What Are The Types Of Biologics
There are several. They include:
- B-cell inhibitor. They affect B cells, which are white blood cells that carry a protein that can trigger your immune response.
- Interleukin-1 blocker. Stops production of an inflammatory chemical your body makes
- Interleukin-6 or interleukin-17 blocker. Stops inflammatory chemicals from attaching to cells
- Blocks proteins that trigger the inflammation process
- T-cell inhibitor. Blocks communication between T cells, a type of white blood cell
- Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Blocks a chemical your body makes that drives the inflammation process
Shedding Light On Other Treatment Options
Eighty-four percent of you reading this will have RA thats making your life miserable, and half of those havent even tried the medication for autoimmune illnesses that has been changing the game for over a decade.
This is borderline criminal and I truly hope that this post will help to not only shed some light on the subject but give you the push you might need to tell your doc its time to try biologics. Now, I have to call my own doctor. Paging Dr. HemsworthTalk soon.
The 8th Annual RA In America survey was conducted online from April 6 to June 25, 2020. A total of 3,511 people completed the survey.
Unmet Needs: Newly Approved And Investigational Treatments
Besides the biologics described above, there are other agents that are newly approved or in late-stage clinical development for the treatment of RA. As outlined in , tocilizumab is a new, once-monthly, IV IL-6âreceptor antagonist that is approved in the US for moderate or severe RA patients who have failed at least one anti-TNF agent. Further information about this agent is not provided, since a focused review is forthcoming. Enhanced understanding of the pathophysiology of RA is also providing opportunities for other treatments with novel modes of action. Denosumab , an antibody directed at receptor-activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand inhibits osteoclast activation and bone destruction. This agent has been used successfully in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, and may also be useful as an adjunctive therapy in RA. In a phase II clinical study, addition of twice-yearly injections of denosumab to ongoing MTX therapy significantly reduced structural damage in patients with RA , but had no effect on clinical signs and symptoms of RA.
Don’t Miss: What Does Ra Feel Like
Your Doctor May Decide Not To Prescribe A Biologic If:
You are pregnant or breastfeeding
You have had tuberculosis in the past
You have had other repeated infections
You have had cancer
You have or had a serious heart condition
You have lung fibrosis
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by pain, swelling, and inflammation of the joints. It most commonly starts in the small joints of the hands and feet. Eventually all joints can be affected. Your joints can feel stiff, particularly in the morning. Symptoms often come and go, and are often accompanied by fever or feeling tired or unwell. As the disease progresses, sufferers can experience severe joint damage and fatigue, making it difficult for them to complete everyday tasks. Flare-ups of rheumatoid arthritis are often unpredictable and difficult to manage. Pain, stiffness, and swelling are worse on some days and easier to bear on others.
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. Some studies show that rheumatoid arthritis may run in families, suggesting a genetic component, yet having a family member who suffers from rheumatoid arthritis does not necessarily mean that you will also develop the disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis can be difficult to diagnose because many other conditions can cause joint stiffness, pain, swelling, and inflammation.
What Is A Biologic Dmard
In the last decade and a half, more than ten different biologic medications have been released and more are coming every year. Just in case some of you dont know what a biologic medication is, well do a quick refresher.
Biologic medications inhibit different parts of the immune system, like B cells and T cells and TNF, in order to help suppress the immune response thats causing that particular patients rheumatoid arthritis. And if you arent fluent in science, all of that just means that biologic medication gives your immune system a big ol kick right in the molecules and makes the RA go away.
