
|
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory autoimmune disease that causes pain, swelling, stiffness, and loss of function in joints. RA tends to be symmetrical in its distribution, meaning joints on both sides of the body are generally involved.
In RA the joint synovium becomes thickened, resulting in swelling and pain around the joint. Over time, the joint cartilage and bones themselves become damaged. Without treatment, joint laxity and deformity can occur. Since joint damage in RA cannot be reversed, early diagnosis and disease-modifying therapy is the key to successful RA management.
How Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Managed
The specific causes of rheumatoid arthritis are unknown, but there are a number of factors associated with an increased risk of developing the disease including family history, smoking, increased age and occupational exposures.Footnote 4Footnote 5 While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are treatment options which aim to alleviate joint symptoms and improve function. Individuals often work with a rheumatologist to develop a treatment plan to prevent further joint damage. Medication is often prescribed as a first line of therapy and is key to controlling disease and preventing damage. Other ways to manage include physical therapy, occupational therapy and education.Footnote 6 Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis who are diagnosed and treated early are less likely to experience long-term joint damage and functional impairments.
Read Also: Does Sugar Affect Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Is Ra Treated
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs biological response modifiers are medications that are an effective second-line treatment. In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
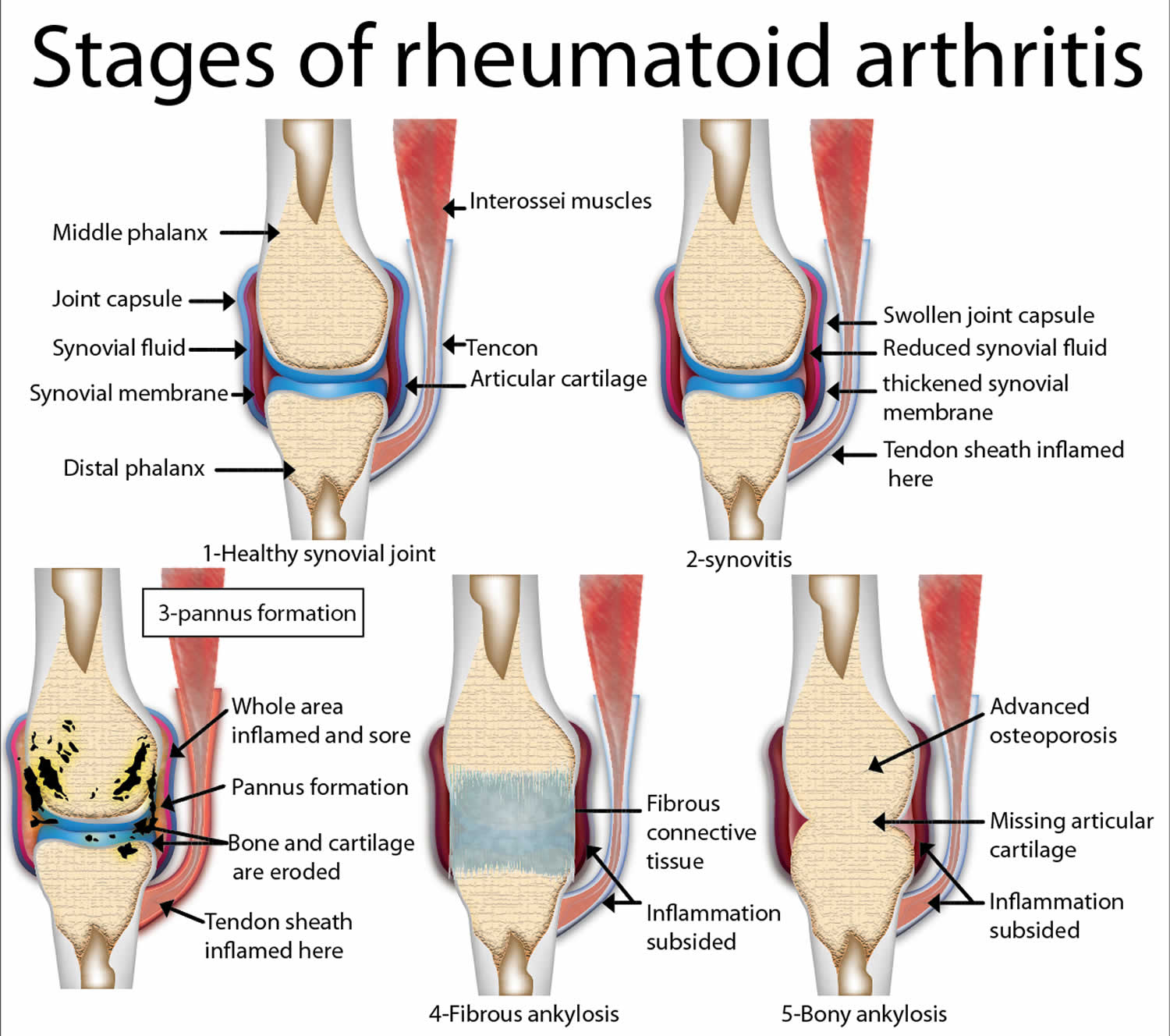
What Are The Four Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stage 1: In early stage rheumatoid arthritis, the tissue around your joint is inflamed. You may have some pain and stiffness. If your provider ordered X-rays, they wouldnt see destructive changes in your bones.
- Stage 2: The inflammation has begun to damage the cartilage in your joints. You might notice stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
- Stage 3: The inflammation is so severe that it damages your bones. Youll have more pain, stiffness and even less range of motion than in stage 2, and you may start to see physical changes.
- Stage 4: In this stage, the inflammation stops but your joints keep getting worse. Youll have severe pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of mobility.
Read Also: How To Treat Arthritis In The Neck Naturally
Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
In the early stages of rheumatoid arthritis, it is common to feel characteristic symptoms of pain and stiffness. The specific symptoms, their severity, and timing differ in each patient and may be related to how aggressively the immune system is attacking the bodys healthy tissues.
Some of the most common RA signs and symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness in joints for at least six consecutive weeks
- Stiffness and loss of range of motion in the joints
- Stiffness in the morning lasting at least 30 minutes and up to several hours
- Pain and soreness in one or multiple joints
- Involvement of joints on both sides of the body
- Pain and soreness in small joints like knuckles and toes
How Is It Treated
Although there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are manytreatments offering relief of symptoms and increasing the ability to functionat, or near, normal levels. Medications include non-steroidalanti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen, which areoften used to reduce pain and swelling. Newer drugs called COX-2inhibitors are used to manage pain and inflammation with fewer stomachulcers than NSAIDs but are much more expensive. Corticosteroidmedications may be used to reduce inflammation and pain. Because of sideeffects, they cannot be used for long periods of time. Disease-modifyinganti-rheumatic agents are used to limit the amount of jointdamage. Biologic response modifiers delay structural damage in patientswith moderately to severely active RA. They target the specific components ofthe immune system that contribute to disease, while leaving other components ofthe immune system intact. Successful management of arthritis pain anddisability includes self-management. It is important for patients tolearn about their disease and take part in their own care. Working with healthcare professionals allows a person to share in decision making and gain a senseof control.
Self-management includes arthritis education, exercise programs, rest,relaxation and stress management, eating well-balance meals and maintainingproper weight, taking care of joints and using assistive devices to rest jointsand relieve pressure.
Also Check: What Is The Reason For Arthritis