How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated
Joint damage generally occurs within the first two years of diagnosis, so its important to see your provider if you notice symptoms. Treating rheumatoid arthritis in this window of opportunity can help prevent long-term consequences.
Treatments for rheumatoid arthritis include lifestyle changes, therapies, medicine and surgery. Your provider considers your age, health, medical history and how bad your symptoms are when deciding on a treatment.
Pathogenesis Of Ra And Psa
A combination of genetic factors and environmental triggers is thought to elicit autoimmune inflammatory responses in both RA and PsA. The pathogenesis of RA and PsA is not completely understood. In addition to the known association with human leucocyte antigen -DR4 in RA, one theory is the development of lung inflammation, typically prior to joint symptoms, with production of antibodies to citrullinated protein antigens that mediate pathogenesis. Gut dysbiosis has been linked with the pathogenesis of PsA. While there is some overlap in the development of inflammation in PsA and RA, some important differences are evident. For example, in both PsA and RA, HLA alleles have been shown to affect disease susceptibility and severity however, the primary genotypes associated with each disease are different. In PsA, HLA-B27 is associated with the development of enthesitis and symmetric sacroiliitis, and HLA-B08 is associated with joint fusion, asymmetric sacroiliitis and dactylitis. In RA, HLA-DRB1 alleles are associated with disease susceptibility and severity in patients who have positive findings for rheumatoid factor and cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies.
Pathogenesisof PsA and RA. Reprinted from Coates et al and Perera et al. IFN, interferon IL, interleukin MHC, major histocompatibility complex PsA, psoriatic arthritis Pso, psoriasis RA, rheumatoid arthritis TCR, T cell receptor TGF-, transforming growth factor- Th, T helper TNF-, tumour necrosis factor-.
