Questions And Information For Your Rheumatologist
Whether you are planning an initial visit to a rheumatologist for an evaluation or are going to see your long-established healthcare provider, to make the most of a visit to the doctors office, consider the following:
- Bring in a full list of the medications you are taking as well as any vitamins or supplements .
- If you are already taking medication, prepare notes about any reactions or side effects that you feel may be related to the drugs that you are taking.
- Be ready to report any physical or emotional changes that you are experiencing, whether or not they are strictly related to your inflammatory arthritis, and
- Bring in reports or copies of any blood tests or imaging tests (X-rays, ultrasounds, MRIs of joints that were done to better understand your arthritis.
- Bring a list of any questions you have about any aspect of your care.
- If it is your first visit, be ready to provide a list of all health conditions, prior surgeries and any allergies.
Some people also find it helpful to bring a loved one, friend or caregiver along on a doctors appointment, in order to have a second “set of ears” for any new information or instructions given. On occasion, close family members cannot fully understand the impact inflammatory arthritis has and it may be helpful for them to join you on a visit to your rheumatologist.
What Is Osteoarthritis Of The Hand
Hand osteoarthritis is inflammation that causes pain and stiffness in your joints. It usually happens in three places:
- The base of your thumb, where it meets your wrist
- One of the joints closest to your fingertips
- The middle joint of a finger
There’s no cure, but there are a lot of ways to protect your joints and feel better.
Without treatment, osteoarthritis gets worse over time. Itâs important to get a diagnosis and a treatment plan as soon as possible.
What Is Hand And Wrist Arthritis
Arthritis literally means âinflamed jointâ, and generally refers to any damage to the joints of the body. There are 36 joints in the hand and wrist, and several sites that are commonly affected by arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type, causing a degenerative breakdown of the joints over time. The CMC joint at the base of the thumb is commonly affected. Less common forms of arthritis include:
- Damage to the joint due to injuries
- Inflammatory arthritis
You May Like: Medical Term Arthritis
Changes In Surrounding Joints
