You Are Not Alone: Finding Support For Ra In The Hands
How does RA in your hands and fingers affect your daily life? Has your rheumatologist found the right medication to manage your symptoms? What helps you successfully get through each day? Share your tips and experiences in a comment below or on myRAteam. You’ll be surprised how many other members have similar stories.
Have You Had The Following Laboratory Tests Performed To Assess The Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Factor . Is it positive or negative?
- Anti-citrullinated protein antibody . Is it positive or negative?
- Are the markers of inflammation, ESR and/or CRP in the blood elevated?
The classification criteria used worldwide to help in classifying an arthritis as RA is the 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria.
I present this here to help you screen for rheumatoid & to help determine the likelihood of having RA.
Dont Miss: Eggs Bad For Arthritis
Other Causes Of Hand And Finger Symptoms
RA hand symptoms can mimic those of other conditions, such as osteoarthritis. Some members of myRAteam discovered their hand pain was actually related to secondary Raynauds disease, a vascular condition that affects 10 percent to 20 percent of people with RA. Psoriatic arthritis, another autoimmune disease, can also cause hand and finger dysfunction as can pinched nerves in the neck.
A rheumatologist can diagnose the specific cause of symptoms in the hand with a physical exam and X-rays. X-rays can detect narrowing of joint space or erosions of the bone that could signal RA. Ultrasound and MRI technology has improved the ability to spot joint damage earlier in the course of the disease.
Recommended Reading: Eggs Bad For Arthritis
Theyll Order Imaging Tests
Rheumatoid arthritis impacts the lining of joints, which leads to damage of joint tissue. Your doctor may order X-rays to check for joint damage caused by RA . Sometimes, doctors order CT scans, ultrasounds or even MRIs as well. X-rays in early stages may not show the changes, caused by RA, Dr. Khan says. Ultrasound and MRI give far more information about the joint lining and whether or not the tissues around the joints are inflamed.
How Does Joint Pain In Hands And Fingers Affect Members
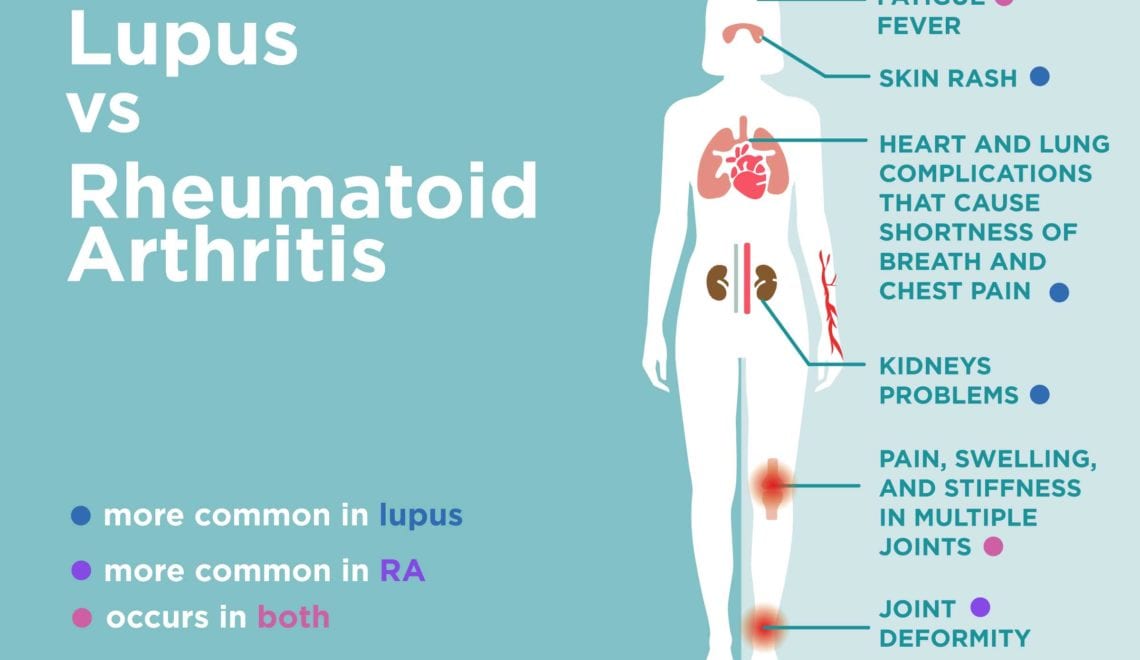
The symptoms of RA in hands and fingers significantly disrupt myRAteam members daily lives in many ways. Many members report that this type of arthritis makes it hard to grip, pinch, or squeeze things with their hands. Its frustrating to not be able to turn a doorknob, open jars, or lift heavy cookware, said one member. I need both hands to balance a coffee mug, explained another. I cant hold onto my pills without dropping them, said another.