Heart And Blood Vessels
People with RA are more prone to atherosclerosis, and risk of myocardial infarction and stroke is markedly increased.Other possible complications that may arise include: pericarditis, endocarditis, left ventricular failure, valvulitis and fibrosis. Many people with RA do not experience the same chest pain that others feel when they have angina or myocardial infarction. To reduce cardiovascular risk, it is crucial to maintain optimal control of the inflammation caused by RA , and to use exercise and medications appropriately to reduce other cardiovascular risk factors such as blood lipids and blood pressure. Doctors who treat people with RA should be sensitive to cardiovascular risk when prescribing anti-inflammatory medications, and may want to consider prescribing routine use of low doses of aspirin if the gastrointestinal effects are tolerable.
You May Like: Can You Work With Rheumatoid Arthritis
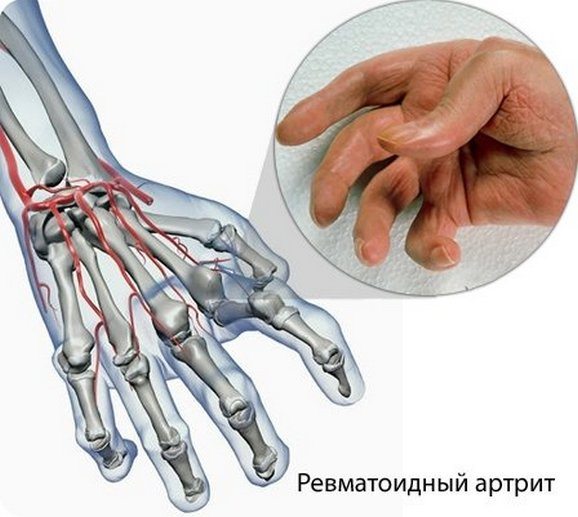
Early Signs Of Arthritis In Hands
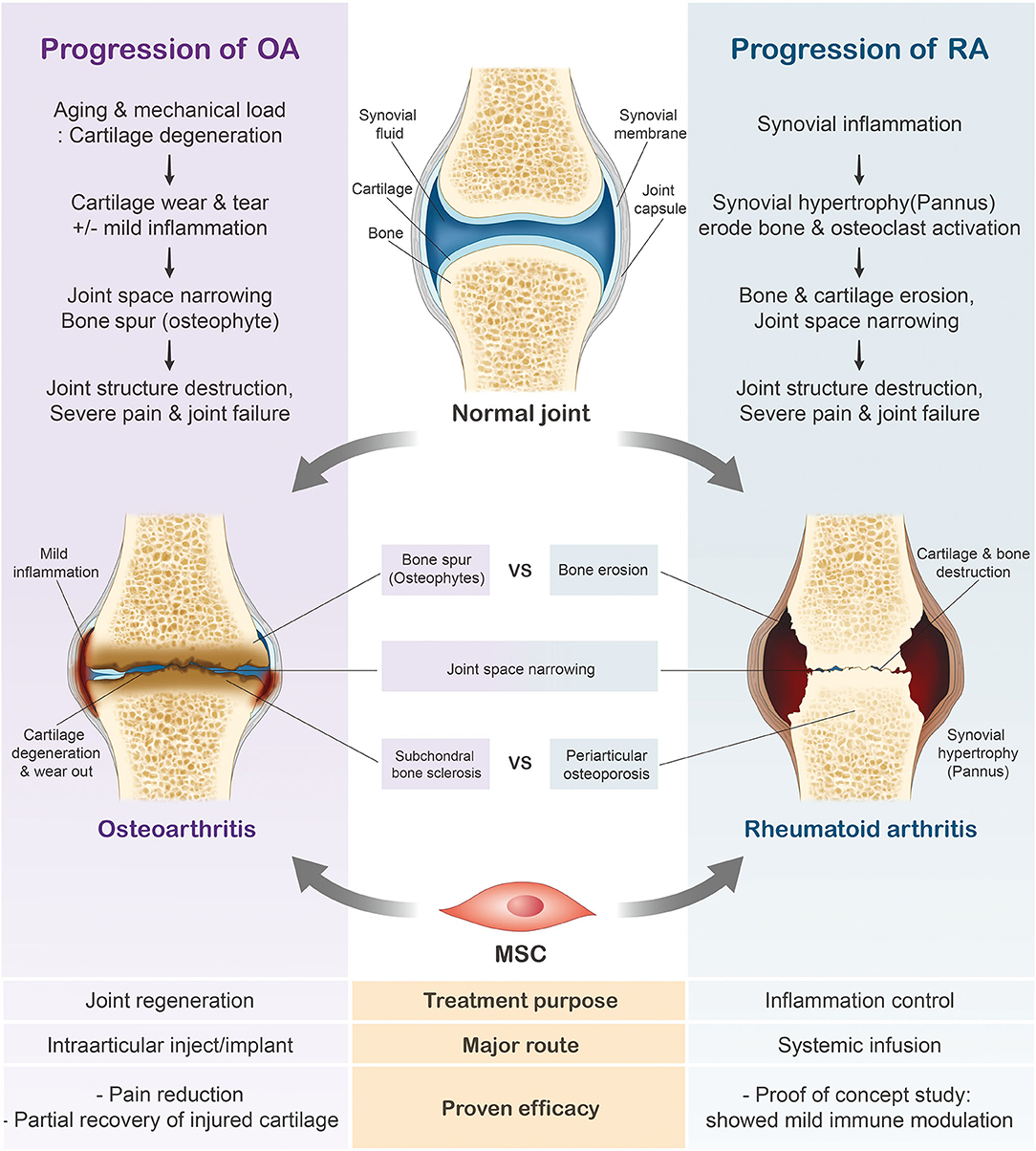
A joint is the area where two bones meet. Within joints is a tissue called cartilage that acts as a cushion between two bony surfaces. Synovial fluid within joints protects them and helps facilitate movement. Synovial fluid is secreted by the inner lining of the joint called the synovial membrane. Hand arthritis occurs when there is inflammation in one or more joints of the hand and wrist. There are over 100 types of arthritis. A few of the common types of arthritis that affect the hands are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis , psoriatic arthritis and gout. The two most common types of arthritis that affect the hands are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Hand osteoarthritis occurs when there is wear and tear of one or more joints of the hand as seen with increasing age. Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the bodys immune system attacks the joints of the hand.