In patients with advanced thumb base arthritis, the neighboring joints may become more mobile than normal.
Thumb extension deformity. This patient has lost mobility at the base of the thumb due to arthritis. The next joint closer to the tip of the thumb has become more mobile than normal to make up for the arthritic joint. Normally, the thumb does not come to a right angle with the rest of the hand.
What Is The Rehabilitation Following Surgery For Arthritis Of The Hand
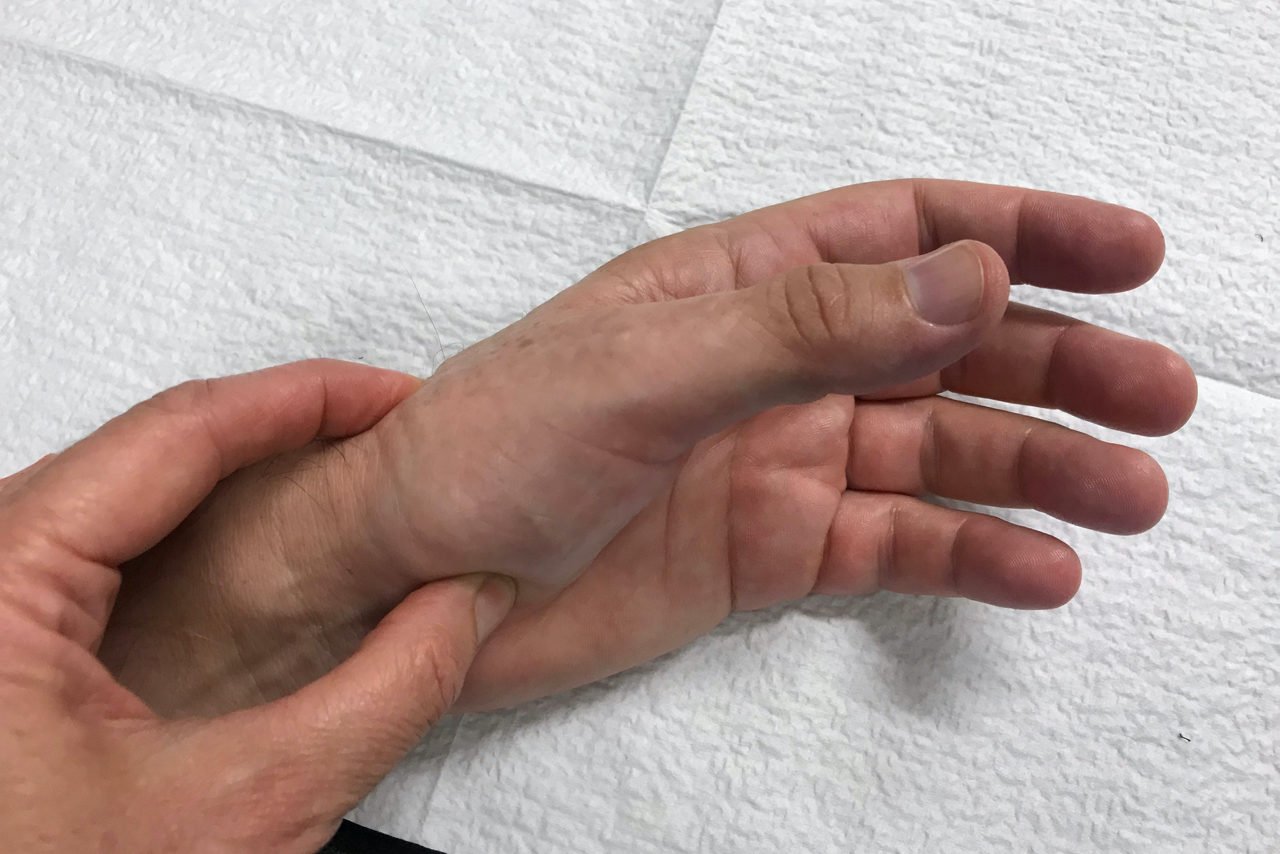
Following surgery, a rehabilitation program, often involving a physical therapist, may help to regain hand strength and movement. You may need to use a postoperative splint for a while after surgery to help protect the hand while it heals. You may need to restrict activities for a minimum of 12 weeks to let the joint reconstruction heal properly. Although recovery is slow, you should be able to resume your normal activities within a few months of surgery.
- Luke Bremner, MDOrthopaedic Surgeon
- Robert I. Gelb, MDOrthopaedic Surgeon
Specialties: Hand and Upper Extremity
- Christopher Hajnik, MDBoard Certified Orthopaedic Surgeon
Specialties: Hip and Knee
- Gregory J. Loren, MDBoard Certified Orthopaedic Surgeon
Specialties: Shoulder, Knee, and Ankle
- Ryan C. Meineke, MDOrthopaedic Surgeon
Specialties: General Orthopedics
- E. Paige Majors, DPMPodiatric Surgeon
Specialties: Foot and Ankle Surgery, Sports Injuries
- Amy L. Dusenberry, PA-CBoard Certified Physician Assistant
Specialties: Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon
Also Check: Can You Get A Rash With Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Is Thumb Arthritis Treated
The first method of treatment for thumb arthritis involves wearing a soft brace to limit the movement of your thumb, which allows the joint to rest. If the condition is more serious, a hard brace can be used, and either type can be worn overnight or intermittently throughout the day.
Other noninvasive steps include taking anti-inflammatory medications, modifying your activities, and icing the joint for 5 to 15 minutes several times a day.
If these methods do not help, the next step would be to inject a steroid medication directly into the joint. The injection may provide relief for several months and can be repeated indefinitely. Both men and women typically respond well to such conservative treatments at first, and for some, they may be all that is needed. But the treatments dont stop arthritis from progressing.