Loss of hand function can also be dangerous. Members say theyve dropped a cup of coffee or lost control of a pot of hot water. One member said, I was changing the toilet paper roll and, because my hands don’t work, the holder shot out of my hand and popped me in the eye!
Read Also: What Does A High Rheumatoid Factor Mean
Human Leukocyte Antigen Tissue Typing
This test checks for a genetic marker called human leukocyte antigen .
Some studies suggest that around 60% of RA cases may be inherited. If a person has specific antigens, it could mean that they have a higher likelihood of developing RA. However, other factors, such as tobacco use, can also trigger the condition.
HLA markers in the blood can help indicate the likelihood of developing an immune-related condition such as RA. These markers may also be a sign of another condition, such as ankylosing spondylitis or reactive arthritis.
The Role Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Testing
Rheumatoid arthritis testing is used to diagnose RA, evaluate the severity of a patients disease, monitor treatment, and detect potential side effects of treatment drugs:
- Diagnosis: Diagnostic testing helps determine the cause of a patients symptoms. If a doctor is concerned that a patients symptoms may be related to rheumatoid arthritis, testing can assist in diagnosing RA and ruling out other health conditions.
- Evaluating severity: The results of several laboratory tests can inform doctors about the severity of a patients RA, the amount of joint damage, and the prognosis or expected course of the disease.
- Treatment monitoring: Monitoring patients diagnosed with RA involves regular medical care, including doctors visits, laboratory testing, and imaging tests. Combining these strategies can assist doctors in tracking the progression of RA and understanding if treatment is effective.
- Detecting side effects: Testing may also be used to detect side effects caused by treatment drugs, as well as other health conditions that are more common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, including osteoporosis, heart disease, and diabetes.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Reactive Arthritis
Getting Tested For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Testing for rheumatoid arthritis is ordered by a doctor or specialist if indicated by a patients symptoms. Blood and urine samples used for testing can be obtained in a doctors office or other medical setting.
Synovial fluid is a liquid that is located in spaces between a persons joints, helping to cushion ends of bones and reduce friction during movement. For a synovial fluid analysis, a sample of synovial fluid is obtained during a procedure called a joint aspiration or arthrocentesis. During a joint aspiration, a doctor uses a needle to withdraw a sample of synovial fluid from a joint.
Diagnosis And Screening For Rheumatoid Arthritis
One of the most important parts of managing RA is making a diagnosis early, and getting on appropriate treatment. Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis can prove to be a difficult task for rheumatologists and doctors, particularly in its early stages. Thatâs because the early symptoms and signs of RA resemble those of a variety of other conditions and disorders and symptoms may not even be present every day. For example, if you experience pain and morning stiffness in symmetrical joints, you may have rheumatoid arthritis. However, other conditions such as a very common form of arthritis called âosteoarthritisâ, or forms of arthritis such as psoriatic arthritis and gout may be present and cause similar symptoms.
Health-care providers can distinguish between forms of arthritis based on your symptoms as well as joint examination findings. However, often tests including blood tests and imaging tests need to be done to help identify if RA is present.
RA Imaging Tests
Your health-care provider may recommend certain imaging tests to check for joint damage. These tests can help determine:
- If joint symptoms are caused by inflammation that is characteristic of RA
- If your joints have been damaged in a pattern that suggests that RA is the cause
- The severity of the joint damage
However, many times imaging tests are not enough to determine if RA is present especially in early RA when there might not be much joint inflammation or damage. Thatâs where blood tests come in handy.
Recommended Reading: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause A Rash
Tender Points In Rheumatoid Arthritis How Do They Help Us
Decision making in rheumatoid arthritis is challenging. The disease is highly variable in its pattern of joint involvement, consequences of inflammation, course, and response to therapy. Pathologically, the primary disease process is synovial inflammation with resultant structural changes to joints, while clinically the patient is affected by pain and functional impairment. Since the introduction of gold compounds in 1932, the first RA disease-modifying drug, a defined set of measures has been used to determine therapeutic efficacy: evaluation of joint swelling and tenderness, laboratory studies of inflammation, and radiography. Other assessment tools have been added, including instruments to measure functional impairment, genetic markers, and more advanced joint anatomic imaging studies. With the introduction of more effective RA therapies, the standard of care is now treat to target, with the target being remission of synovitis and improvement in its clinical manifestations. While each disease assessment measure contributes to evaluating treatment response, all have limitations and must be used in concert for effective decision making.