Comorbidities Occurring In Ra And Psa
Differences in patient comorbidities may help clinicians differentiate between RA and PsA . Overall, comorbidity burden may be higher in RA than in PsA, but both diseases are similarly associated with increased risk for comorbidities linked to systemic inflammation . Han and colleagues found that patients with RA and PsA had similarly increased prevalence ratios of ischaemic heart disease, atherosclerosis, peripheral vascular disease, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, hyperlipidaemia and hypertension compared with healthy controls. However, registry data suggest that the rates of obesity, diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome are significantly higher in patients with PsA compared with those with RA. Notably, most patients with PsA are overweight or obese. Cardiometabolic comorbidities of PsA are associated with higher levels of systemic inflammation and increased disease severity. In addition, psoriatic skin lesions are associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease and mortality. Of interest, PsA is an independent predictor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with psoriasis, while in patients with RA, the rates of NAFLD are similar to those observed in the general population.
Summary of differences in common comorbidities associated with PsA and RA
Don’t Miss: What To Eat For Arthritis In Hands
What Are The Early Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early signs of rheumatoid arthritis include tenderness or pain in small joints like those in your fingers or toes. Or you might notice pain in a larger joint like your knee or shoulder. These early signs of RA are like an alarm clock set to vibrate. It might not always been enough to get your attention. But the early signs are important because the sooner youre diagnosed with RA, the sooner your treatment can begin. And prompt treatment may mean you are less likely to have permanent, painful joint damage.
Epidemiology Pathophysiology And Diagnosis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Synopsis
Allan Gibofsky, MD, JD, FACP, FCLMSupplements and Featured Publications
Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the more common autoimmune disorders, affecting approximately 1% of the population worldwide. The exact cause of RA is not known however, initiation of disease seems to result from an interaction among genetic susceptibility, environmental triggers, and chance. RA is characterized by dysregulated inflammatory processes in the synovium of the joint that eventually leads to the destruction of both cartilaginous and bony elements of the joint, with resulting pain and disability. Systemic inflammation associated with RA is associated with a variety of extra-articular comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, resulting in increased mortality in patients with RA. RA is also associated with several psychosocial disorders. Classification criteria for RA that were promulgated jointly by the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism in 2010 emphasize early detection of RA so that effective management can be initiated before pathological changes become irreversible.
The pain, fatigue, and disability associated with RA result in a significant reduction in health-related quality of life.4 Additionally, RA imposes a substantial economic burden upon patients, due to both increased cost of medical care and loss or reduction of employment, frequently during peak working years.5,6
Epidemiology
Pathophysiology
Assessment of Disease Activity
Read Also: Does Magnetic Therapy Work For Arthritis
Drugs For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The goal is to reduce inflammation as a means of preventing erosions, progressive deformity, and loss of joint function. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are used early, often in combination. Other drug classes, including biologic agents such as tumor necrosis factor -alpha antagonists, an interleukin -1 receptor inhibitor, IL-6 blockers, B-cell depleters, T-cell costimulatory molecule modulators, and Janus kinase inhibitors, seem to slow the progression of RA. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are of some help for the pain of RA but do not prevent erosions or disease progression, may increase cardiovascular risk, and thus should be used only as adjunctive therapy. Low-dose systemic corticosteroids may be added to control severe polyarticular symptoms, usually with the objective of replacement with a DMARD. Intra-articular depot corticosteroids can control severe monarticular or even oligoarticular symptoms but with chronic use may have adverse metabolic effects, even in low doses.
The optimal combinations of drugs are not yet clear. However, some data suggest that certain combinations of drugs from different classes are more effective than using DMARDs alone sequentially or in combination with other DMARDs. In general, biologic agents are not given in combination with each other due to increased frequency of infections. An example of initial therapy is
What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis affects everyone differently. In some people, joint symptoms develop over several years. In other people, rheumatoid arthritis symptoms progress rapidly. Many people have time with symptoms and then time with no symptoms .
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Pain, swelling, stiffness and tenderness in more than one joint.
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods.
- Pain and stiffness in the same joints on both sides of your body.
Read Also: How To Help Relieve Arthritis Pain In Dogs
What Are The Four Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stage 1: In early stage rheumatoid arthritis, the tissue around your joint is inflamed. You may have some pain and stiffness. If your provider ordered X-rays, they wouldnt see destructive changes in your bones.
