What Is The Treatment For Rheumatoid Arthritis Rashes
The treatment for a rheumatoid arthritis-related rash depends on its cause and severity. A treatment that works well for one type of rash may be useless for another. Treatment usually focuses on managing pain and discomfort, and preventing an infection. Its also important that treatments target the underlying condition, since rashes may be a sign that your rheumatoid arthritis isnt well-controlled.
Common over-the-counter medications that may reduce the pain of a rash include acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs . There are several types of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen , naproxen sodium , and aspirin .
If your pain is severe, your doctor may also consider prescription NSAIDs. Opioid pain drugs are usually only prescribed for very severe pain since they have a high risk of addiction.
Your physician may also prescribe corticosteroids to reduce the inflammation of your rash, which may in turn reduce painful symptoms. However, these drugs arent recommended for long-term use. If your doctor is concerned that your rash could get infected, theyre likely to prescribe either a topical or oral antibiotic, or both.
When it comes to treating the underlying condition, there are several different medication options available:
Treatments for interstitial granulomatous dermatitis include topical steroids and antibiotics. Doctors may also prescribe etanercept , a medication thats also used to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
How Is Spinal Arthritis Diagnosed
Your doctor may use some or all of the following diagnostic methods to confirm spinal arthritis:
-
Medical history and physical exam
-
Blood tests for genetic markers and/or RA antibodies
-
X-rays of the spine to locate the arthritic joint
-
MRI, CT scan, myelography, bone scan and/or ultrasound to zero in on the damage, detect nerve and spinal cord involvement or rule out other causes
-
Joint aspiration: testing of the synovial fluid inside a joint
To pinpoint the painful joint, your doctor may numb it with an injection and check whether the pain goes away.
Over The Counter Medication
The first course of treatment for OA flare-ups is usually OTC pain medication. Your doctor may recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs commonly used to treat arthritis-related pain. These drugs include:
-
Creams or ointments containing NSAIDs
If you can’t tolerate NSAIDs, your doctor may recommend acetaminophen . It is crucial to keep in mind the adverse side effects of these medications. Talk to your physician about the best option, their side effects, and how to take them.
Read Also: Can You Get Arthritis In Your Heel
How Is Spinal Arthritis Treated
The treatment for spinal arthritis depends on many factors. They may include your age, level of pain, type and severity of arthritis and personal health goals. Because the joint damage caused by arthritis is irreversible, the treatment usually focuses on managing pain and preventing further damage.
Nonsurgical treatments for spinal arthritis may include:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids to reduce pain and swelling
-
Other medications targeting specific symptoms or triggers of inflammatory arthritis
-
Physical therapy to improve back muscle strength and range of motion in the spine
-
Lifestyle changes to reduce inflammation or stress on your spine: losing weight, quitting smoking, changing your posture, etc.
What Triggers Osteoarthritis Flare

Flare-ups can be caused by several factors. However, the most common triggers of the episodes are overdoing an activity or trauma to the joint. The following are some of the primary risk factors associated with OA flare-ups:
Too much activity
When you feel good about a physical activity you are doing, there is a high chance of overdoing it and creating the perfect conditions for a flare-up. OA often flares after overexertion of the joint or joints involved in vigorous physical activities.
Weather
Pressure changes and humidity can also lead to increased joint pain in persons living with osteoarthritis. Patients with OA and other types of arthritis or inflammatory conditions often complain that their joints are achier in cold and humid weather². However, studies are not conclusive on the relationship between flare-ups and the weather.
Infection
Infections that affect the immune system, including respiratory viruses, can also cause OA flare-ups.
Stress
Several studies³ reveal stress can induce OA flares. Typically, stress leads to the production of high amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines responsible for worsening OA symptoms.
Injury
If you have suffered an injury to the part of the body affected by OA, you may suffer a flare-up as the symptoms will be aggravated by the injury.