When nonsurgical approaches are no longer effective, surgery is an option. The best type of surgery for you depends on a number of factors, including the progression of the disease and how painful the symptoms are. In most cases, surgery for thumb arthritis involves removing some or part of trapezium with varying ways of stabilizing the joint.
When To See A Doctor
Hand and wrist pain often gets better with things you can do at home.
However, youll need to visit your GP surgery if:
- your pain isnt getting better after treatment at home for two weeks
- the pain is getting worse
- the pain keeps returning
- the pain is stopping you from doing your everyday activities
- your hands are stiff and swollen, particularly in the mornings and these feelings dont get better after half an hour
- as well as being swollen and stiff, your hands are warm and red
- you also feel generally unwell, especially if you have a high temperature
- you have ongoing tingling, numbness or weakness in the hands or fingers.
Its important to get urgent medical attention, if:
- you think youve broken a bone
- you have extreme pain
- any part of your hand, wrist or fingers is a funny shape or colour
- you have lost the feeling of part or all of your hand
- there was a snap, grinding or popping noise when you injured your hand or wrist
- you cant move your hand, wrist or fingers properly.
If you have ongoing hand and wrist pain or a specific condition affecting the hand and wrist it could be helpful to see a hand therapist. These are healthcare professionals with expertise in treating conditions affecting the hand and wrist. Your GP, rheumatology department or orthopaedic department could refer you to one.
Don’t Miss: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause A Rash
How Are The Hands And Wrists Structured
There are 27 small bones that make up each hand and wrist. Eight of those bones are in your wrist. Each finger has three bones, and the thumb has two. There are five bones in the palm of your hand, connecting each finger and the thumb with the wrist.
There are more than 30 muscles that control the hand and wrist. These are in your hands, wrists and forearms.
Muscles are attached to bones by tendons. These are small but very tough pieces of connective tissue. Tendons pass through a bony passage in your wrist, known as the carpal tunnel. The median nerve also passes through this tunnel.
How To Handle Possible Surgery
If mobility problems or pain from osteoarthritis becomes so severe it affects your quality of life, then surgery may be necessary. Here, the damaged cartilage in the joint is removed and the bones then fused together. Another option is joint replacement, which involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an implant. But keep in mind that surgery is not a miracle cure. “It doesn’t reverse the damage caused by osteoarthritis, and you don’t regain normal function. And with fusion, you lose all motion at that joint,” says rheumatologist Dr. Robert Shmerling, at Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
You May Like: Psoriatic Arthritis Rash On Face
Arthritis In Hands: Signs Complications And How Can You Manage It
More than likely, you know of at least one person who has arthritis. Its quite a common condition. Or even, you probably have it. Its common, yes, but not quite well understood. There are different types.
The pain you get from pain may not be frequent but it may cause reduced motion in your affected joint, some deformity and even in terms of function.
Arthritis affects almost any joint in your body but it mostly affects your hand and wrist. So, hand arthritis which is also known as rheumatoid arthritis is a disorder that affects the joints in your hands.
What Causes Thumb Arthritis
Joints are connections between two or more bones. A normal joint is made of two smooth, cartilage-covered bone surfaces that fit well together and glide when the body moves. But if the smooth surface wears outoften, just from the wear and tear that comes with agethen the bone surfaces no longer fit together and arthritis can develop.
There are many different types of arthritis, but the kind that most often affects the thumb is osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis. With osteoarthritis, the cartilage inside your joints starts to break down, causing changes in the bone that typically start slowly and worsen over time.
An injury to the thumb raises the likelihood that you will develop thumb arthritis. Other conditions, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, might also cause deterioration of the basal joint.
Recommended Reading: What Relieves Arthritis Pain
Which Joints In The Hand Are Affected
The index and middle fingers and the thumb are the parts of the hand most commonly affected. Many people find that the hand they use most is affected more than the other.
