How Does Liver Disease Affect Psoriatic Arthritis
Dr. Dimitrios Vassilopoulos reviews current guidelines, screening, and treatment options for liver disease and viral hepatitis.
The video was produced by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation Center for Continuing Education and RJ Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology.
Interested in related CME education? Visit http://www.ccfcme.org/rheumcme
my hcv was psoriatic hcv.my recently deceased partner had shingles.my only defense other. than my pituitary glands still intact ie appendix thyroid is that l was not immunised for German measles so having this psoriasis predisposed genectilly brother suffered from bad psoriasis as a child.l have cleared hcv.
My good friend has had Skin psoriasis since she was a young girl and was told to make use of this skin psoriasis treatment method, nited Moladoz Weebly . It simply took 2 applications for me to observe good results! This was the only real product I`ve tried that actually works in my case.
My husbands redness and also flaking under and also around his eyes and nose were almost removed after a few days of applying this psoriasis treatment solution. Right after Five days, it`s as if the flakiness and redness never existed. He simply wanted the issue to disappear for good so he still keeps making use of the treatment until recently. Got this guide thanks to Google, the guide`s name calls Kyden Molonduzregards
What Causes Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Risk factors most commonly linked with NAFLD are obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome . Among people who have diabetes and obesity, the rate of NAFLD is estimated to be as high as 60 to 90 percent.
Its very prevalent, says Nilanjana Bose, MD, a rheumatologist with the Rheumatology Center of Houston. Its likely a combination of the Western diet, which is high in carbs and fat a sedentary lifestyle and certain medications. My patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, and osteoarthritis can all have fatty liver.
How To Ease The Pain
Managing HCV-related joint pain can be a double-edged sword. Some of these drugs can have their own toxic effects on the liver or can worsen the viral infection. HCV-related joint problems can cause severe discomfort and make it difficult to perform daily activities. To help manage the condition, it is important to see a rheumatologist and to ensure there is good communication between the doctor managing your liver disease and the doctors managing your extra hepatic symptoms.
