Arthritis Pain Or Muscle Pain: How To Tell The Difference
As a Good Samaritan, you helped your neighbour who was moving his couch up to the third floor. The result: your back is throbbing with pain.
Most active people sometimes come up against a few obstacles that can temporarily affect their ability to move and require taking pain medication. A wrong move, a fall or an injury are a few events that can be a source of muscle pain or inflammation. When these events occur, it seems a lot of us line up to read the dizzying selection of product packages on display in the analgesics and anti-inflammatory section at the pharmacy. Faced with such a wide choice of products, it is normal to get confused, especially when we are not exactly certain just what kind of pain is bothering us.
Risk Factors For Arthritis
Certain risk factors have been associated with arthritis. Some of these are modifiable while others are not.
Non-modifiable arthritis risk factors:
- Age: the risk of developing most types of arthritis increases with age.
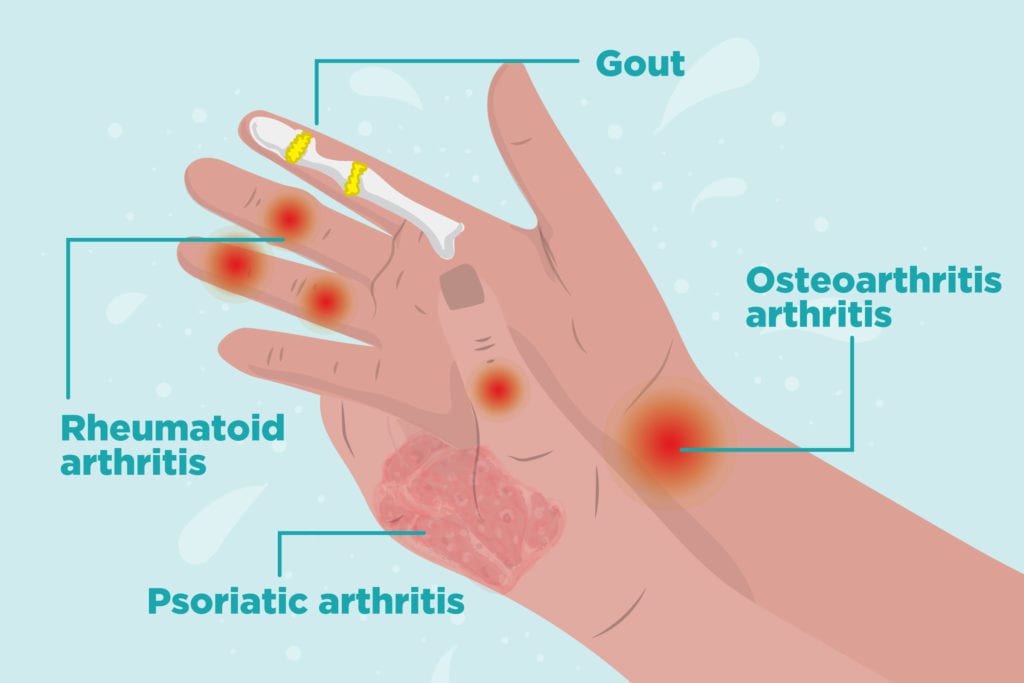
- Sex: most types of arthritis are more common in females, and 60 percent of all people with arthritis are female. Gout is more common in males than females.
- Genetic factors: specific genes are associated with a higher risk of certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis , systemic lupus erythematosus and ankylosing spondylitis.
Modifiable arthritis risk factors:
- Overweight and obesity: excess weight can contribute to both the onset and progression of knee osteoarthritis.
- Joint injuries: damage to a joint can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis in that joint.
- Infection: many microbial agents can infect joints and trigger the development of various forms of arthritis.
- Occupation: certain occupations that involve repetitive knee bending and squatting are associated with osteoarthritis of the knee.
