Measures To Reduce Bone Loss
Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can cause bone loss, which can lead to osteoporosis. The use of prednisone further increases the risk of bone loss, especially in postmenopausal women.
You can do the following to help minimize the bone loss associated with steroid therapy:
- Use the lowest possible dose of glucocorticoids for the shortest possible time, when possible, to minimize bone loss.
- Get an adequate amount of calcium and vitamin D, either in the diet or by taking supplements.
- Use medications that can reduce bone loss, including that which is caused by glucocorticoids.
- Control rheumatoid arthritis itself with appropriate medications prescribed by your doctor.
What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include the following:
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods
- Fatigue
Rheumatoid arthritis affects each person differently. In most people, joint symptoms may develop gradually over several years. In other people, rheumatoid arthritis may proceed rapidly. A few people may have rheumatoid arthritis for a limited period of time and then go into remission .
Cartilage normally acts as a shock absorber between the joints. Uncontrolled inflammation causes the destruction and wearing down of the cartilage, which leads to joint deformities. Eventually, the bone itself erodes, potentially leading to fusion of the joint . This process is aided by specific cells and substances of the immune system, which are produced in the joints but also circulate and cause symptoms throughout the body.
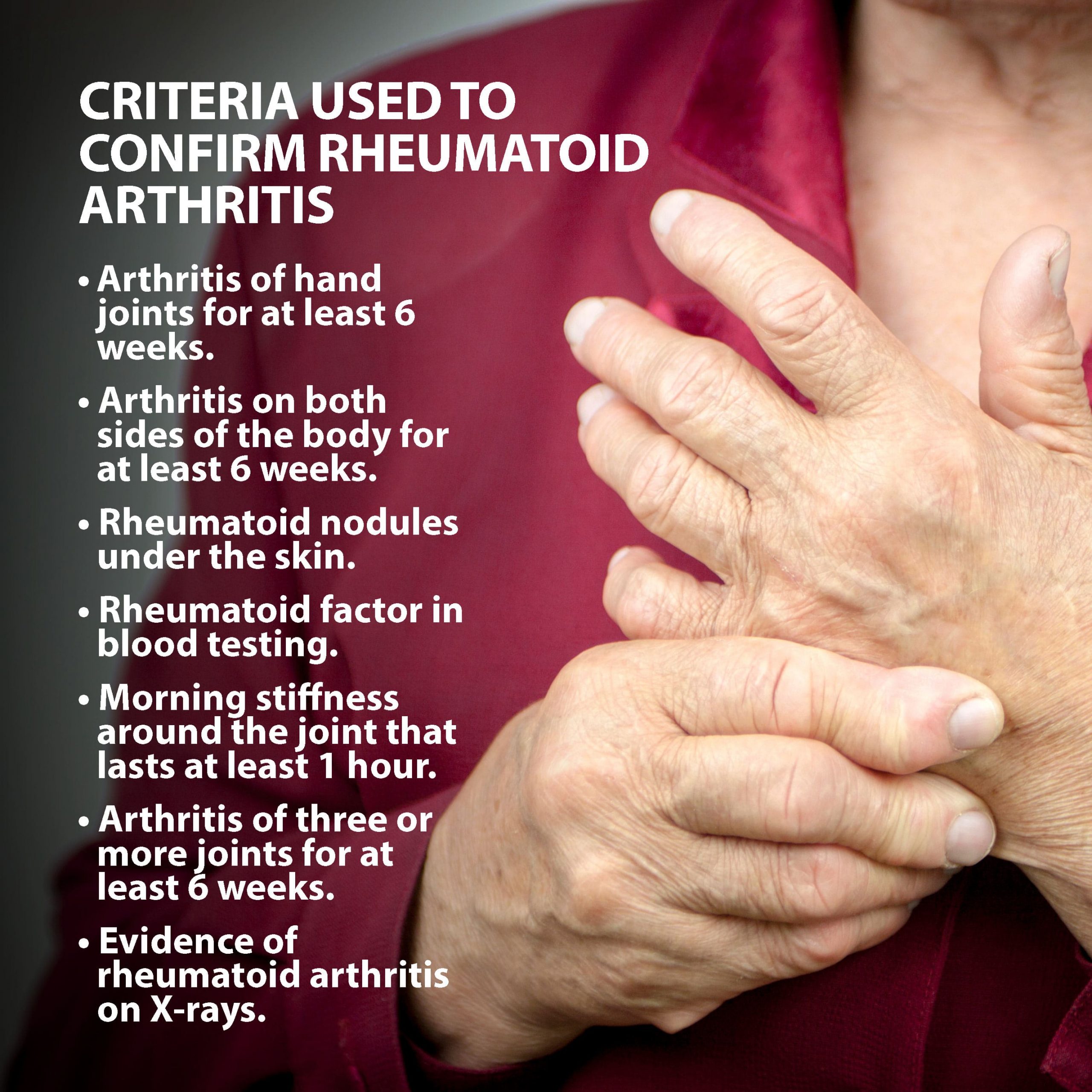
The Diagnostic Criteria For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis cant be established with just one test. Instead, rheumatologists rely on a combination of your medical history, a physical exam, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging tests to pinpoint the disease.