In other words, patients should receive care from a multidisciplinary team of doctors who can work together to find the best treatments with the lowest risks. Anti-tumor necrosis factor drugs, or anti-TNF drugs, have been used successfully to help patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and have also been found to be helpful in patients with HCV, seeming to cause no additional harm to the liver or increase in viral load. Another drug used for treating rheumatoid arthritis, rituximab, is also being tested in patients with HCV.
Home remedies can be helpful for non-arthritis joint pain, including using a heating pad or soaking in a warm bath. Gentle massage and stretching exercises might also help.
Also Check: How To Help Arthritis In Your Hands
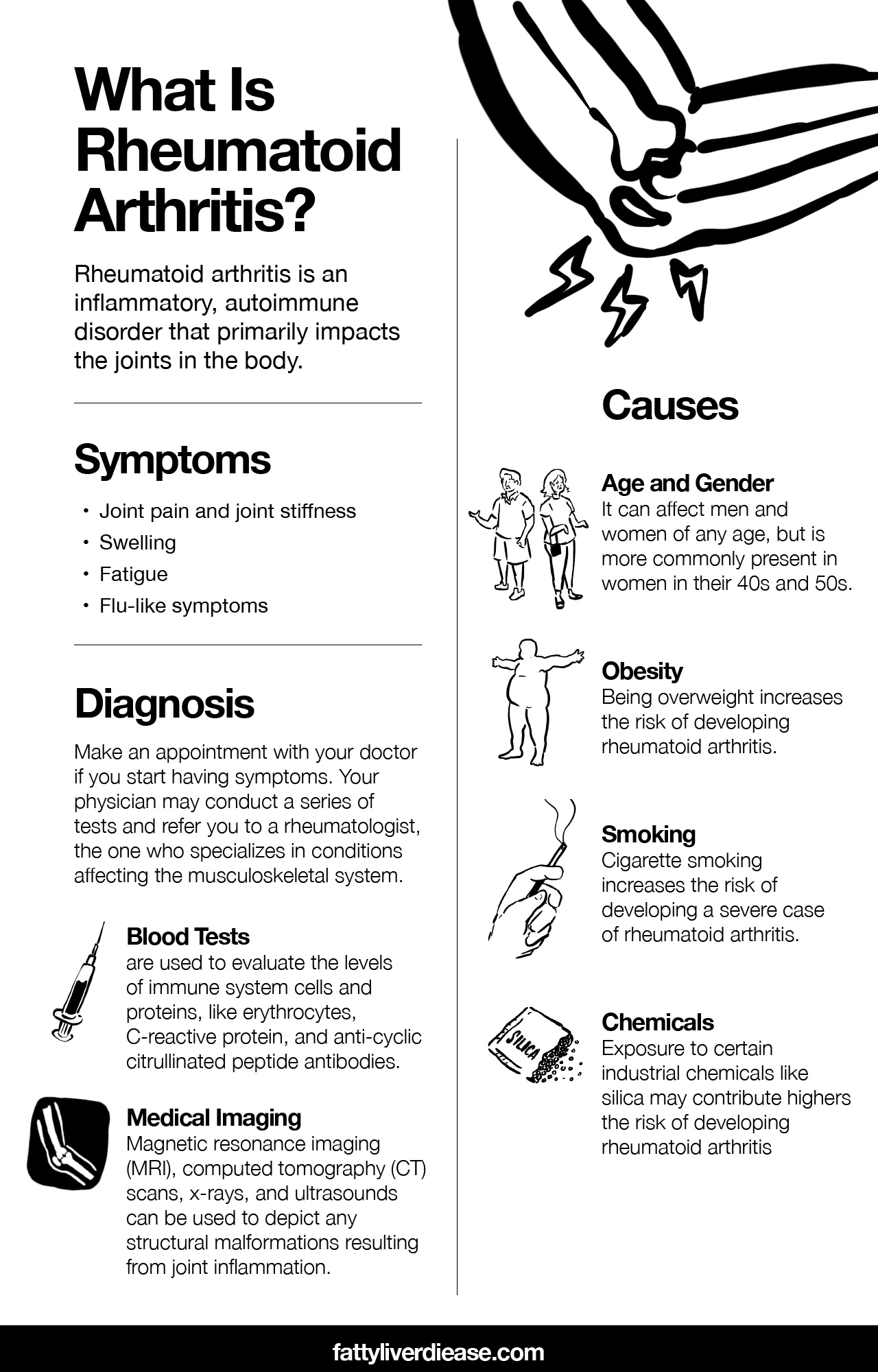
What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Symptoms include fever, joint pain, swollen joints, lack of flexibility in the joints, and morning stiffness or stiffness in joints.
For more information on arthritis, types of arthritis, symptoms and their causes, visit BYJUS.
Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click Start Quiz to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the Finish buttonCheck your score and answers at the end of the quiz
The Liver And Vasculitis

Vasculitis can affect every organ of the digestive system but the liver is not commonly involved. Liver involvement is limited to polymyalgia/Horton’s arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Wegener’s granulomatosis, and Behçet’s disease . Abnormal liver function tests commonly manifest a cholestatic pattern with elevated alkaline phosphatase and -glutamyl transferase levels that characterize up to 62% of patients with rheumatic polymyalgia . Polymyalgic patients with elevated liver enzymes have an increased risk to develop Horton’s arteritis .
Liver involvement occurs in a variable proportion of patients affected by polyarteritis nodosa, although clinical manifestations related to liver disease are quite rare conversely, necrotizing arteritis of the liver has been found in the vast majority of patients with polyarteritis . Liver injury is rare in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Both granulomatous necrotizing hepatic involvement and mild nonspecific lobular hepatitis have been described. Liver involvement is rarely observed in patients with Behçet’s disease, with a predominance of Budd-Chiari syndrome.
Recommended Reading: Does Arthritis Hurt All The Time
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Humans immune system is very protective. It releases antibodies when a foreign material like bacteria and fungus enters the human body. Those antibodies fight the foreign material and kill them.