Comorbidities
More than half of adults in the U.S. with arthritis report high blood pressure. High blood pressure is associated with heart disease, the most common comorbidity among adults with arthritis.
Around 1 in 5 of adults in the U.S. who have arthritis are smokers. Smoking is associated with chronic respiratory conditions, the second most common comorbidity among adults with arthritis.
Causes Of Morning Stiffness From Arthritis
Feeling stiff when you first wake up in the morning is a common problem associated with arthritis. Morning stiffness causes you to hurt all over as you get out of bed. As you take your first steps, your joints and muscles ache so much, you want to crawl right back into bed. In fact, morning stiffness can be the most severe pain you feel all day and it can impair or interfere with your ability to function and perform routine tasks and activities of daily living.
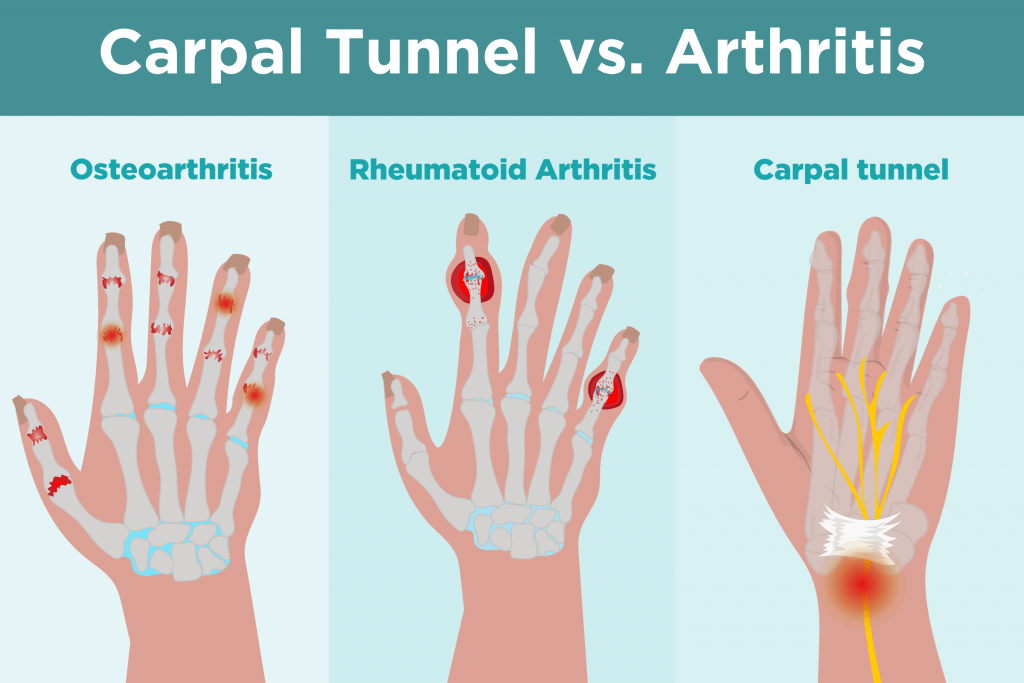
Paying attention to the duration of your morning stiffness will help both you and your healthcare provider decide how to deal with it. Morning stiffness that lasts more than an hour and in some cases up to several hours is characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis or other inflammatory types of arthritis. Morning stiffness that is less prolonged is more likely to be osteoarthritis or another non-inflammatory, musculoskeletal condition. In spite of having a regular treatment regimen, morning stiffness is a persistent problem for many people with arthritis.
Recommended Reading: Ways To Help Arthritis In Hands
What Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain And Discomfort Feels Like
Rheumatoid arthritis can be like the old box of chocolates adage you never know what youre going to get, according to the blogger Katie Singh, 38, of Austin, Texas. Singh was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis when she 23 years old. Sometimes it feels like burning, other times it feels like throbbing throbbing so bad that you can’t think about anything else, Singh explains. There are times I’ve almost considered wanting to cut off a foot or a hand, the pain is so excruciating.
