Early Stage Signs And Symptoms
A person can develop RA at any stage in their life. However, the condition most commonly develops between the ages of 30 and 50 years old.
People with early stage RA may not see redness and swelling in their joints. However, they may experience some joint tenderness and pain. A general feeling of stiffness throughout the body in the morning may suggest a person has RA.
Someone with early stage RA may also experience fatigue. Fatigue can be both mental and physical and can cause a person to feel extremely tired, preventing them from performing their usual daily tasks.
The inflammation that comes with RA may cause a person to develop a fever. A person has a fever if their body temperature rises above the typical range of 98100°F . Fever is a common sign of inflammation in people with autoimmune diseases.
A person may also experience weight loss due to the inflammation from RA. In addition, someone with fatigue and fever may experience appetite loss, which can contribute to weight loss.
As the inflammatory process of RA progresses, symptoms can worsen. A person may experience more extreme fatigue and continue to have fevers and lose weight.
Common symptoms of RA include the below.
Reviewing Your Risk Factors
Your doctor may suspect you’re dealing with rheumatoid arthritis if youre a woman because about 75% of people who are diagnosed with RA are female. Some women are diagnosed with RA early, in their 20s or 30s, but a number are diagnosed later, in their 50s or 60s. Men who are diagnosed tend to be older. If you have first-degree family members who have been diagnosed with RA, tell your doctor, because that increases your risk as well.
You Are Not Alone: Finding Support For Ra In The Hands
How does RA in your hands and fingers affect your daily life? Has your rheumatologist found the right medication to manage your symptoms? What helps you successfully get through each day? Share your tips and experiences in a comment below or on myRAteam. Youll be surprised how many other members have similar stories.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Disability For Arthritis In Hands
What Can I Do To Manage My Pain
Pain may limit some of the things you do, but it doesnt have to control your life. Your mind plays an important role in how you feel pain. Thinking of pain as a signal to take positive action rather than being scared or worried about it can be helpful. Also you can learn ways to manage your pain. What works for one person may not work for another, so you may have to try different techniques until you find what works best for you.
Here are some things you can try:
Contact your local Arthritis Office for details of self management courses that can teach you these techniques. You may also find it useful to see a psychologist to learn other mind techniques to help you cope with pain.
Also Check: Mayo Clinic Arthritis Treatment
What Do The Results Mean
If rheumatoid factor is found in your blood, it may indicate:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Another autoimmune disease, such lupus, Sjogren’s syndrome, juvenile arthritis, or scleroderma
- An infection, such as mononucleosis or tuberculosis
- Certain cancers, such as leukemia or multiple myeloma
About 20 percent of people with rheumatoid arthritis have little or no rheumatoid factor in their blood. So even if your results were normal, your health care provider may order more tests to confirm or rule out a diagnosis.
If your results were not normal, it doesn’t necessarily mean you have a medical condition needing treatment. Some healthy people have rheumatoid factor in their blood, but it’s not clear why.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Recommended Reading: What Medication Is Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Affected Joints In Oa
OA is less symmetrical. You might have pain in both your left and right knee, for example, but one side or one joint is worse.
OA, like RA, is common in the hand and fingers. OA often affects the spine and hips in addition to the knees.
The primary goal in treating both OA and RA is to:
- minimize damage to your joints
Your doctor will approach these goals differently, depending on which condition you have.
Anti-inflammatory and corticosteroid medications are generally effective for both OA and RA, but use of corticosteroids is minimized.
If you have RA, drugs that suppress your immune system can prevent damage by stopping your body from attacking your joints, and prevent joint damage.
The following are some of the questions you may have about RA and OA:
Ra And Your Eyes: What You Need To Know
Rheumatoid arthritis is known for joint pain, but it can also affect other parts of the body, including your eyes. Learn which rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and eye issues are most common, and how to manage them.
Most people think of rheumatoid arthritis as a joint disease, but like other autoimmune disorders, it can impact different areas of the body as well. One of the more common complications for people with rheumatoid arthritis is eye problems, which can lead to corneal damage and ultimately impact vision if left untreated.
Some common eye conditions, like the ones described below, may affect people with rheumatoid arthritis . But there are steps to take to safeguard eye health and avoid permanent damage.
Dry Eyes
RA can be associated with extra-articular manifestations, and dry eyes are one of the most common problems, says Ana-Maria Orbai, MD, instructor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore. A person with dry eyes might experience itching, a sand-like sensation in the eyes, and redness. They may also notice a lack of moisture or tears in the eyes, as well as blurred vision.