- Stage 2: The inflammation has begun to damage the cartilage in your joints. You might notice stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
- Stage 3: The inflammation is so severe that it damages your bones. Youll have more pain, stiffness and even less range of motion than in stage 2, and you may start to see physical changes.
- Stage 4: In this stage, the inflammation stops but your joints keep getting worse. Youll have severe pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of mobility.
How Is Ra Diagnosed
RA is diagnosed by reviewing symptoms, conducting a physical examination, and doing X-rays and lab tests. Its best to diagnose RA earlywithin 6 months of the onset of symptomsso that people with the disease can begin treatment to slow or stop disease progression . Diagnosis and effective treatments, particularly treatment to suppress or control inflammation, can help reduce the damaging effects of RA.
Read Also: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Hives
What Are The Risk Factors For Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are several risk factors for developing rheumatoid arthritis. These include:
- Family history: Youre more likely to develop RA if you have a close relative who also has it.
- Sex: Women and people designated female at birth are two to three times more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
- Smoking:Smoking increases a persons risk of rheumatoid arthritis and makes the disease worse.
- Obesity: Your chances of developing RA are higher if you have obesity.
Can I Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis
Researchers are looking at ways to prevent RA, but there are currently no specific ways to do this. They have been able to delay, but not prevent, the onset of RA. Currently, smoking is the only lifestyle factor that appears to have a strong link with RA, so quitting smoking may be able to reduce the risk.
You May Like: Does Omega 3 Help Rheumatoid Arthritis
Serological Features Of Ra And Psa
RA is a seropositive arthropathy, with approximately 80% of patients having a positive test result for RF or CCP antibodies. CCP antibodies are a more specific marker for RA than RF, but both biomarkers are considered to be distinct and complementary predictors of disability and joint erosion.
In contrast, PsA is a seronegative inflammatory arthropathy. RF and CCP are absent in most patients with PsA, and if patients do have positive test findings for RF or CCP, the titres are usually low. In a study comparing patients with RA or PsA and controls, the mean RF and anti-CCP titre values were substantially higher in patients with RA compared with PsA . Titres in patients with PsA were similar to values in controls. Although the presence of serum RF or CCP antibodies is generally not used to exclude diagnosis of non-rheumatic diseases , data suggest that at anti-CCP titre values 11.6 U/mL, it is highly probable that patients have RA rather than PsA. In both patients with RA and PsA, the presence of anti-CCP antibodies is associated with bone destruction, suggesting that the osteocatabolic effect of anti-CCP antibodies is not found only in RA as previously thought.
Increased ESR and CRP levels are markers of inflammation, but not necessarily just in RA. Other rheumatological diseases associated with elevated ESR and CRP levels include polymyalgia rheumatica, Sjögrens syndrome and ankylosing spondylitis.
Medications To Manage Symptoms
Some drugs can help relieve symptoms and slow the diseases progression.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are available from pharmacies over the counter . Examples include Motrin, Advil, and Aleve. Long-term use and high doses can lead to side effects, including:
- high blood pressure
- kidney and liver problems
Corticosteroids reduce pain and inflammation and may help slow joint damage, but they cannot cure RA. If NSAIDs do not work, a doctor may inject a steroid into the joint. Relief is usually rapid, but the effect is variable. It can last a few weeks or months, depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Corticosteroids can help with acute symptoms or short-term flare-ups. However, a doctor will limit these injections to no more than three times per year because of their impact on the soft tissue structures around the joints. More frequent injections can potentially damage these structures or cause them to tear off from where they attach to bone.
Learn more about steroid injections here.
Also Check: What Is Arthritis Of The Spine
What Are The Goals Of Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
The most important goal of treating rheumatoid arthritis is to reduce joint pain and swelling. Doing so should help maintain or improve joint function. The long-term goal of treatment is to slow or stop joint damage. Controlling joint inflammation reduces your pain and improves your quality of life.
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Go Away
No, rheumatoid arthritis doesnt go away. Its a condition youll have for the rest of your life. But you may have periods where you dont notice symptoms. These times of feeling better may come and go.