However, in some cases, the immune system mistakenly sends antibodies to attack their lining of joints. This is the root cause of Rheumatoid Arthritis. The reason why the immune system behaves like that is still unknown.
This autoimmune disorder is observed more in women compared to men. Some evidence suggests that people who smoke have more chances of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis.
How Rheumatoid Arthritis Affects More Than Joints
Learn more about how the inflammation associated with RA can impact organs and systems beyond the joints.
Arthritis can cause painful, swollen knees or fingers that are impossible to ignore. But other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes and lungs can also be affected. Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease, meaning it can affect many parts of the body.
In addition, the drugs used to treat RA can also cause health problems. Many of these problems such as bone thinning or changes in kidney function cause no immediate symptoms so your doctor may monitor you through lab tests or checkups. For other problems such as skin rashes or dry mouth its important to report any symptoms to your doctor, who can determine the cause, and adjust your treatments accordingly.
Its important to be aware of the affected areas of the body and side effects you may experience. This way, early aggressive treatment can help you avoid RA-related health issues.
Recommended Reading: Why Do You Get Arthritis
Dietary Fibers And Whole Grains
Most of the staple food consumed all over the world are comprised of dietary fibers and whole grains. A definitive explanation for dietary fibers can be put as remnants of food not digested in small intestine, which then moves to large intestine and gets fermented by the microflora and induces several health promoting effects . Insoluble fibers such as cellulose and lignin are found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and soluble fibers include pectin, guar gum, and mucilage . Earlier studies have found an inverse relationship between intake of dietary fiber and inflammatory biomarkers such as plasma fibrinogen, hs-CRP, TNF-, IL-6 levels which are indicators of RA . However, contradictory reports were published as well by Hu and the group .
When germ, endosperm, and bran are present in same proportions as in intact grains, they are regarded as whole grains. Whole wheat, whole rice, oats, corn, rye, barley, millets, sorghum, canary seed, fonio, and wild rice are generally included in the category of common whole grains . Whole grains provide rich amounts of antioxidants, phytic acid, vitamin E and selenium, and these components are known to be involved in anti-inflammatory processes .
Blood Tests For Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are several types of blood tests that help your healthcare provider or rheumatologist determine whether you have RA. These tests include:
- Rheumatoid factor test. The RF blood test checks for a protein called rheumatoid factor. High levels of rheumatoid factor are associated with autoimmune diseases, especially RA.
- Anticitrullinated protein antibody test . This test looks for an antibody thats associated with RA. People who have this antibody usually have the disease. However, not everyone with RA tests positive for this antibody. The anti-CCP Ab is more specific for RA than the RF test
- Antinuclear antibody test. The antinuclear antibody panel tests your immune system to see if its producing antibodies. Your body may make antibodies as a response to many different types of conditions, including RA.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The ESR test helps determine the degree of inflammation in your body. The result tells your doctor whether inflammation is present. However, it doesnt indicate the cause of the inflammation.
- C-reactive protein test. A severe infection or significant inflammation anywhere in your body can trigger your liver to make C-reactive protein. High levels of this inflammatory marker are associated with RA.
You May Like: How To Prevent Arthritis In Knees
Liver Adverse Events With Analagous Medications
All of this begs the question, what is the rate of transaminase elevations in a healthy population? Most laboratory tests define normality as lying within 2 standard deviations of the mean in a Gaussian distribution. In a normally distributed sample approximately 95% of values will lie within 2 standard deviations of the mean. Therefore 2.5% of the population will have transaminase levels above the normal range and 2.5% will have transaminase levels below the normal range. The importance of this is that the rate of abnormality is not zero and never can be if normality is defined in this manner. This must be born in mind in evaluating any reported rate of abnormalities. Since studies show a higher incidence of liver enzyme abnormalities and since there is well-documented hepatotoxic potential, understanding the relationship between the mild enzyme rises and long-term outcomes is necessary, but unclear at this time.