If you decide to go the over-the-counter route, avoid eye-drop products that have preservatives or vasoconstrictive agents, such as some from Visine and Clear Eyes, which often promise to relieve redness or take the red out, Orbai explains.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Way To Treat Arthritis
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Anyone experiencing symptoms of joint swelling, pain or tenderness, particularly worse in the morning, and/or fatigue for several weeks, should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
A rheumatologist is a specialist who diagnoses and treats RA and other autoimmune illnesses. While primarily targeting the joints, RA can lead to inflammation elsewhere in the body, including of the heart or lungs, so untreated disease can lead to serious complications and long-term disability.
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis With Blood Tests
Rheumatoid arthritis blood tests are only one way to help doctors reach a diagnosis. If a patient is positive for any of these tests, they must also exhibit specific symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Doctors look at multiple other criteria besides blood test results when determining their diagnosis.
In some cases, patients can still be diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis even if they dont test positive for the various types of antibodies found in rheumatoid arthritis blood tests.
Read more about diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis and the different types of rheumatoid arthritis here.
Read Also: Do You Use Heat Or Cold On Arthritis
Treatment Of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
Just like seropositive rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative rheumatoid arthritis cannot be reversed.
Treatment of this disorder is focused on alleviating pain and discomfort associated with inflammation around the body. Treatment can also slow the progression of this disease, or stop the progression altogether.
Its important to listen to your body and be aware of the signs and symptoms of RA, because the earlier we can detect this disorder, the greater our chances are of slowing its progression. Seronegative RA causes serious damage to the joints and bones because the body attacks the synovial tissues that cushion the bones. When the synovial tissue and supporting cartilage deteriorate, the bones no longer have the padding they need, and they start to rub against each other, which deteriorates the bones over time.
Medications
The symptoms of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis can be treated with NSAIDs medications, like ibuprofen. NSAIDs are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with joint swelling. These medications can increase range of motion, as they reduce the swelling that causes stiffness and inhibits movement.
Other medications, specifically disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs , can be taken to slow joint damage caused by seronegative RA. Sulfasalazine is a common DMARD used to slow the progression of seronegative RA and psoriatic arthritis.
Intra-articular Injections
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
Also Check: What To Do For Arthritis Pain
Oa Treatments Are Largely About Lifestyle And Relieving Pain
Two of the most important treatments for OA are exercise and weight loss, says Soo Kim, M.D., medical director of Johns Hopkins Musculoskeletal Center in Baltimore. By strengthening the muscles surrounding the joint, more stress gets distributed onto those muscles, and less of it lands on the joint, says Dr. Kim.
To manage the pain, acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help. Topical agents can be applied over the joint. And for severe pain, steroid or hyaluronic acid injections may help, Dr. Kim says.
Treatment Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis continues to improve, which can give many people relief from symptoms, improving their quality of life. Doctors may use the following options to treat RA:
- Routine monitoring and ongoing care.
- Complementary therapies.
Your doctor may recommend a combination of treatments, which may change over time based on your symptoms and the severity of your disease. No matter which treatment plan your doctor recommends, the goals are to help:
- Prevent, slow, or stop joint and organ damage.
- Improve your ability to participate in daily activities.
Rheumatoid arthritis may start causing joint damage during the first year or two that a person has the disease, so early diagnosis and treatment are very important.
Also Check: What Type Of Dr For Arthritis
Human Leukocyte Antigen Tissue Typing
This test checks for a genetic marker called human leukocyte antigen .
Some studies suggest that around 60% of RA cases may be inherited. If a person has specific antigens, it could mean that they have a higher likelihood of developing RA. However, other factors, such as tobacco use, can also trigger the condition.
HLA markers in the blood can help indicate the likelihood of developing an immune-related condition such as RA. These markers may also be a sign of another condition, such as ankylosing spondylitis or reactive arthritis.
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Go Away
No, rheumatoid arthritis doesnt go away. Its a condition youll have for the rest of your life. But you may have periods where you dont notice symptoms. These times of feeling better may come and go.