When the fingers are affected, it may be in the joints closest to the fingernails or the ones in the middle of the fingers. It’s less common to have osteoarthritis in the large knuckle joints, where the fingers meet the hand.
The joint at the base of the thumb can also be affected by osteoarthritis. And occasionally the wrist joint may be affected.
Hand Joints Are Synovial Joints
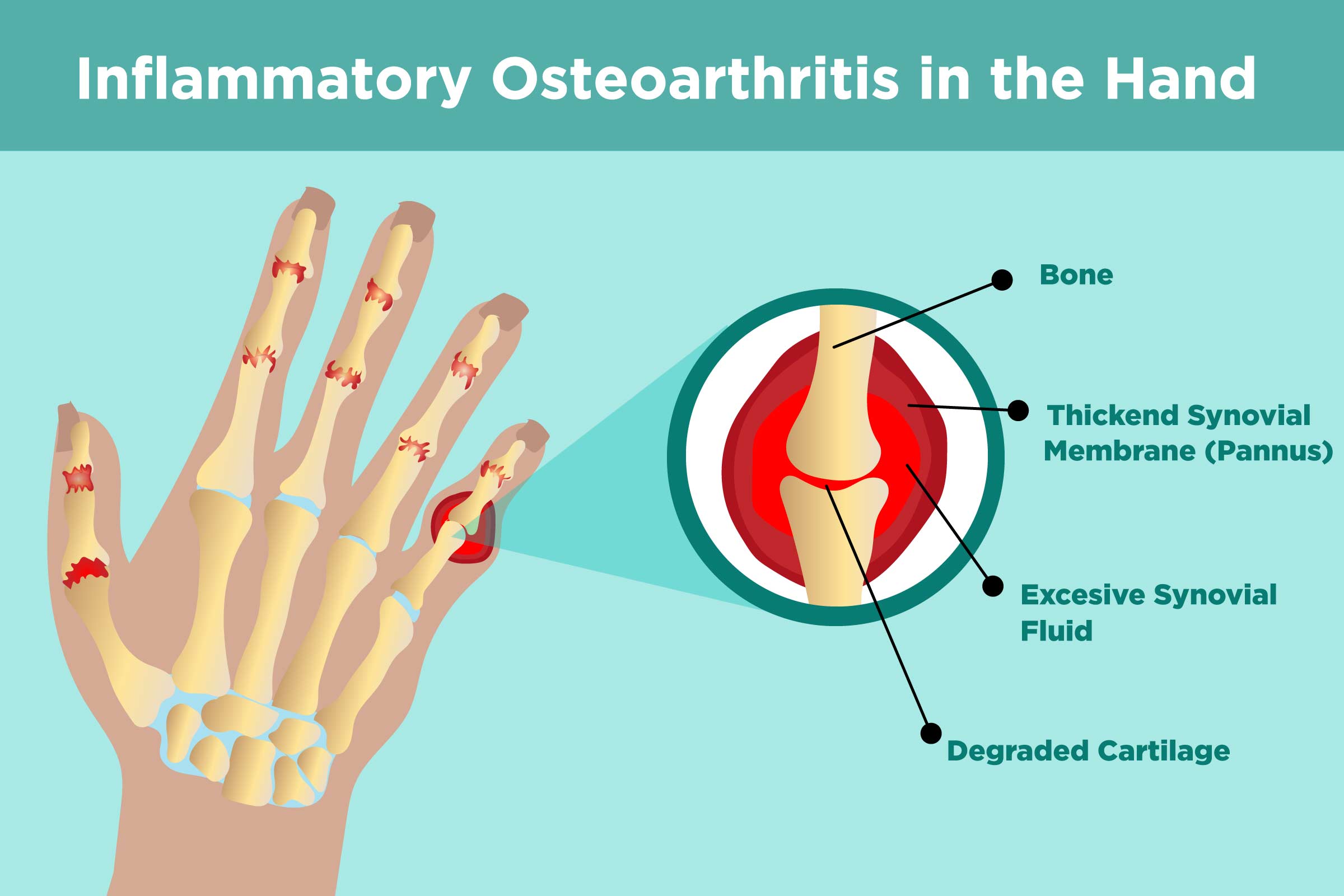
The small joints of the hands are an example of synovial joints. Rheumatoid arthritis attacks synovial joints.