Recommended Reading: Pain From Ra
Classes Of Biologics For Rheumatoid Arthritis
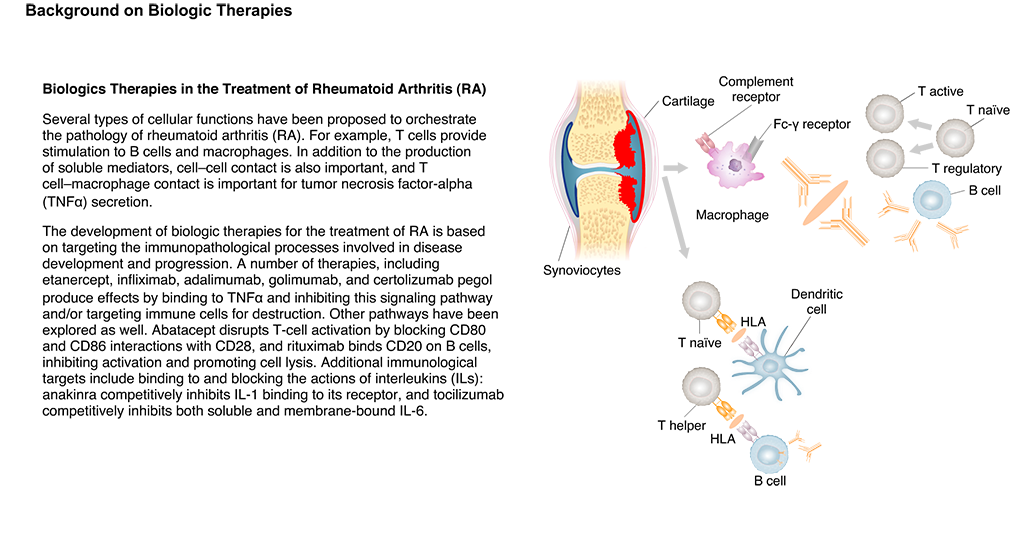
There are four main classes of biologics used to treat RA, including B-cell inhibitors, tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors, selective costimulation modulators, and interleukin inhibitors. Each class of biologics interferes with different aspects of the immune system involved in inflammation and joint damage in RA.
What Is A Biosimilar
Biosimilars are drugs that are a type of biologic therapy. Biosimilars are named for the fact that they are very similar to an already-approved biological product. You can think of biosimilars as a copycat of biologics. They are not exactly the same as the biologic. But they are similar enough to be approved for all the same uses as the biologic.1
Like biologics, biosimilars have bioengineered proteins. These proteins mimic certain functions in human genes or cells, and they are made from living cells. Biologics are used to reduce or better regulate the inflammatory response, which is overactive in conditions like RA.1,2
Below is a list of biosimilars for RA and their reference products.
Biosimilars to Humira® :3,4
- Truxima
Also Check: Why Is My Arthritis Acting Up
Types Of Biologics For Treating Ra
Biologics are a newer type of DMARD and have greatly improved treatment outcomes for people with RA. They work by blocking the activity of key proteins involved in inflammation. Biologics target specific parts of the immune system.
While biologics are not a cure for RA, they can slow down the diseases progression. Biologics also cause fewer side effects than other RA therapies.
Your doctor might prescribe a biologic with or in place of methotrexate or another antirheumatic. Taking a biologic with methotrexate is helpful and effective for many people with RA.
| Biologics for Rheumatoid Arthritis | |
|---|---|
| T-cell | Intravenous infusion and subcutaneous injection |
There are different types of biologics used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Your rheumatologist is in the best position to advise you on whether you might benefit from biologic treatment and which biologic might best help. In general, these drugs are prescribed to people with moderate to severe RA.
They are also prescribed for people for whom other treatments havent worked or who cant take other treatments because of side effects or some other reason.
The types of biologics prescribed to people with RA include B-cell inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, interleukin inhibitors, and T-cell inhibitors.
Biologic Drugs Versus Biosimilars
Because biologics are made with living cells and not chemicals, generic equivalents are not possible. However, a biologic alternative known as biosimilars are hitting the market to offer additional therapeutic options and increase access to people who could benefit from these drugs. One example of the growing biosimilar industry is the 2016 FDA approval of Erelzi for spinal inflammatory arthritis.
As the name suggests, a biosimilar is very similar to an approved biologic drug, but its not an exact replica. Thats what makes a biosimilar different from a generic drug, which has identical active ingredients to its brand name counterpart. Because biologic drugs are so complex, they are unable to be have an identical match.
Generic drugs are sought after for their low cost, and biosimilars are designed to be more affordable compared to biologics. But, biosimilars are not expected to drive as much cost savings as generic drugs, as they do take considerable time and money to develop.
Also Check: How To Ease Arthritis Pain In Hands
Also Check: Rheumatoid Arthritis Remission Naturally
Is There A Permanent Cure For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects many joints, mainly the small joints of the hands and feet. It is a lifelong condition without a cure.