That said, the damage RA causes in your joints is here to stay. If you dont see a provider for RA treatment, the disease can cause permanent damage to your cartilage and, eventually, your joints. RA can also harm organs like your lung and heart.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have rheumatoid arthritis, you may feel like youre on a lifelong roller coaster of pain and fatigue. Its important to share these feelings and your symptoms with your healthcare provider. Along with X-rays and blood tests, what you say about your quality of life will help inform your treatment. Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms and recommend the right treatment plan for your needs. Most people can manage rheumatoid arthritis and still do the activities they care about.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/18/2022.
References
You May Like: Is Psoriatic Arthritis An Inflammatory Disease
How Is Gout Treated
Gout can be effectively treated and managed with medical treatment and self-management strategies. Your health care provider may recommend a medical treatment plan to
- Manage the pain of a flare. Treatment for flares consists of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, steroids, and the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine.
- Prevent future flares. Making changes to your diet and lifestyle, such as losing weight, limiting alcohol, eating less purine-rich food , may help prevent future attacks. Changing or stopping medications associated with hyperuricemia may also help.
- Prevent tophi and kidney stones from forming as a result of chronic high levels of uric acid. Tophi are hard, uric acid deposits under the skin. For people with frequent acute flares or chronic gout, doctors may recommend preventive therapy to lower uric acid levels in the blood using drugs like allopurinol, febuxostat, and pegloticase.
In addition to medical treatment, you can manage your gout with self-management strategies. Self-management is what you do day to day to manage your condition and stay healthy, like making healthy lifestyle choices. The self-management strategies described below are proven to reduce pain and disability, so you can pursue the activities important to you.
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Fatigue
Everyones experience of rheumatoid arthritis is a little different. But many people with RA say that fatigue is among the worst symptoms of the disease.
Living with chronic pain can be exhausting. And fatigue can make it more difficult to manage your pain. Its important to pay attention to your body and take breaks before you get too tired.
What are rheumatoid arthritis flare symptoms?
The symptoms of a rheumatoid arthritis flare arent much different from the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. But people with RA have ups and downs. A flare is a time when you have significant symptoms after feeling better for a while. With treatment, youll likely have periods of time when you feel better. Then, stress, changes in weather, certain foods or infections trigger a period of increased disease activity.
Although you cant prevent flares altogether, there are steps you can take to help you manage them. It might help to write your symptoms down every day in a journal, along with whats going on in your life. Share this journal with your rheumatologist, who may help you identify triggers. Then you can work to manage those triggers.
Read Also: What Can Be Done For Arthritis In Thumb Joint
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Ra
With RA, there are times when symptoms get worse, known as flares, and times when symptoms get better, known as remission.
Signs and symptoms of RA include:
- Pain or aching in more than one joint
- Stiffness in more than one joint
- Tenderness and swelling in more than one joint
- The same symptoms on both sides of the body
What Aggravates Rheumatoid Arthritis
Sugar, saturated fats, trans fats, omega-6 fatty acids, refined carbohydrates, MSG, gluten, aspartame, and alcohol are among the foods and additives thought to be pro-inflammatory. A diet for rheumatoid arthritis should include anti-inflammatory foods, while pro-inflammatory foods are reduced or avoided.
Also Check: What Can Help With Arthritis Pain
What Is The Prognosis For Rheumatoid And Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
As a rule, the severity of rheumatoid arthritis waxes and wanes. Periods of active inflammation and tissue damage marked by worsening of symptoms are interspersed with periods of little or no activity, in which symptoms get better or go away altogether . The duration of these cycles varies widely among individuals.
Outcomes are also highly variable. Some people have a relatively mild condition, with little disability or loss of function. Others at the opposite end of the spectrum experience severe disability due to pain and loss of function. A disease that remains persistently active for more than a year is likely to lead to joint deformities and disability. Approximately 40% of people have some degree of disability 10 years after their diagnosis. For most, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic progressive illness, but about 5%-10% of people experience remission without treatment. This is uncommon, however, after the first three to six months.
Rheumatoid arthritis is not fatal, but complications of the disease shorten the life span by a few years in some individuals. Although generally rheumatoid arthritis cannot be cured, the disease gradually becomes less aggressive and symptoms may even improve. However, any damage to joints and ligaments and any deformities that have occurred are permanent. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect parts of the body other than the joints.