RELATED: Celebrities With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis With Involvement Of The Connective Tissues
Connective tissues include tendons, ligaments and cartilages. When someone suffers from arthritis, it is possible that the inflammatory process extends and affects the connective tissues as well.
In such situations, the leg pain becomes more severe and the overall functionality is severely reduced.
As opposed to other types of arthritis, this type is progressive the inflammation becomes worse with the passing of time and it can affect not only the connective tissues and joints but also the muscles, skin and vital organs, such as the lungs and the kidneys.
Examples of such medical conditions include systemic sclerosis, SLE and dermatomyositis.
Recommended Reading: What Relieves Arthritis Pain In The Hands
Why Is Osteoarthritis So Painful & How Bad Can It Get
Osteoarthritis is a common type of arthritis and it affects millions of people across the world. The problem mainly takes place whenever the protective cartilage wears down with time, where cartilage is responsible to provide cushions to your bones ends. Osteoarthritis damages almost every joint but the disorder mainly affects your spine, hips, hands, and knees.
Even though damages caused to the joints are irreversible, symptoms related to osteoarthritis are easily manageable. You should stay active, maintain a healthy weight and follow a few of the essential treatment procedures to slow the progression of osteoarthritis and to improve the joint function as well as related pain.
Osteoarthritis Of The Hip
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. The ball is the top of your thigh bone, and it sits in a socket thats formed by part of your pelvic bone. Slippery tissue called cartilage covers the bone surface and helps cushion the joint. Osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage gradually wears down, which over time leads to pain and stiffness. The most common symptom of hip osteoarthritis is pain around the hip joint. As hip OA disease progresses, low-grade inflammation can set in, explains physical therapist Colleen Louw, PT, spokesperson for the American Physical Therapy Association . That results in increased sensitivity of the surrounding nerves, which can cause pain in and around the low back and buttocks.
You May Like: Elevated Rheumatoid Levels
When To See A Healthcare Provider
New joint pain is a reason to see your healthcare provider. If you have a pain condition but are experiencing pain in a new area or a markedly different type of pain, be sure to get an appointment.
Many people with one pain condition go on to develop another. For example, it’s common for someone with rheumatoid arthritis or lupus to eventually develop secondary fibromyalgia.
Seek urgent medical attention if your joint pain is severe or you have any of the following additional symptoms:
- Fever
- Hot or significantly swollen joint
- Sudden numbness or burning and/or muscle weakness
What Blocks Pain Signals
Many scientists think pain control methods help reduce pain by blocking pain signals. Pain signals are sent through a complex system of nerves in the brain and spinal cord.
There are many things that can block these signals and thus prevent the pain message from reaching your brain.
Pain signals are blocked by chemicals made by the brain called endorphins. There are several things that can cause the brain to produce endorphins. These include “natural” controls, such as your own thoughts and emotions, or “outside” controls such as medicines.
Natural controls
A father driving with his children is hurt in a car accident. The father is so worried about his children that he doesn’t feel the pain from his own broken arm. The concern for his children somehow blocked the pain signal and kept the pain from affecting him.
Outside controls
Certain medicines such as morphine imitate the body’s endorphins and block the pain signal. Other pain control methods, such as heat and cold treatments, physical therapy, exercise, relaxation and massage can stimulate the body to release its own endorphins or to block the pain signal in other ways.
Recommended Reading: Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Reversible
Evidence Of Central Pain Processing From Neuroimaging Studies
Schematic diagram of central pain-processing pathways implicated in OA pain processing.