Epidemiology Of Methotrexate Related Liver Disease
Reported rates of liver blood abnormalities during methotrexate treatment vary. Initial reports of hepatic toxicity, and death from hepatic toxicity, as well as cumulative incidences of 48.9% for elevated transaminases and 16.8% for transaminases elevated more than twice the upper limit of normal have been reported. Hepatic toxicity is not universal with prolonged chemotherapeutic regimes and some demonstrated normal liver histology despite several months of therapy. The reported rates of hepatic toxicity appear to have decreased progressively over time, likely related to refinements in dosing and monitoring strategies. A 2009 systematic review of observational studies up to that time reported that elevated transaminases were found in 20% of patients treated with methotrexate for 1 year, with transaminases greater than twice the upper limit of normal in 13%. Present day monitoring strategies and treatment regimens appear to have significantly lower risks than those which have been historically associated with methotrexate use. Two high quality recent studies reported elevated transaminases in 22% but with as little as 1% having transaminases greater than twice the upper limit of normal. A higher rate occurs when used in combination with other therapies. A number of other risk factors for hepatotoxicity have been identified including obesity and hypercholesterolaemia.
You May Like: Can You Have Rheumatoid Arthritis Without Swelling
Baseline Characteristics Of Ra Patients With Chc
illustrates the baseline characteristics of RA patients with CHC. Leflunomide, sulfasalazine, and corticosteroids were prescribed more often in MTX users than in MTX non-users, indicating more severe disease activity of RA in MTX users compared with MTX non-users. In our 255 MTX users, the average cumulative MTX dosage was 1.6±1.6grams during a mean duration of 44 months. We categorized these MTX users into 3 groups based on the cumulative dose. The average durations of treatment were 18, 62, and 108 months and the mean weekly doses were 8.3, 9.3, and 10.7mg, within these groups of MTX users . After a median follow-up of more than 5 years since diagnosis of CHC, a total of 55 patients developed liver cirrhosis: 19 of 255 MTX users and 36 of 195 MTX non-users. Among the 19 MTX users who developed liver cirrhosis, 17 patients had a cumulative dose of 1.5grams and 2 patients had a cumulative dose of 1.5grams and < 3.0grams. One of 255 MTX users and 3 of 195 MTX non-users developed decompensated liver cirrhosis. Notably, there was no occurrence of liver cirrhosis among 43 MTX users with a cumulative dose of 3grams.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis patients with CHC.
Methotrexate Related Adverse Events
The first papers on methotrexate use detailed the acute toxicity associated with high dose therapy for cancer, and later long-term sequelae. Later studies in non-malignant disease showed similar problems with high dose therapy but not so with lower doses, weekly regimens and concomitant use of folic acid. The adverse events associated with methotrexate use can be divided into two broad subsets those symptomatic but rarely life-threatening adverse events experienced by patients, and those rarely symptomatic but potentially life-threatening adverse events which require careful monitoring by physicians.
Methotrexate-induced lung disease is a good example, an entity widely believed to be common, serious and potentially fatal. Incorrectly apportioning blame on methotrexate can result in two potential risks to the patient: denying them an effective drug and delaying the appropriate investigation and treatment of the real cause of their symptoms. Recent studies show this is in fact a rare occurrence and may not exist at all. Furthermore, it appeared that any increased risk was likely due to a small increase in respiratory infections with methotrexate use, rather than interstitial lung disease. This knowledge has the potential to significantly change clinical practice as cessation of methotrexate frequently occurs as a knee jerk reaction to any cough or dyspnoea.
You May Like: Is Humira Good For Arthritis
Patients With Psoriasis Have Higher Risk Of Liver Disease Compared With Patients With Ra
Patients with psoriasis and with rheumatoid arthritis are often treated with similar drugs, but those with psoriasis are at a higher risk for serious liver disease, according to a new study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Patients with psoriasis and with rheumatoid arthritis are often treated with similar drugs, but those with psoriasis are at a higher risk for serious liver disease, according to a new study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania studied more than 197,000 patients with psoriasis, 12,000 patients with psoriatic arthritis, 54,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis , and 1.2 million matched controls. Outcomes of interest were any liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis.