They also try to rule out the possibility of other conditions that may resemble RA, such as lupus, psoriatic arthritis, gout, or osteoarthritis. This is called a differential diagnosis.
To begin the diagnostic process, a rheumatologist will take your medical history, which includes asking questions about your current symptoms particularly pain, swelling, and stiffness and their location, duration, and severity.
Theyll also ask about your familys medical history as it pertains to RA and other autoimmune conditions. Conditions like RA can be more common in families with RA or other immune system-related health problems. For example, research recently published in the journal Arthritis Care & Research found that people who have a first-degree relative with RA are more than twice as likely as the general population to develop RA. A family history of lupus, scleroderma, thyroid disease, or inflammatory bowel disease also substantially increased the risk of RA.
Your rheumatologist will also perform a physical examination, testing each of your joints for things like swelling, tenderness, and limited range of motion. The location of affected joints is important to diagnosis.
Read Also: Arthritis On One Side Of Body
Clinical Diagnosis Of Inflammatory Arthritis Is Not Always Straightforward
The history of swelling in joints, early morning stiffness lasting > 30 minutes, systemic symptoms such as tiredness combined with objective evidence of synovitis would favour a diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis . However, reality can be more complex:
-
Objective signs may be lacking or have been suppressed by anti-inflammatory medication
-
Joint swelling can be difficult to identify in obese patients
-
The sensation that joints are swollen may be reported even by some patients with fibromyalgia
-
Osteoarthritis as well as RA can cause morning stiffness, though in osteoarthritis it usually lasts less than 30 minutes
-
Inflammatory markers such as the ESR or C-reactive protein are normal in about 60% of patients with early RA
-
In a patient with preceding osteoarthritis, radiographic changes can be misleading, especially if those suggestive of inflammatory arthritis have not yet developed.
Ra Blood Tests: What Lab Tests Show Rheumatoid Arthritis

To diagnose rheumatoid arthritis there is no one test that can on its own reach a diagnosis. Instead, there are a number of criteria that must be established in order to reach a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
As part of the criteria for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis, doctors will order multiple blood tests. These blood tests look for specific indicators that support the possibility that the patient could have rheumatoid arthritis.
Recommended Reading: Joint Pain Medical Term
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are many effective methods for decreasing the pain and inflammation and slowing down the disease process. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are very important.
Extensive research is being done to learn the cause of rheumatoid arthritis and the best methods of treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/17/2017.
References
Not All Patients With ‘early Polyarthritis’ Develop Persistent Disease
When a patient with inflammatory arthritis cannot definitely be labelled as having RA, it becomes important to decide whether the arthritis is likely to remit or to persist. Clearly, if spontaneous remission seems likely, the patient should be spared potentially toxic DMARD therapy. On the other hand, a patient with persistent inflammation should be started promptly on DMARDs since the condition may represent RA in evolution. From the Norfolk Arthritis Register there is evidence that an overwhelming majority of patients with persistent polyarthritis in due course come to satisfy diagnostic criteria for RA . Thus, since joint damage and functional loss occur early, most patients develop these irreversible changes before a definite diagnosis of RA can be made.
How can the clinician predict persistence of disease? Several research groups have tried to identify pointers in patients with early arthritis but their results are not easily combined because of heterogeneity in populations, predictive factors used and duration of follow-up. Among the predictive factors suggested, the most useful seems to be disease duration exceeding 12 weeks: a patient who has had inflammatory joint symptoms for this long is very unlikely to experience a spontaneous remission. Other features suggesting the unlikelihood of remission are positive tests for rheumatoid factor or cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and the presence of erosions on radiographs.
Don’t Miss: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Itching
Other Diagnostic Methods Used To Confirm Rheumatoid Arthritis
Blood tests arent the only method that can be used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. You might also have a variety of other tests done to help confirm rheumatoid arthritis. These include:
- Physical assessment. A physical assessment can help determine how much your symptoms are impacting your daily life. You might be asked how well you can do daily tasks such as showering, eating, and dressing. A physical therapist might also assess your grip, walk, and balance.
- Joint scan. A joint scan looks for inflammation and damage in your joints. It can help confirm a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
- Imaging tests. X-rays and MRIs create detailed pictures of your bones, muscles, and joints that can help diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.