Weight gain
Rapid weight gain can trigger flare-ups due to the relatively sudden and large increase in weight that the joints need to support.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Arthritis In Your Shoulder
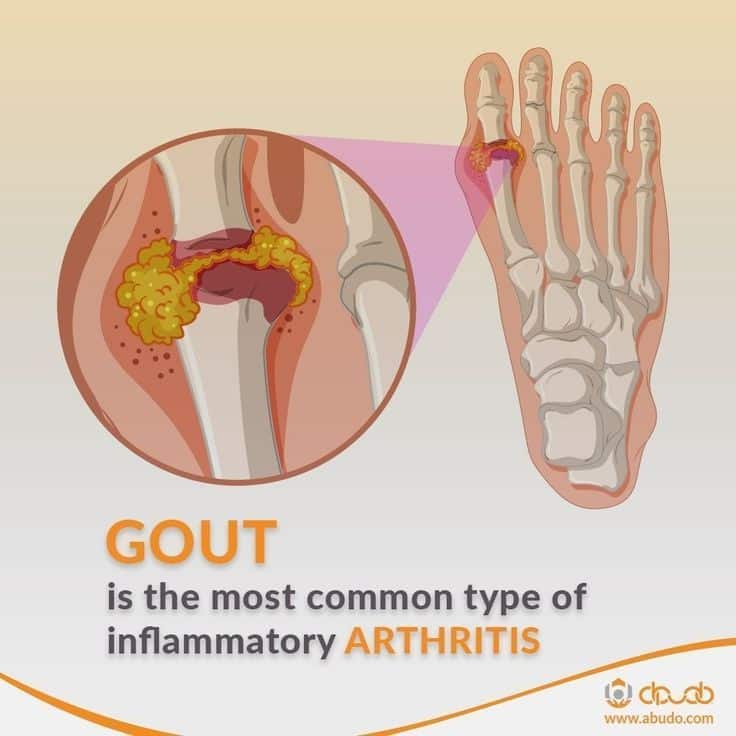
How Is Gout Diagnosed
In a clear-cut case, a primary care physician can make the diagnosis of gout with a high level of confidence. However, often there are two or more possible causes for an inflamed toe or other joint, which mimics some of the symptoms of gout, so tests to identify the presence of uric acid is performed.
Since the treatment for gout is lifelong, its very important to make a definitive diagnosis. Ideally, the diagnosis is made by identifying uric acid crystals in joint fluid or in a mass of uric acid . These can be seen by putting a drop of fluid on a slide and examining it using a polarizing microscope, which takes advantage of the way uric acid crystals bend light. A non-rheumatologist, when possible, can remove fluid from the joint by aspirating it with a small needle and send it to a lab for analysis. A rheumatologist is likely to have a polarizing attachment on their microscope at their office. Gout crystals have a needle-like shape, and are either yellow or blue, depending on how they are arranged on the slide .
Figure 11: Uric Acid Crystals Under Polarizing Light Microscopy
There are many circumstances where, however ideal it would be, no fluid or other specimen is available to examine, but a diagnosis of gout needs to be made. A set of criteria has been established to help make the diagnosis of gout in this setting .2
Table 1: Diagnosing gout when no crystal identification is possible
Ideally, 6 of 10 features will be present of the following:
How Long Do Ra Flares Last
The length of time an RA flare lasts can vary widely, from a few hours to several days or weeks. If a flare does not improve after 7 days, it may be a good idea to contact a physician. The doctor may suggest adjusting the persons medication.
Before a RA flare begins, a person may experience fatigue or feel that something is not quite right.
During a flare, symptoms tend to increase until they reach their peak. As the peak passes, the symptoms will lessen and may completely disappear.
The frequency and severity of flares can vary widely between individuals. With treatment, a person may spend months or years in remission, while others may experience flares more frequently.
RA flares can be predictable or unpredictable. A flare will occur when something triggers an increase in disease activity, which means that levels of inflammation go up.
Predictable flares usually occur in response to one or more triggers.
Some flares have no apparent trigger, and a person may be unable to identify why it started. This can make them harder to avoid.
In 2017, a involving 274 people with RA who attended a clinic in Turkey found the following appeared to worsen their symptoms:
- emotional or physical stress
You May Like: How To Reduce Arthritis Pain In Back
Measures To Reduce Bone Loss
Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can cause bone loss, which can lead to osteoporosis. The use of prednisone further increases the risk of bone loss, especially in postmenopausal women.
You can do the following to help minimize the bone loss associated with steroid therapy:
- Use the lowest possible dose of glucocorticoids for the shortest possible time, when possible, to minimize bone loss.
- Get an adequate amount of calcium and vitamin D, either in the diet or by taking supplements.
- Use medications that can reduce bone loss, including that which is caused by glucocorticoids.
- Control rheumatoid arthritis itself with appropriate medications prescribed by your doctor.