Patients with psoriatic skin or joint disease had a higher risk for serious liver disease, and patients with psoriasis taking a systemic therapy drug had the highest risk. Patients with RA taking similar drugs had the lowest liver disease risk.
The study also found that as the body surface area affected by psoriasis increased, so did the prevalence of liver disease and cirrhosis. In general, previous research has found that severity of psoriasis is linked to an increased risk of death. A study from UPenn researchers published in the same journal in August found that patients with psoriasis on 10% or more of their body had nearly double the risk of death.
The Link Between Arthritis Arthralgia And Hepatitis
Hepatitis C virus primarily causes inflammation to the liver, but sometimes the virus can also cause health problems that affect other parts of the body. When this happens, it is known as extrahepatic disease. Extrahepatic symptoms of hepatitis C infection can result in arthritis , muscle pain and weakness, and vascular problems.
Also Check: Does Smoking Make Arthritis Worse
Fatty Liver Disease And Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis
People with these inflammatory conditions may be particularly at risk of NAFLD and liver damage. For one thing, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis have been linked with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome all risk factors for NAFLD. A study at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia, reported in a 2017 issue of the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, found that people with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis were at increased risk for liver disease, including NAFLD, whether or not they were taking systemic therapy, such as methotrexate. The risk was even higher for those who were. Its estimated that almost half of patients with psoriasis may have NAFLD.
Psoriasis Tied To Higher Risk Of Serious Liver Disease
By Lisa Rapaport, Reuters Health
5 Min Read
– People with chronic inflammatory disorders like psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis may have an increased risk of developing serious liver damage, a recent study suggests.
These inflammatory disorders are often treated with methotrexate, a medication linked to an increased risk of liver disease. For the current study, researchers followed more than 1 million people for an average of six years to see how having conditions like psoriasis or rheumatoid arthritis – and taking methotrexate – influenced the odds of developing serious liver disorders.
Compared to people without chronic inflammatory diseases, people with psoriasis were 37 percent more likely to develop liver disorders. When psoriasis patients took methotrexate, they had roughly twice the odds of liver damage.
With psoriatic arthritis, the increased risk of liver disease was 38 percent without drug therapy and 67 percent with methotrexate. For rheumatoid arthritis, there was no increased risk of liver disease when people took methotrexate, but when they didnt they had 49 percent higher odds of liver damage.
Medications which are toxic to the liver, such as methotrexate, should be used cautiously in patients with psoriatic disease, especially those with additional risk factors such as obesity or regular alcohol use, Gelfand said by email.
SOURCE: bit.ly/2zyiP6L Journal of Investigative Dermatology, online November 2, 2017.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Difference In Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Monitoring And Diagnosis For Fatty Liver Disease
Since there are few to no symptoms of NAFL, doctors must determine which patients are at increased risk when deciding to monitor for the condition. Many dermatologists routinely screen their psoriasis patients. Some rheumatologists make liver testing a routine part of their practice, too. I always do a liver function panel at baseline to make sure patients are ready if I need to put them on meds, says Dr. Bose. The blood tests are also used for monitoring drug treatment.
Other rheumatologists screen or monitor for NAFLD on a case-by-case basis. Somebody who is taking a high dose of methotrexate. Somebody with psoriasis who also has type 2 diabetes. Someone age 50 or older with diabetes and another inflammatory condition. In cases like these its probably reasonable for the liver to be evaluated, says Dr. Loomba.
A blood test with a complete metabolic profile is the first step. Ask What is my ALT , advises Dr. Loomba. ALT is an enzyme primarily found in the liver high levels in the blood may indicate a liver problem. Imaging scans like ultrasounds, CTs, or MRIs can diagnose NAFLD. In fact, many times NAFLD is detected incidentally, when someone has an abdominal scan for another reason.