- Each synovial joint is encapsulated in a pliable membrane, called a synovial membrane or synovium. When the joint is healthy, this membrane is very thinâjust one or two cells thick.
- The joint capsule contains synovial fluid. This fluid is produced by the membrane. It is thin, clear, and viscous, and it normally nourishes and lubricates the joint, enabling movement.
Synovial joints in the hand are quite small and normally contain just a tiny amount of synovial fluid.
When rheumatoid arthritis occurs, the immune system attacks a synovial jointâs delicate membrane. The affected finger, thumb, and/or wrist joints can become inflamed, swollen, and painful.
The disease process involves these 5 steps:
Read Also: What Is The Rheumatoid Arthritis Blood Test
How Is Arthritis In The Hand Treated
Treatment options depend on the type of arthritis, stage of arthritis, how many joints are affected, your age, activity level, the hand affected and other existing medical conditions.
Goals of treatment are to:
- Improve mobility and function.
- Increase your quality of life.
- In the case of rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis, to slow the progression of the disease.
Treatment options include splinting/bracing, medications, injections, non-drug approaches and surgery.
Splinting/braces
Splits or braces support and protect the affected joint, reduce deformity, provide joint stability, lessen strain, and promote proper joint alignment. Your healthcare provider, occupational therapist or hand therapist will discuss splinting/bracing options, how and when to wear them and how long to wear them .
Medications
Steroid injections
Steroids reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Steroids are usually used if medications dont control inflammation or if the inflammation is limited to a few joints. Injections are administered directly into the affected joint. Because steroids can weaken tendons and ligaments, injections are repeated only a few times.
Other management strategies
A complete treatment plan for arthritis of the hand includes these additional approaches:
Surgery
If nonsurgical treatments no longer provide relief and the cartilage at the ends of your bones has worn away, surgery may be an option. There are several approaches:
Hand Joints Most Affected By Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are 27 joints4 in a hand. The joints most likely to show signs of RA are:
- The metacarpophalangeal joints, or large knuckles, where the fingers and thumb meet the hand
- The proximal interphalangeal joints, or middle knuckles
- The joints of the wrist that connect the wristâs eight carpal bones with each other and the bones of the forearm , including the carpometacarpal joint, midcarpal joint, radiocarpal joint, and intercarpal joints
The distal interphalangeal joints, the joints closest to the tips of the fingers and thumb, are less likely to be affected by rheumatoid arthritis. When DIP joints are affected, it is typically only after symptoms appear in the MCP or PIP joints. It is more common for DIP joints to be affected by osteoarthritis than by RA.
See Recognizing Osteoarthritis in the Hand
Recommended Reading: Ra In Hand Symptoms
About Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Hand
Rheumatoid arthritis affects the cells that line and normally lubricate the joints . This is a systemic condition , which means that it may affect multiple joints, usually on both sides of the body. The joint lining becomes inflamed and swollen and erodes the cartilage and bone. The swollen tissue may also stretch the surrounding ligaments, which are the connective tissues that hold the bones together, resulting in deformity and instability. The inflammation may also spread to the tendons, which are the rope-like structures that link muscles to bones. This can result in stretching out of and ruptures of the tendons. Rheumatoid arthritis of the hand is most common in the wrist and the finger knuckles .
Risks Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a condition that can lead to joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of function. This debilitating autoimmune disease affects the entire body, but it can also have serious effects on other parts of your health. Risks associated with Rheumatoid arthritis range from minor inconveniences to life-threatening complications.