Recent work by Baliki et al. has reported that painful mechanical knee stimulation in OA was associated with bilateral activity in the thalamus, secondary somatosensory, insular and cingulate cortices, with unilateral activity in the putamen and amygdala. These data suggest that painful stimulation in subjects with OA of the knee engages with many brain regions commonly observed in acute pain. Local treatment of the knee with lignocaine resulted in reduction of brain activity detected on fMRI in the regions described previously, suggesting that central activation of the brain mediates pain during OA. Such results also help to disentangle pain responses from anxiety or other emotional, non-painful responses. In the same study, patients who had spontaneous back pain in a cohort of patients with low back pain showed activity by fMRI in the medial prefrontal cortex, with reduced brain activation after treatment with lignocaine . The regions activated in these studies of OA subjects show patterns in brain regions similar to those in touch-evoked pain and acute pain .
What Is The Pain Of Arthritis Like
In general, the first sign of arthritis is pain, also called arthralgia. This can feel like a dull ache or a burning sensation. Often, pain starts after you’ve used the joint a lot, for example, if you’ve been gardening or if you just walked up a flight of stairs. Some people feel soreness first thing in the morning.
Read Also: How To Deal With Arthritis
Other Causes Of Joint Pain
There are many causes of joint pain other than arthritis, Dr. Cotter says, such as injury and overuse, bursitis and tendinitis .
Joint pain can also result from abnormal pain processing, which occurs in conditions such as fibromyalgia.
Because joint pain and swelling can have many different causes, she stresses that obtaining the correct diagnosis is the most important part. You have to learn the cause of the joint pain and swelling in order to treat it correctly. Treatment options can vary widely, so it’s important that you don’t try to fix your joint pain or swelling on your own.
How Fast Does Arthritis Spread

Generally, radiological lesions gradually and slowly increase. However, the pace of this progression can be very variable. In extreme cases, some cases of osteoarthritis may remain stable for decades, while others progress very rapidly to complete destruction of the cartilage in the space of a few months.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Severe Arthritis
How Bad Can Osteoarthritis Get
Osteoarthritis makes your joint cartilage stiff and in turn, forces it to lose elasticity and makes it highly susceptible to cause damage. With time, the cartilage wears away in various areas to reduce the ability to work as a shock absorber.
Wearing of cartilage causes stretching of ligaments and tendons and thereby, causes pain. If your pain becomes worse or condition becomes worse, the bones rub against one another to cause elevated levels of pain combined with the loss of your physical movement.
Other than cartilage breakdown, osteoarthritis may affect the bone joints completely. It mainly leads to changes in various bones followed by deterioration of connective tissues responsible to hold your joints together, while attaching muscles and bones. The problem also causes joint lining inflammation to make the entire situation worse.
But besides the breakdown of cartilage, osteoarthritis affects the entire joint. It causes changes in the bone and deterioration of the connective tissues that hold the joint together and attach muscle to bone. It also causes inflammation of the joint lining.
Arthritis With Involvement Of The Soft Tissues
It can happen that the inflammatory process present in the joints of the leg extends to the soft tissues, aggravating the present symptomatology .
When this happens, the whole dynamics of the leg is affected and the patient is prevented from engaging in daily living activities.
*All individuals are unique. Your results can and will vary.
This type of arthritis is common in those who have overused their joints for example, professional athletes, runners, joggers. Physical injuries can trigger the appearance of this form of arthritis as well.
The inflammatory process can stem from the soft tissues as well, affecting the joints as consequence. In making the diagnosis of arthritis, it is important to diagnose the root of the problem and treat it accordingly.
If the leg pain is severe, involving a large surface and being resistant to medication, the condition one is suffering from might be fibromyalgia.
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Rheumatoid Arthritis In Hands
How To Manage Arthritic Pain Naturally
There are many treatment options available for people with arthritis. Alongside physician-led treatments, there are plenty of self-care remedies to help minimize chronic pain symptoms.
Biowave offers chronic pain patients a natural form of pain relief. Talk to us to learn more about how electrical stimulation could help reduce your chronic arthritic pain symptoms.
Leg Pain: Arthritis Or Peripheral Artery Disease
If you suffer from leg pain while walking, you may blame arthritis. But if the problem is peripheral artery disease , it can have serious consequences.