Nutrition And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an inflammatory autoimmune disease in which the bodys immune system attacks the lining of healthy joints, causing pain, inflammation, stiffness and sometimes loss of function. Over time, inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis can lead to deformities, chronic pain or struggles with balance. While there is no cure, interventions such as medications and lifestyle and nutrition modifications may help prevent or slow the progression of joint damage and help with symptom management.
Signs and SymptomsCommon symptoms include pain, swelling or stiffness in more than one joint, usually on both sides of the body. Stiffness is typically worse in the morning, getting better as the day progresses. Joints most impacted by rheumatoid arthritis are in the hands, wrists and knees, but other joints and organs such as the lungs, heart and eyes can be affected. Other symptoms may include weight loss, fever, weakness or fatigue.
It is common for people with RA to experience flares times when symptoms get worse and remission, when symptoms improve.
Of studies included in a 2020 systematic review on the effects of diet and dietary supplements on Disease Activity Score in 28 joints, or DAS28 which measures rheumatoid arthritis severity, one reported a significant improvement after 12 weeks of following the Mediterranean diet, while another reported benefits after 10 weeks, but those results were not statistically significant.
References
Recommended Reading: Back Arthritis Remedies
What Should Be Done If Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Suspected
Any person who is suspected of having RA should be referred to a specialist rheumatologist. Early referral is important so that disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs may be prescribed as soon as possible so as to slow or halt the disease process. Delay in referral or receiving a definitive diagnosis and treatment can result in significant costs to the individual, particularly those who are employed. This is because joint damage occurs most rapidly in the early stages of the disease, and often the treatment drugs can take several months to work.
Many areas now offer Early Arthritis Clinics where a rapid assessment is performed by specialists/specialist nurses in order to limit any delays. An ultrasound of the affected joints may be performed during this assessment.
If your symptoms are particularly severe when you first see your GP, then they may refer you urgently but also ring to speak to one of the local rheumatologists to ask for assistance in how to best help you in the meantime. Sometimes people are started on treatments other than those mentioned above, e.g. steroid tablets or a steroid injection, prior to being seen, in order to improve their condition. This though can affect what the specialists see and find at the first appointment, which can potentially delay their making a diagnosis or there may be increased uncertainty of the diagnosis.
Heart And Blood Vessels
People with RA are more prone to atherosclerosis, and risk of myocardial infarction and stroke is markedly increased.Other possible complications that may arise include: pericarditis, endocarditis, left ventricular failure, valvulitis and fibrosis. Many people with RA do not experience the same chest pain that others feel when they have angina or myocardial infarction. To reduce cardiovascular risk, it is crucial to maintain optimal control of the inflammation caused by RA , and to use exercise and medications appropriately to reduce other cardiovascular risk factors such as blood lipids and blood pressure. Doctors who treat people with RA should be sensitive to cardiovascular risk when prescribing anti-inflammatory medications, and may want to consider prescribing routine use of low doses of aspirin if the gastrointestinal effects are tolerable.
You May Like: Can You Get Arthritis In Your Legs
Other Conditions And Joint Pain
Other forms of arthritis, and other conditions, can also cause joint pain. Examples include:
- fibromyalgia syndrome, a condition in which your brain processes pain in your muscles and joints in a way that amplifies your perception of the pain
- scleroderma, an autoimmune condition in which inflammation and hardening in your skin connective tissues can lead to organ damage and joint pain
Reaching A Ra Diagnosis

Once all of these steps have been conducted, doctors will look at all of the test results and reach a conclusion based on the overall picture. Some doctors take a more symptom based approach to diagnosing RA while others rely on blood tests and medical history to confirm a RA diagnosis.
This is why its possible to be diagnosed with RA but not test positive for antibodies or have a medical history of RA in your family. If the symptoms themselves are consistent with RA, then it can still be diagnosed.
That being said, the main criteria for diagnosing RA do not change. The patient must exhibit symptoms for greater than six weeks, symmetrical symptoms, as well as multiple joints being affected including fingers and hands.
You May Like: Knuckle Arthritis Pain Relief
Which Patients Should Be Referred
Early treatment of RA can be a realistic goal only if general practitioners and other non-rheumatologists recognize the clinical picture of early inflammatory arthritis and refer patients promptly for a specialist opinion. Patients with joint pains that have persisted for more than 68 weeks should be referred especially in the presence of the following features:
-
Joint swelling
How Is Ra Diagnosed
RA is diagnosed by reviewing symptoms, conducting a physical examination, and doing X-rays and lab tests. Its best to diagnose RA earlywithin 6 months of the onset of symptomsso that people with the disease can begin treatment to slow or stop disease progression . Diagnosis and effective treatments, particularly treatment to suppress or control inflammation, can help reduce the damaging effects of RA.