RA occurs when the immune system malfunctions and attacks healthy tissues. Untreated or severe RA can cause inflammation that also affects the organs. When RA attacks the joints, its target is the synovium . Over time, chronic inflammation can lead to bone erosion and joint deformity.
There is no permanent cure for RA. However, healthcare providers have many options for treating RA symptoms and getting the disease into remission. Remission is a time in which a person experiences few or no signs of the disease.
Keep reading to learn about how RA is treated, the latest research, and how remission in RA occurs.
I Basically Have No Limitations When It Comes To Lifting Weights
At 10 years old, Randi B Likely dreamed of being a college gymnast, but her knee swelled up with pain for no apparent reason. Although it got better after a week, the same thing happened to her shoulder. Then, she started having periods of pain and swelling in her hands and feet. At the time, her doctor assumed it was tendonitis caused by her intense gymnastics training. Likely switched to basketball during her freshman year of high school, but the pain continued. I felt like my fingers were jammed, but I didnt remember jamming them, Likely, now 24, tells SELF.
When she was 16, Likelys mobility got so bad that she couldnt even twist a doorknob, so she and her mom searched for answers. After six months of visiting multiple specialists, Likely was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis in 2013. She first tried a steroid and a DMARD, but eventually moved onto a biologic which helped after the other two didnt work. But in 2018, during Likelys senior year of college, her symptoms started flaring up again. Her condition progressed to the point where she couldnt even stand up to cook meals, let alone do a workout.
Read Also: How To Ease Arthritis
How Long It May Take
Relief happens gradually. You may notice a small improvement after your first or second dose of a biologic. Over time, you could get more relief.
It typically takes 3-4 months to see a big improvement. But it can take longer, Kaplan says, even 6 months or more.
How quickly you see an improvement may depend on how often you take your biologic. If you get an injection once a week, you might start to feel better within a few weeks. If you take it less often, it could take longer.
A Recent Comparison Of 3 Biologics For Rheumatoid Arthritis

Adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab were compared by Danish doctors who published a paper at the end of 2009. Seventy percent improvement according to the American College of Rheumatology criteria was achieved in 19% of patients after 6 months.
Their findings: Infliximab had the lowest rates of treatment response, disease remission, and drug adherence, adalimumab had the highest rates of treatment response and disease remission, and etanercept had the longest drug survival rates.
Note: Remember, in this last study, treatment response was measured at ACR 70 which is stricter than ACR 50. Drug adherence and drug survival rate means that the patient did not quit the Biologic during the eight year period. Various studies have shown that patients who use Biologics with methotrexate show less RA damage than patients who do not. It is not known exactly why individual patients have better responses to a particular Biologic.
Edit: Thanks to Jakki for posting this link on Facebook right after this posted. New data on predictive biomarkers for RA treatment as I hinted at in the post. I mentioned that this study was underway, but how is this for timing? Havent reviewed this new info yet on the blog, but will soon. Kelly
Recommended Reading: Arthritis Symptoms In Arms
How Can I Manage The Risk Of Side Effects
If you take a biologic drug, its important to learn how to recognize and respond to potential adverse side effects. Your doctor might also recommend strategies for limiting your risk of side effects. For example, they might order medical tests to check for signs of infection, liver damage, or other issues.
Before you start taking a biologic drug, ask your doctor:
- Should I undergo any medical tests before, during, or after treatment with this drug?
- What signs and symptoms of adverse side effects I should watch out for?
- What should I do if I develop signs or symptoms of adverse side effects?
- Are there any medications, supplements, or vaccines that I should avoid while taking this drug?
- Are there any other steps that I can take to lower my risk of side effects?
You should talk to your doctor before getting any vaccines while taking a biologic drug. While most vaccines are safe to get while youre taking biologics, some live virus vaccines may not be. Your doctor might advise you to get your vaccinations updated before you start taking biologics.
If you experience any signs or symptoms of adverse side effects, let your doctor know right away.
What Are The Risks Associated With The Drug
For many people, the potential benefits of taking a biologic drug outweigh the risks. But like any medication, biologic drugs can cause adverse side effects.
All biologic drugs for RA suppress your immune system. This raises your risk of contracting infections, such as the common cold, sinus infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections.