Recommended Reading: The Symptoms Of Arthritis
Ial Rotator Cuff Tears
As the rotator cuff continues to age or degenerates, a portion of the rotator cuff might separate from the bone that it is normally attached to. This is usually part of the natural progression of tendinosis.
If enough of the rotator cuff starts to separate then we have a small cleft or defect in the rotator cuff attachment. We call that a partial tear. Partial tears are not large enough to cause weakness of the shoulder. However, if you have a painful partial tear, you can have pain on top or on the side of the shoulder. In addition, you may find it very painful when trying to lift the arm overhead.
Some partial tears hurt, while others do not. Determining if your partial tear is painful is usually possible with a physical exam. Most people with partial tears of the rotator cuff are going to respond to physical therapy. If physical therapy and other non-surgical treatments do not improve your pain, then surgery to place a unique biological patch has a high likelihood of alleviating your night pain and pain with lifting your arm. See this post for more information about the patch and how it works.
Home Remedies And Self Care
Some home remedies can help you to prevent and relieve hand and nail symptoms of PsA.
For relieving hand and finger joint pain, try:
- Applying ice to hand joints for ten minutes at a time as needed to reduce pain and swelling
- Massaging affected areas
- Wearing hand splints to support and protect wrist, hand and finger joints
- Taking breaks from writing and typing
- Performing hand exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles and joints of the hand and fingers
For managing nail symptoms:
- Treat nail fungus infections with antifungal creams
- Avoid fake nails as they can injure nail beds
- Trim cuticles, and avoid pulling at the cuticles to avoid injuries and flares
- Keep fingernails trimmed and clean to prevent injuries
- Wear gloves when doing household chores or gardening
- Use clear nail polish in order to notice nail changes quickly
- Dont use nail polish if you have an active nail infection
Read Also: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Itching
Treatment Goals: Manage Pain And Improve Function
Osteoarthritis treatment plans often include exercise, rest and joint care, pain relief, weight control, medicines, surgery, and complementary treatment approaches. Current treatments for osteoarthritis can relieve symptoms such as pain and disability, but there are no treatments that can cure the condition.
Although health care professionals can prescribe or recommend treatments to help you manage your arthritis, the real key to living well with the disease is you. Research shows that people with osteoarthritis who take part in their own care report less pain and make fewer doctor visits. They also enjoy a better quality of life.
Arthritis Of The Hand And Wrist
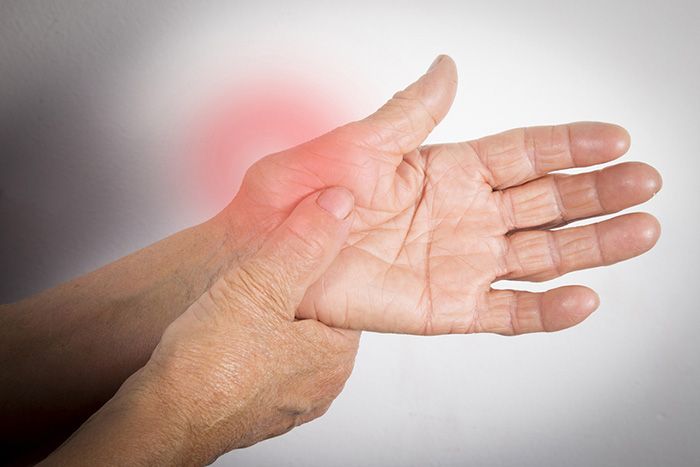
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of joints. There are several types of arthritis and the most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis. Arthritis affects various joints in the body and the arthritis in hand affects the joint at the base of the thumb. Arthritis may also affect the joints of other digits and the symptoms include swelling, pain, stiffness, and malformation all of which interfere with use of the hand.
Don’t Miss: How To Help Arthritis Pain In Hands