Don’t Miss: What Does Ra Feel Like
Other Tests For Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis
Blood tests are not only used to detect RF and anti-CCP antibodies. They’re also used to reveal if you have:
- Anemia, or low red blood cell count, which occurs in up to half of people with RA
- A high erythrocyte sedimentation rate, also known as a sed or ESR rate, a crude measure of inflammation in your body
- High C-reactive protein levels, another marker of inflammation
Aside from blood tests, an X-ray can help your doctor determine the degree of destruction in your joints, but may only be useful when RA has progressed to a later phase.
Rheumatoid Factor And Anti
One blood test measures levels of rheumatoid factors in the blood. Rheumatoid factors are proteins that the immune system produces when it attacks health tissue.
About half of all people with rheumatoid arthritis have high levels of rheumatoid factors in their blood when the disease starts, but about 1 in 20 people without rheumatoid arthritis also test positive.
A related blood test known as anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide test is also available. Anti-CCPs are antibodies also produced by the immune system.
People who test positive for anti-CCP are very likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis, but not everybody with rheumatoid arthritis has this antibody.
Those who test positive for both rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP may be more likely to have severe rheumatoid arthritis requiring higher levels of treatment.
Also Check: Remedies For Arthritis Pain In Hands
Prediction Of Early Ra
A patient with inflammatory arthritis may pass several stages from the onset of arthritis to a specific form of rheumatic diseases such as RA . The first phase is the period leading up to the onset of arthritis .The second is the period during which persistence or remission is determined. The third and the fourth phases are the evolution into specific form of inflammatory arthritis and the outcome/severity of that arthritis. In some patients, these four phases follow in rapid sequences whereas in other patients the time course may prolong and continue for several months or years. Different genetic backgrounds and environmental factors or treatment can affect the various evolutionary phases of arthritis and alter the natural history of initial inflammatory arthritis .
Amplification In The Synovium
Once the generalized abnormal immune response has become established which may take several years before any symptoms occur plasma cells derived from B lymphocytes produce rheumatoid factors and ACPA of the IgG and IgM classes in large quantities. These activate macrophages through Fc receptor and complement binding, which is part of the intense inflammation in RA. Binding of an autoreactive antibody to the Fc receptors is mediated through the antibody’s N-glycans, which are altered to promote inflammation in people with RA.
This contributes to local inflammation in a joint, specifically the synovium with edema, vasodilation and entry of activated T-cells, mainly CD4 in microscopically nodular aggregates and CD8 in microscopically diffuse infiltrates. Synovial macrophages and dendritic cells function as antigen-presenting cells by expressing MHC class II molecules, which establishes the immune reaction in the tissue.
Recommended Reading: What Does Arthritis Do To You
Who Should Get Testing
Patients who experience inflammation, pain, or loss of mobility in joints should discuss testing for rheumatoid arthritis with their doctor, especially if symptoms occur in multiple joints or in matching joints on both sides of the body, such as both wrists. Other symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Stiffness in the morning for 30 minutes or longer
- Fatigue
- Dry eyes and mouth
- Firm lumps beneath the skin
These symptoms are often due to something other than RA when they last less than six weeks. The longer a patient experiences symptoms, the more likely the symptoms are to be due to RA.
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in its early stages can be challenging, as patients may experience few symptoms, but early diagnosis is important because early treatment may prevent joints from worsening or at least slow the process. When symptoms are present, they often differ from person to person and mimic the symptoms of other diseases. Testing is an important part of the process of determining whether symptoms are due to RA or another condition.
After receiving a diagnosis of RA, its important for patients to continue rheumatoid arthritis testing. Testing can assist doctors in assessing the severity of RA, as well as monitoring the efficacy of treatment, tracking disease progression, and detecting potentially serious side effects of treatment drugs.
How To Prepare For An Initial Doctors Appointment
During your first appointment, your doctor will conduct a physical exam, collect details about your medical history, and discuss which symptoms you may be experiencing.
Generally, they will evaluate your joints for inflammation, swelling, and redness and may order imaging tests or blood work to determine if you have RA.
Be sure to keep track of all your symptoms and consider logging the time, duration, and severity of each symptom as it occurs. You should also provide your doctor with information about any medications that you are taking, including the frequency and dosage.
Keep in mind that you may not receive a definitive diagnosis on your first visit, as many autoimmune disorders develop slowly over time.
However, your doctor may discuss possible treatment options with you, which can include medications, physical therapy, pain management, exercise, and other modifications to your diet and lifestyle.
Its important to discuss any questions you have regarding your treatment plan with your doctor. Some questions you may want to consider asking:
- What treatment options are right for me?
- What are the potential side effects from my treatment?
- What types of exercise would be beneficial? How often should I work out?
- Are there other ways to treat symptoms at home, such as by using a hot or cold compress?
- What options available for mental health support, if needed?
- Would I benefit from physical therapy, nutrition counseling, or other complementary treatments?
You May Like: High Rheumatoid Levels