That said, the damage RA causes in your joints is here to stay. If you dont see a provider for RA treatment, the disease can cause permanent damage to your cartilage and, eventually, your joints. RA can also harm organs like your lung and heart.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have rheumatoid arthritis, you may feel like youre on a lifelong roller coaster of pain and fatigue. Its important to share these feelings and your symptoms with your healthcare provider. Along with X-rays and blood tests, what you say about your quality of life will help inform your treatment. Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms and recommend the right treatment plan for your needs. Most people can manage rheumatoid arthritis and still do the activities they care about.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/18/2022.
References
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Arthritis In The Thumb
Characteristics Of The Population
A group of 50 men and a control group of 50 women were randomly chosen. Only patients over 18 years of age were included. Patients with other connective tissue diseases and those who did not wish to participate in the study were excluded. After informed consent was obtained, information was collected about demographic data, habits, clinical manifestations, comorbidities, treatment, painful and swollen joint count, visual analogue scale for pain , and physician assessment. Alcohol consumption was defined as consuming 15 drinks or more per week in men and 8 drinks or more per week in women. A smoker was defined as a person who currently smokes cigarettes or who has smoked 100 cigarettes in his lifetime.
In addition, patients filled the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index to assess functional capacity and the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for depression.
The laboratory data from the patient’s last clinical history was accessed, from which we obtained C-reactive protein , erythrocyte sedimentation rate , rheumatoid factor , and anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide . With these data, the DAS-28 disease activity index was calculated.
What Are The Less Common Forms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis can begin in less common forms. For example, it can begin with the involvement of only a single joint or a few joints. Sometimes, this can later evolve to the more common presentation of many joints on both sides of the body.
- Rarely, the earliest symptom of rheumatoid disease is inflammation of a body area that does not even involve a joint. For example, the lining of the lungs can become inflamed to cause pleurisy many months before arthritis develops.
- Occasionally, only a few joints are involved and the doctor may suspect another type of inflammatory arthritis. Again, this can sometimes only later evolve to become the more typical symmetrical polyarthritis by including many joints on both sides of the body.
- The caveat is that by recognizing the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis rheumatologists and their patients can address the disease early, thereby affording optimal outcomes for those affected.
Don’t Miss: What Medications Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis
Who Should Diagnose And Treat Ra
A doctor or a team of doctors who specialize in care of RA patients should diagnose and treat RA. This is especially important because the signs and symptoms of RA are not specific and can look like signs and symptoms of other inflammatory joint diseases. Doctors who specialize in arthritis are called rheumatologists, and they can make the correct diagnosis. To find a provider near you, visit the database of rheumatologistsexternal icon on the American College of Rheumatology website.
Treatment Options For Ra And Psa
Because of the differences in disease pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and response to therapy between RA and PsA, treatment strategies may differ. provides a summary of current Food and Drug Administration -approved treatments for RA and PsA. Agents targeting more upstream factors are effective in both PsA and RA, while agents targeting more downstream cytokines are more disease-specific, demonstrating significant efficacy in either RA or PsA , but not in both diseases.
Read Also: Which Doctor Do You See For Arthritis
What Types Of Lifestyle Changes Can Help With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Having a lifelong illness like rheumatoid arthritis may make you feel like you dont have much control over your quality of life. While there are aspects of RA that you cant control, there are things you can do to help you feel the best that you can.
Such lifestyle changes include:
Rest
When your joints are inflamed, the risk of injury to your joints and nearby soft tissue structures is high. This is why you need to rest your inflamed joints. But its still important for you to exercise. Maintaining a good range of motion in your joints and good fitness overall are important in coping with RA.
Exercise
Pain and stiffness can slow you down. Some people with rheumatoid arthritis become inactive. But inactivity can lead to a loss of joint motion and loss of muscle strength. These, in turn, decrease joint stability and increase pain and fatigue.
Regular exercise can help prevent and reverse these effects. You might want to start by seeing a physical or occupational therapist for advice about how to exercise safely. Beneficial workouts include:
- Range-of-motion exercises to preserve and restore joint motion.
- Exercises to increase strength.
- Exercises to increase endurance .