What Is The Treatment For Rheumatoid And Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Despite significant advances in treatment over the past decades, rheumatoid arthritis continues to be an incurable disease. While there is no cure, the goal of disease remission is frequently attainable. Treatment of RA symptoms has two major components:
Rheumatoid arthritis is a progressive inflammatory disease. This means that unless the inflammation is stopped or slowed, the condition will continue to worsen with joint destruction in most people. Although rheumatoid arthritis does occasionally go into remission without treatment, this is rare. Starting treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is strongly recommended. The best medical care combines medication and nondrug approaches.
Nondrug approaches include the following:
Drug approaches include a variety of medications used alone or in combinations.
The medications for rheumatoid arthritis fall into several different categories. These RA medications include
- disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs ,
Surgery may relieve pain and improve function.
Wednesday August 18 2021
Lets begin by defining a few terms. Arthritis is an umbrella term that describes the inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis is also known as degenerative joint disease. So, in simple terms, there is no difference between osteoarthritis and degenerative arthritis.
However, there is another form of arthritis called rheumatoid arthritis. Although osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are both forms of arthritis characterised by similar symptoms, the main difference between them is what causes these symptoms.
Here, were clearly defining osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, the similarities and differences between them, and how you can treat both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Dont Miss: What Does The Rash From Psoriatic Arthritis Look Like
How Is Oa Treated
There is no cure for OA, so doctors usually treat OA symptoms with a combination of therapies, which may include the following:
- Increasing physical activity
- Medications, including over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription drugs
- Supportive devices such as crutches or canes
- Surgery
In addition to these treatments, people can gain confidence in managing their OA with self-management strategies. These strategies help reduce pain and disability so people with osteoarthritis can pursue the activities that are important to them. These five simple and effective arthritis management strategies can help.
Physical Activity for Arthritis
Some people are concerned that physical activity will make their arthritis worse, but joint-friendly physical activity can actually improve arthritis pain, function, and quality of life.
Also Check: Arthritis In Fingers Remedy
Tips For Identifying Oa
OA isnt a disease that cycles, like PsA. Instead, it can gradually get worse.
OA pain may be mild at first. You might notice a slight twinge in your knee when you bend it, or your joints might ache after a workout.
The pain, swelling, and stiffness will get worse as the joint damage increases. Along with the pain, your joints will feel stiff especially when you first wake up in the morning.
OA will most likely affect the joints of your body that move the most.
This includes the joints in your:
- hands
Emerging Lessons From Mri Pattern Of Enthesitis In Oa And Psa
MRI of peripheral joints has long demonstrated a capsular pattern of inflammation in PsA as well as evidence for diffuse enthesitis related to pathology in a proportion of patients . Also, it may be impossible to clearly differentiate OA from PsA DIP disease, with both seeming to have prominent abnormalities in the entheses and ligaments . Even using dynamic contrast enhanced MRI, synovitis assessment as determined by gadolinium-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid uptake between the two arthropathies was comparable . Studies have noted that enthesitis-related bone oedema seen in PsA is also common in OA . With respect to spinal disease, an association was evident, with bone oedema at the enthesis attachment observed occasionally in healthy subjects, OA and SpA .
MRI of a PIP joint in OA and PsA demonstrating overlapping features as recently reported
You May Like: What Can You Take For Arthritis In Your Fingers
You May Like: What Does A High Rheumatoid Factor Mean
How Is Osteoarthritis Treated
Your doctor will develop an individualized treatment program especially for you based on several factors, including:
- how severe your disease is
- which joints are affected
- the nature of your symptoms
- any other conditions you have and medications you take
- your age, occupation and everyday work activities
Do Psoriatic Arthritis And Osteoarthritis Look Similar On X
In osteoarthritis, X-rays may show signs like worn cartilage. In psoriatic arthritis, X-rays can show joint damage in later stages of the disease.
But they arent especially helpful in making a diagnosis in the early stages. X-rays can help make an arthritis diagnosis. But they arent always a slam dunk, Dr. Rosian says.
X-rays can also reveal bone spurs, which can develop in people with osteoarthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Those images may reveal differences between the two diseases:
- Osteoarthritis bone spurs are more common in areas where cartilage and bone meet.
- Psoriatic arthritis bone spurs are more likely to form in the regions where tendons and ligaments attach to bone.
To diagnose joint disease, your healthcare provider will probably consider several factors in addition to X-rays, including:
- Blood tests.
Don’t Miss: Arthritis Flare Up In Hands
> > > Erase Joint Pain Without Surgery Or Injections
Anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and Tylenol are available over-the-counter to alleviate joint pain. The same medications can be prescribed by a doctor. If you are experiencing more severe joint pain, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. If your pain is caused by an injury, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible. You should be aware of the symptoms and make sure that they are not caused by a serious condition.
WhatS The Difference Between Osteoarthritis And Psoriatic Arthritis Inflammation can lead to joint pain. Inflammation can lead to joint damage. Your doctor can prescribe medication to stop the inflammation. While over-the-counter medications can help relieve the pain, they have side effects and should be taken only as directed by your doctor. Your doctor will discuss your treatment options and advise you on any side effects that may occur. If your joint pain is chronic or doesnt respond to these medicines, you may need to see a surgeon.