Gowers statements remain true today. Tender points can provide important information for the evaluation and decision making in RA. Lets use them.
When Should I See A Specialist For Rheumatoid Arthritis
In general, patients with RA will benefit from seeing a specialist as early as possible. Most often the specialists treating this disease are trained in rheumatology. Their knowledge of medications to treat this disease can help patients make informed decisions consistent with their values and goals. These specialists can also help provide a balanced perspective on the benefits of treating the disease well vs. any potential side effects.
Patients diagnosed with RA are encouraged to become the captain of their multidisciplinary team of health providers. These include the primary care physician, the rheumatologist, the physical therapist, social worker, education programs and other members of the health care system will bring about a coordinated treatment program that is both safe and effective. The primary care physician or internist commonly works in partnership with a rheumatologist. Referral to a specialist in rheumatology most commonly occurs in the following situations:
- when the diagnosis is in question
- at the start of therapy, in order to provide expert input into the optimal medication and physical therapy regimen
- during the course of the illness to define response to or alteration in the treatment regimen
- in the setting of possible medication side effects
- progressive disease despite therapy
- a single joint that is leading to significant functional limitation
- the presence of fever, marked fatigue, or weight loss
- prior to orthopedic surgery
Read Also: What Can I Do For Arthritis In My Hands
Making A Diagnosis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosis of RA is not straight forward as there is no individual test for RA. A diagnosis tends to be made by a consultant rheumatologist on the basis of tests, examination and ruling out other possible causes for symptoms.
Sometimes it is clear from symptoms and initial blood tests that someone has rheumatoid arthritis, but not always. Specialist criteria have been developed jointly by American and European experts to try to help make a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis in people presenting with new-onset swollen, painful joints with no obvious cause . These should be used with care though as people with osteoarthritis or a crystal arthritis could meet the criteria and end up being incorrectly diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, which could have significant consequences for treatment. They have also been developed to classify, not diagnose, rheumatoid arthritis and so should not be used to decide who gets referred.
As already mentioned above, there are a number of other conditions that can cause very similar symptoms to rheumatoid arthritis and your GP will have to consider these when assessing each case.
Shed Your Misconceptions About Arthritis
There are many misconceptions about arthritis, Some of these can leave people feeling discouraged even before theyve begun treatment, and worse yet, some myths can even leave people feeling blamed for their disease.
It is a misconceptionand probably the biggest misconceptionthat only old people develop arthritis. Anyone at any age can be affected by arthritis. Actually, it is a little-known fact that about 300,000 children have a juvenile type of arthritis.
Some of the other misconceptions include the claim that arthritis is curable, that arthritis is caused by a bad diet , that arthritis only causes mild aches and pains and that wearing a copper bracelet relieves arthritis. It is no wonder that people newly diagnosed with arthritis dont know which way to turn.
The fact is that osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are just two of the many types of arthritis that exist, and these different forms require different treatments and are managed in different ways.
Start by learning basic facts about your type of arthritis. Find quality resources and always take questions that you may have to your healthcare provider.
Also Check: Rheumatoid Arthritis Knee Pain Relief
Why You Have Arthritis
There are over 100 different types ofarthritis that can develop as you get older or following an injury. The many types of arthritis target your joints, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness and limiting your joints flexibility.
The two most common types of arthritis that affect many adults in the United States include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
How Is Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed
Some patients still have RA but do not test positive for either anti-CCPs or RF they have seronegative RA.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
Your doctor may also conduct a synovial biopsy, which involves removing a small piece of the tissue lining one of your joints.
Read Also: Rheumatoid Arthritis Article
Also Check: How To Reduce Arthritis Swelling In Hands
Lab And Blood Tests For Ra
Here are some of the things you can expect to happen at your appointment if the doctor thinks you have RA.
Personal and family medical history: Your doctor will ask about your past and your relativesâ. If someone in your family tree has RA, you may be more likely to have the disease.
Physical exam: The doctor will check your joints for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion. RA tends to strike several joints.
Antibody blood tests: Doctors look for certain proteins that show up in your blood when you have RA. These proteins mistakenly target healthy cells and kick off the inflammation process. So a high or positive test result means inflammation is in your body.