Some types of biologic drugs may also:
- interact with other drugs, supplements, or herbal products that you take
- trigger an injection-site or infusion-related reaction, which might result in redness, swelling, itching, rash, nausea, vomiting, trouble breathing, or other symptoms
- increase your risk of developing certain types of cancer, congestive heart failure, multiple sclerosis, shingles, or liver damage
- cause false results in blood glucose readings
- cause other adverse side effects
The risks vary, depending on the specific biologic drug that you take and your personal medical history. Before you start taking a drug, ask your doctor about the associated risks and tell them about any:
- potential signs or symptoms of infection that you have
- health conditions that youve been diagnosed with, such as tuberculosis, diabetes, or COPD
- medications and supplements, and herbal products that you take, including recent vaccinations
- surgeries that youve recently undergone or scheduled
You May Like: Rheumatoid Arthritis Better With Movement
Assessment Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity
In terms of assessing clinical response to therapy, there is no universally accepted tool for monitoring RA disease activity in daily practice.104, 105 While ACR criteria are used extensively to evaluate responses in RCTs, these criteria are difficult to apply to routine care settings and have not been widely adopted. The DAS and its popular derivative DAS28 are widely used in clinical trials. DAS provides an absolute score for current disease activity (as
Biologics: Weighing The Benefits And Risks
When you first get diagnosed with RA, you might have doubts about treatment. If you’re only having mild joint pain right now, are the risks of biologics and other DMARDs worth it? Can’t you wait and see how it goes?
But a wait-and-see approach can have serious consequences.
“We know what will happen if we don’t treat someone with rheumatoid arthritis,” says Bingham. “They will get worse.” In some cases, the damage may become so severe that even surgery won’t help.
Matteson compares RA to other chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure. At first, they might not seem like a problem. But untreated, they can lead to serious disease and even early death.
While the side effects from biologics might look scary, Bingham points out that the risks of untreated RA go far beyond achy joints. They include debilitating pain, heart problems, infections, and cancer.
We still don’t have a cure for RA. But biologics offer hope to people who once had no good options.
“Biologics and other DMARDs are more successful than anything we could have imagined 15 years ago,” Bingham tells WebMD. “These treatments have reshaped the face of the disease.”
Show Sources
Clifton Bingham, MD, associate professor of medicine, Johns Hopkins University associate director, Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center, Baltimore.
Eric L. Matteson, MD, chair, department of rheumatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Agency for Healthcare Research.
You May Like: Muscle Arthritis Treatment
The Side Effects Sound Scary Which Ones Do I Need To Worry About Most
The most common misconception or concern I hear in my practice is that taking biologics will wipe out someones immune system, leading to infections, health problems and risk of death. When you take a drug that affects your immune system, you do have to keep an eye out for cancer and infections. So, before you start a biologic, you will be screened for cancer as appropriate for your age and sex, and for infections like tuberculosis and hepatitis. We also recommend everyone on these drugs gets the appropriate immunizations for their age, like flu and pneumonia shots, to reduce infection risk. But people live better and longer with these drugs than without. Major risks are associated far more with the disease and the consequences of untreated disease than these drugs. Biologics reduce the risks of premature death, increased heart disease and the need for joint surgery. Patients with uncontrolled RA are also at higher risk of infection, so controlling the arthritis can also reduce overall infection risk. On balance, you are much better off with treated disease than untreated.
Lifestyle And Home Remedies
There are self-care steps you can take to manage RA. Along with your medications, the following can help with pain and other symptoms of RA:
- Exercise: Gentle exercise can help strengthen joints and muscles and reduce daily fatigue. You should check with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise routine and avoid exercising when joints are tender or inflamed. Walking, stretching, water exercises, swimming, and tai chi are all safe exercises for people with RA.
- Diet: There is no specific or recommended diet to treat RA, but some foods can help lower inflammation in your body. To manage RA, foods to add to your diet include fruits and vegetables, whole grains, fatty fish, and healthy oils like olive oil.
- Apply heat or cold: Heat can help to ease pain and relax stiff joints and muscles. Cold can help to dull down pain and decrease swelling.
- Relax: Find ways to reduce stress in your life to control RA pain. Try deep breathing, guided imagery, and other relaxation techniques.
Also Check: Home Remedy For Arthritis Pain In Hands