Osteoarthritis
Read Also: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Show On X Ray
Serologic Testing For Ra
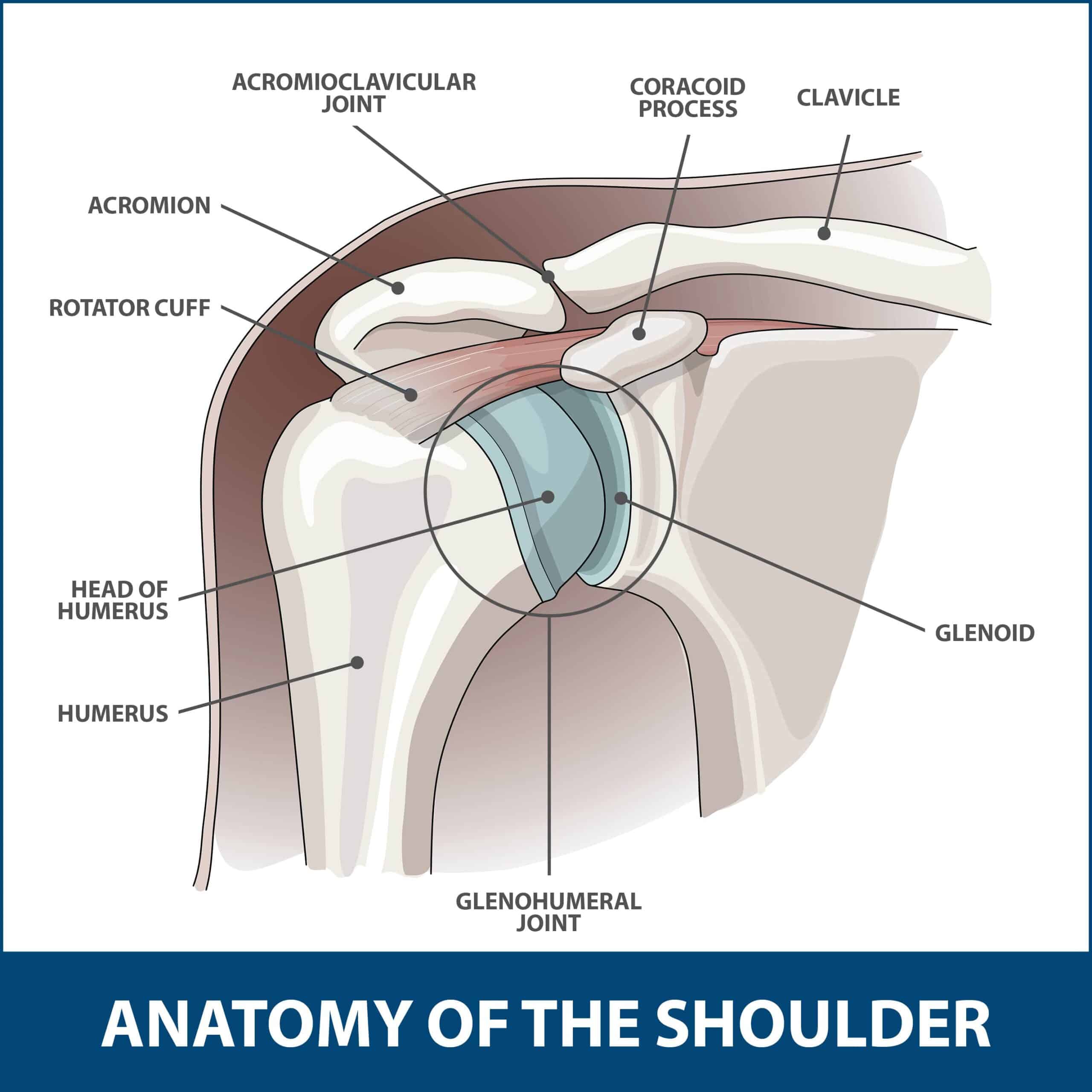
RF and/or anti-CCP antibodies may be positive in people with RA, leading to whatâs referred to as âseropositive RA.â However, approximately 20% of people with RA will not have either a positive RF or CCP antibody, thus having âseronegative RA.â Seropositive RA is associated with more aggressive disease.
Finally, since RA is a systemic inflammatory condition, it is only natural that inflammatory markers such as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein , may be elevated at various times throughout the disease. Elevation in either the ESR or CRP is included in the 2010 EULAR/ACR diagnostic criteria for RA and can be used to monitor and gauge disease activity.
Once adequate and appropriate management is achieved, these markers should return to normal.
Recommended Reading: How Does Psoriatic Arthritis Feel