What Are The Symptoms Of Inflammatory Arthritis
The most common symptoms of inflammatory arthritis are:
- Joint pain and stiffness after periods of rest or inactivity, particularly in the morning
- Swelling, redness and/or a feeling of warmth in the affected joints
- Inflammation of other areas in the body, such as the skin or internal organs like the lungs and heart
People with inflammatory arthritis generally experience alternating periods of âflaresâ of highly intense symptoms with periods of inactivity.
You May Like: How I Cured My Rheumatoid Arthritis
The Possible Causes Of Arthritis Flare
Arthritis doesnt suddenly get worse on its ownsomething has to trigger a flare-up. In most cases, it stems from one of the following:
- The affected joint has been excessively or repeatedly used.
- The person has sustained an injury to the joint.
- Daily stress is creating more inflammation throughout the body.
- Certain foods have triggered inflammation.
- The person has changed up their medication.
- A sudden drop in barometric pressure .
What Does An Arthritis Flare Feel Like
Symptoms of arthritis flares are similar to the symptoms you experience with your chronic disease, only more intense. They include joint pain and stiffness. Some people have swollen joints. There can be fatigue due to joint pain interfering with sleep during the night. In a severe flare, there can be low-grade fevers due to activation of the immune system and inflammatory pathways.
You May Like: What Can I Use For Arthritis Pain
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors Of Arthritis
The cause of arthritis may vary according to the type of the disease. Most types of arthritis do not have a known cause.
Research has revealed the role of three major factors in certain types of arthritis:
- Genetic factors cause some types of arthritis to run in families.
- Physical activity and diet affect arthritis symptoms.
- The presence of other medical conditions such as infections and chronic diseases such as lupus puts you at risk for arthritis.
Several factors may increase a personâs risk for arthritis:
- Age: The risk of getting arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, increases with age. Age may also worsen the symptoms of arthritis.
- Gender: Arthritis generally affects women more often than men.
- Weight: Being obese or overweight puts extra stress on the joints that support an individualâs weight. Increased weight beyond the normal range for a personâs age and height increases joint wear and tear, and the risk of arthritis.
- Occupation: Certain jobs may involve the worker to keep doing the same movements repeatedly. These include jobs where one needs to do heavy lifting or repeated fine work as done by musicians. It can cause joint stress and/or an injury, which may lead to arthritis.
- Injury: Joint injury or trauma may cause osteoarthritis.
- Autoimmune diseases: These may misdirect the immune system towards the joints as seen in rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
- Infections: Certain infections may lead to joint inflammation as seen in tubercular arthritis and .
Tips To Reduce Your Risk Of Infection
- Try to avoid close contact with people you know have an infection.
- Wash your hands regularly and carry around a small bottle of antibacterial hand gel.
- Keep your mouth clean by brushing your teeth regularly.
- Stop smoking if youre a smoker.
- Make sure your food is stored and prepared properly.
- Try to keep your house clean and hygienic, especially the kitchen, bathrooms and toilets.
If you are prescribed a drug you may find more information about it here.
You May Like: What To Take To Prevent Arthritis
Who Gets Reactive Arthritis
Anyone can get reactive arthritis, and it occurs worldwide. A bacterial infectionin the digestive or urinary tract or the genitalstypically precedes it by a few weeks. Although sexually transmitted infections can occur just before the onset of reactive arthritis, many cases of reactive arthritis are associated with other types of infections that are not transmitted sexually. Certain factors increase the risk of the condition, including:
- Sex. Both men and women can get reactive arthritis, but men are more likely to develop it as a result of a sexually transmitted infection. Men and women are equally affected if the condition is from a gastrointestinal infection.
- Age. It occurs most often in people between ages 20 and 40.
- Genetics. People who have a gene called HLA-B27 have a higher risk of getting reactive arthritis and of experiencing more severe and more long-lasting symptoms. But people who lack HLA-B27 can still get the condition.
- HIV infection. Having AIDS or being infected with HIV increases the risk of reactive arthritis.
What Exactly Is An Arthritis Flare
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of the condition, and it is a degenerative disease, which means it will only tend to get worse over time. But, most patients describe their symptoms fluctuating wildly from day to day. A flare-up is defined as a sudden increase in pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joint. While they tend to seemingly come out of nowhere, there are a few factors that are known to cause them.