- Rheumatoid factor : high levels
- Anti-CCP : high levels
- ANA, or antinuclear antibodies: the results are positive or negative
Not all people with RA have these proteins.
Other blood tests: Besides RF and anti-CCP, other blood tests could include:
Complete blood count: It helps your doctor find anemia , which is common in RA. It looks for four things:
- White blood cells 4.8-10.8
- Hematocrit 42-52
- Platelets 150-450
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate: This measures how fast your red blood cells clump and fall to the bottom of a glass tube within an hour. Your doctor might call it a sed rate.
Normal ranges are:
- Men younger than 50: 0-15 mm/h
- Men older than 50: 0-20 mm/h
- Women younger than 50: 0-20 mm/h
- Women older than 50: 0-30 mm/h
Rheumatoid Factor And Anti
One blood test measures levels of rheumatoid factors in the blood. Rheumatoid factors are proteins that the immune system produces when it attacks health tissue.
About half of all people with rheumatoid arthritis have high levels of rheumatoid factors in their blood when the disease starts, but about 1 in 20 people without rheumatoid arthritis also test positive.
A related blood test known as anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide test is also available. Anti-CCPs are antibodies also produced by the immune system.
People who test positive for anti-CCP are very likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis, but not everybody with rheumatoid arthritis has this antibody.
Those who test positive for both rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP may be more likely to have severe rheumatoid arthritis requiring higher levels of treatment.
Don’t Miss: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Itching
Who Should Get Testing
Patients who experience inflammation, pain, or loss of mobility in joints should discuss testing for rheumatoid arthritis with their doctor, especially if symptoms occur in multiple joints or in matching joints on both sides of the body, such as both wrists. Other symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Stiffness in the morning for 30 minutes or longer
- Fatigue
- Dry eyes and mouth
- Firm lumps beneath the skin
These symptoms are often due to something other than RA when they last less than six weeks. The longer a patient experiences symptoms, the more likely the symptoms are to be due to RA.
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in its early stages can be challenging, as patients may experience few symptoms, but early diagnosis is important because early treatment may prevent joints from worsening or at least slow the process. When symptoms are present, they often differ from person to person and mimic the symptoms of other diseases. Testing is an important part of the process of determining whether symptoms are due to RA or another condition.
After receiving a diagnosis of RA, its important for patients to continue rheumatoid arthritis testing. Testing can assist doctors in assessing the severity of RA, as well as monitoring the efficacy of treatment, tracking disease progression, and detecting potentially serious side effects of treatment drugs.
What Tests Are Done For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The diagnosis of RA is based on a person’s clinical signs and symptoms, but it is supported by laboratory tests, including X-rays and various blood tests, including but not exclusively the rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP.
If a person exhibits a clinical pattern of symptoms and signs that suggestive they have rheumatoid arthritis, a variety X-rays and blood tests will be performed. Certain blood tests can help to confirm the diagnosis, but a negative test does not necessarily mean a person does not have RA it.
Approximately half of people developing rheumatoid arthritis will have blood test results that demonstrate inflammation. These tests are called acute phase reactants. Examples of these are an erythrocyte sedimentation rate and a C-reactive protein . These tests are performed to assess the activity of the disease in combination with an assessment of the patients symptoms and physical findings.
Read Also: Pain Relief For Rheumatoid Arthritis In Hands
Ra And Your Eyes: What You Need To Know
Rheumatoid arthritis is known for joint pain, but it can also affect other parts of the body, including your eyes. Learn which rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and eye issues are most common, and how to manage them.
Most people think of rheumatoid arthritis as a joint disease, but like other autoimmune disorders, it can impact different areas of the body as well. One of the more common complications for people with rheumatoid arthritis is eye problems, which can lead to corneal damage and ultimately impact vision if left untreated.
Some common eye conditions, like the ones described below, may affect people with rheumatoid arthritis . But there are steps to take to safeguard eye health and avoid permanent damage.
Dry Eyes
RA can be associated with extra-articular manifestations, and dry eyes are one of the most common problems, says Ana-Maria Orbai, MD, instructor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore. A person with dry eyes might experience itching, a sand-like sensation in the eyes, and redness. They may also notice a lack of moisture or tears in the eyes, as well as blurred vision.
If you decide to go the over-the-counter route, avoid eye-drop products that have preservatives or vasoconstrictive agents, such as some from Visine and Clear Eyes, which often promise to relieve redness or take the red out, Orbai explains.