When fatty deposits–called plaque–accumulate in your bodys arteries, the condition is called atherosclerosis. In PAD, these fatty deposits build up in the arteries that carry blood to your legs.
Untreated, PAD can lead to gangrene and even leg amputation. Its also a warning sign that arteries in the heart and brain may be blocked, increasing your chances for heart attack and stroke.
Signs of PAD
PAD starts slowly and may go unnoticed. Discomfort can occur in the affected legs, thighs, calves, hips, buttocks, or feet. In addition to pain, other common sensations are heaviness, numbness, or aching in the leg muscles. Rest usually helps. Other symptoms include:
- Pale or bluish skin
- Lack of leg hair or toenail growth
- Sores on toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly or not at all
See your health care provider if you have any of these symptoms. PAD can be diagnosed with a simple test that measures blood flow by comparing blood pressure in your arms and legs.
Arthritis Affects Joints
Because PAD is such a serious and progressive disease, its important to know the difference between arthritis pain and symptoms that indicate blocked blood flow.
If joint pain lasts beyond three days, see a health care provider. Also get medical attention for:
Recommended Reading: Best Remedy For Arthritis In Fingers
Osteoarthritis Of The Spine
The bones in your spine are separated by spongy discs, which act as shock absorbers. With age, these discs can wear or shrink, which narrows the space between the spinal joints, or facet joints. The facet joints are a series of small joints in the lower back that contain the same type of cartilage that is found in your knees, explains Louw. Disc changes can lead to more strain on the joints, which can cause the cartilage to wear down and the facet joints in the vertebrae to rub against one another, leading to the pain and stiffness of OA. It is not uncommon for these joints to refer pain into the buttocks, especially with prolonged standing or even walking, says Louw.
Causes Of Fatigue In Arthritis
Inflammation, pain, inactivity and lifestyle factors can cause extreme tiredness when living with arthritis.
Everyone gets worn out from time to time. But exhaustion that disrupts your daily life and doesnt get better after a good nights sleep has its own medical term: fatigue. Fatigue significantly affects the quality of life for people with many forms of arthritis-related diseases, includingrheumatoid arthritis,psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthritis, lupus, fibromyalgia andosteoarthritis. Your lack of energy may be caused by your inflammatory disease and other health conditions you have, as well asmedications side effectsand lifestyle habits.
You May Like: Ra Leg Pain
When Should I See My Doctor
Joints get sore and swollen for many reasons. It could be due to an injury, overuse, or doing a new type of physical activity.
See your doctor if you have pain and stiffness that starts with no clear reason, lasts for more than a few days, and also causes swelling, redness and warmth. It is important to start treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from getting worse and causing long-term damage.
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Muscle Pain
To work properly, your joints require muscles. Together, they are essential elements to support your movement. Rheumatoid arthritis or RA can affect the muscles in the involved joints, causing muscle pain. The bad news, the pain could be widespread.
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms how do they progress?
Typically, the symptoms of this autoimmune disorder of arthritis develop gradually. The occurrence can take several weeks until you notice the first symptom.
It usually starts with stiffness in one joint such as wrists, soles of feet, or hands particularly in the morning and will improve by mid-day. This symptom may be vague for a while or may come & go at first, but it will become a regular occurrence as the disease gets worse. It will be followed with other classic symptoms of joint problem such as pain and swelling. Then other joints such as knees, elbows, or ankles could be affected, too.
Another interesting fact, the symptoms of RA tend to affect the joint symmetrically. For instance, once you have it in the left wrist, you are more likely to also have it in your right wrist. See also the differences between RA and OA in this section!
However in a few cases, the occurrence of the symptoms could be slightly different, these include:
And each case can be unique and different. Sometimes RA is off for several months or even years, but in a few cases it can be constantly progressive.
Don’t Miss: Rashes And Rheumatoid Arthritis