Read Also: What’s The Best Knee Brace For Arthritis
Triggers For Flare Ups
Rheumatoid arthritis An RA flare is mostly due to inflammation, but what triggers inflammation? The triggers for inflammation are not specifically known yet, though extensive medical research is in progress. It may be stress, weather or too much physical activity. There is no definitive medical research proving weather impacts arthritis, but many patients have noted their joints react to a change in barometric pressure and humidity or when it is cold. Other triggers include infection or any illness compromising the immune system, and medications.
Osteoarthritis Flare ups are not triggered by inflammation from an immune system response, but inflammation may be one of the symptoms of an osteoarthritis flare. Scientifically proven flare triggers still do not exist, but there are certain activities that have often triggered flare ups. They include falling on or injuring a joint, repetitive motions and overuse. Other causes include infection, stress, weather and obesity or being overweight. In some cases, continued deterioration of the cartilage can lead to bone spurs developing which then further irritates the joint and possibly the surrounding tissue.
Psoriatic arthritis Most people experience a flare of psoriasis before a flare of psoriatic arthritis. The suspected triggers for a flare are stress, weight gain, physical trauma, joint strain, infection and medications.
Search For Rheumatologists Near You And Schedule Your Next Appointment Today
Dietary choices are always important to overall health, but if you have arthritis, the foods you choose can have a surprising impact on your joint health. You may find some arthritis trigger foods cause pain, stiffness, and swelling, while others actually alleviate your symptoms.
There are several common trigger foods to avoid if you have arthritis. For happier, healthier joints, try these simple food swaps.
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Fibromyalgia And Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Spine
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the immune system turns on itself. It attacks synovium the lining of the joints. Although rheumatoid arthritis is more common in other joints, it can also affect the spine, specifically the cervical region . Rheumatoid arthritis of the spine is not caused by wear and tear, so its considered an inflammatory arthritis. It may cause back pain even when these joints are not in use. It tends to affect women more than men.
Salmon Tuna Sardines And Mackerel
These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which studies have found can decrease inflammation. According to the Arthritis Foundation, eating a 3 to 4 ounce serving of these fish two or more times a week is recommended for protecting the heart and reducing inflammation.
While fresh fish can get pricey quickly, one tip to make it more affordable is by looking in the freezer section or buying canned sardines, salmon or tuna. Be sure to choose lower sodium options when purchasing canned items if you need to keep your sodium in check.
You May Like: How To Reduce Joint Swelling In Fingers
Read Also: What Does Arthritis In The Neck Look Like
Try Hot And Cold Packs
A heating pad or an ice pack can increase your pain threshold wherever you apply it, which helps decrease the sensation of pain, Dr. Ormseth says.
Use cold therapy if joints are swollen, as heat can worsen swelling. Apply a cold pack, like a bag of frozen vegetables, to swollen joints two to four times a day for 15 minutes each time.
Use heat if joints are painful but not swollen during your flare. Try applying a heating pad, warm compress, or heat patch to the affected joints two or three times a day for 15 minutes at a time, or soak in a warm bath.
Just make sure you dont overdo either hot or cold treatment.
Ways To Prevent Future Arthritis Flare

Luckily, you may be able to cut down on the number of arthritis flare-ups you are experiencing by doing a few simple things.
Know Your Triggers
The things that trigger your arthritis flare-ups might not cause a problem for someone else. Every persons body responds differently. Try to document the circumstances around every flare-up and see if you notice any patterns so that you can better prepare for future issues. Once you know your triggers, you can try to avoid or at least limit your exposure to them.
Get Help
You need to give yourself a break and not try to do it all alone. Try to find someone who can help with some or all of the activities that may aggravate your arthritis. It can be hard to admit when you are having a hard time, but you are only increasing the likelihood of an arthritis flare by pushing yourself too hard.
Protect Yourself From Infection
For inflammatory types of arthritis that are triggered by an immune response, an illness or infection can really set your arthritis symptoms off. Take extra precautions to avoid illnesses like the flu and go see the doctor if you believe you could have any kind of infection.
Get Enough Rest
Our bodies need rest. You need to make sure you are getting plenty of sleep to prevent your body from becoming run down. Getting quality rest with arthritis pain can sometimes be difficult, so dont hesitate to add in a nap during the day if you need to. Try to learn the limits of your body and not overdo them.
Exercise
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Biologic For Rheumatoid Arthritis