WhatS The Difference Between Osteoarthritis And Psoriatic ArthritisSymptoms of osteoarthritis usually start slowly and gradually worsen over time. You should visit your doctor if your joint pain persists. A doctor will examine you to make sure theres no swelling or redness in the joints. They may order X-rays and perform lab tests to rule out any underlying diseases. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the goal of treatment is to reduce pain and improve joint function.
You May Like: Does Arthritis Cause Swelling
What Tests Are Done For Osteoarthritis
Laboratory tests are helpful for diagnosing OA, because they are used to rule out forms of inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis. In other words, if you have joint pain and your lab results are normal, it would confirm a diagnosis of OA. These tests include:
- complete blood counts
- rheumatoid factor
- antinuclear antibody titer tests
When these tests return normal or negative results, this usually indicates that your arthritis is osteoarthritis. It should be noted, however, that as people age, they sometimes develop a low-level positive rheumatoid factor, ANA titer and/or elevated sedimentation rate without experiencing any obvious illness. This is why doctors do not rely on laboratory tests alone, but rather to confirm a suspected diagnosis for osteoarthritis.
Another lab test that may help confirm the diagnosis is the extraction and analysis of synovial fluid from the joint. Synovial fluid is a liquid normally found within the joints. It helps nourish and lubricate them and is usually present in only very small amounts. However, when certain forms of arthritis are present, synovial fluid will change.
In osteoarthritis, white blood cell count is usually normal and the fluid is clear . Higher white cell counts should suggest inflammatory arthritis or infection, rather than osteoarthritis. In this way, extracting synovial fluid can help to confirm the diagnosis. It can also reduce pain and swelling if the fluid is contributing to inflammation.
Read Also: What Can I Do For Arthritis Pain In My Hands
How Does Bursitis Form
Bursitis can occur from an injury to the joint or from repetitive stress or overuse. Repetitive stress can occur from doing the same activity over and over, like stair climbing, standing for long periods, kneeling for cleaning or gardening, or resting on your elbows for long periods.
Some conditions increase your risk for developing bursitis, including rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes. The risk of bursitis also increases with age, and being overweight can add stress to the knees and hips, which can increase the risk of bursitis in those joints.3
What Causes Psa And Who Is At Risk
PsA is an autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases cause your body to mistakenly attack its own cells.
PsA typically only develops in people who have psoriasis. Psoriasis is a common skin condition that causes rapid skin cell buildup. The excess skin cells form red patches, which are often covered in whitish-silvery scales.
About 7.5 million Americans have psoriasis. Between 20 to 30 percent of people with psoriasis also have PsA.
In most people with PsA, psoriasis develops first. The arthritis usually starts later. About 15 percent of the time, arthritis starts before a skin rash appears.
Other risk factors for PsA include:
- Family history. About 40 percent of people with a parent, sibling, or other close relative who has psoriasis or PsA will get this condition.
- Age. This form of arthritis can develop at any age, but its most commonly diagnosed in people ages 30 to 50.
- Infections. People who are exposed to certain viruses, such as HIV, are more likely to get PsA.
Treatments for PsA aim to do two things: Slow or stop the joint damage and relieve pain.
A typical treatment plan will involve one or more of the following:
- medication
- steroid creams and ointments
- vitamin D-based creams, such as calcipotriene
You can also try light therapy . This treatment uses ultraviolet light to clear plaques on your skin.
Physical or occupational therapies are recommended for PsA patients to maintain joint health and improve their quality of life.
Don’t Miss: What Really Causes Arthritis
How Can I Manage Oa And Improve My Quality Of Life
CDCs Arthritis Program recommends five self-management strategies for managing arthritis and its symptoms.
- Learn self-management skills. Join a self-management education class, which helps people with arthritis and other chronic conditionsincluding OAunderstand how arthritis affects their lives and increase their confidence in controlling their symptoms and living well. Learn more about the CDC-recommended self-management education programs.
- Get physically active. Experts recommend that adults engage in 150 minutes per week of at least moderate physical activity. Every minute of activity counts, and any activity is better than none. Moderate, low impact activities recommended include walking, swimming, or biking. Regular physical activity can also reduce the risk of developing other chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Learn more about physical activity for arthritis.
- Go to effective physical activity programs. For people who worry that physical activity may make OA worse or are unsure how to exercise safely, participation in physical activity programs can help reduce pain and disability related to arthritis and improve mood and the ability to move. Classes take place at local Ys, parks, and community centers. These classes can help people with OA feel better. Learn more about CDC-recommended physical activity programs.
The Difference Between Osteoporosis And Osteoarthritis

What is the difference between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis? Actually, quite a bit. While the diseases have similar names, they are not related conditions. Osteoporosis affects a persons bones, whereas OA affects a persons joints. Another key difference is that OA can cause many painful symptoms, whereas osteoporosis might not produce symptoms at all.
Recommended Reading: How Painful Is Ra
What Will Happen To Me
The impact of OA on your normal activities and lifestyle depends on which joints are affected. However the outlook for most people with OA is very positive. For many people OA will be mild and not cause major problems. OA of the hip and knee can sometimes cause severe disability and surgery to replace joints may be necessary. Joint surgery is usually only an option if less invasive treatments, such as weight loss, exercise, and medicines, have failed to control your symptoms.
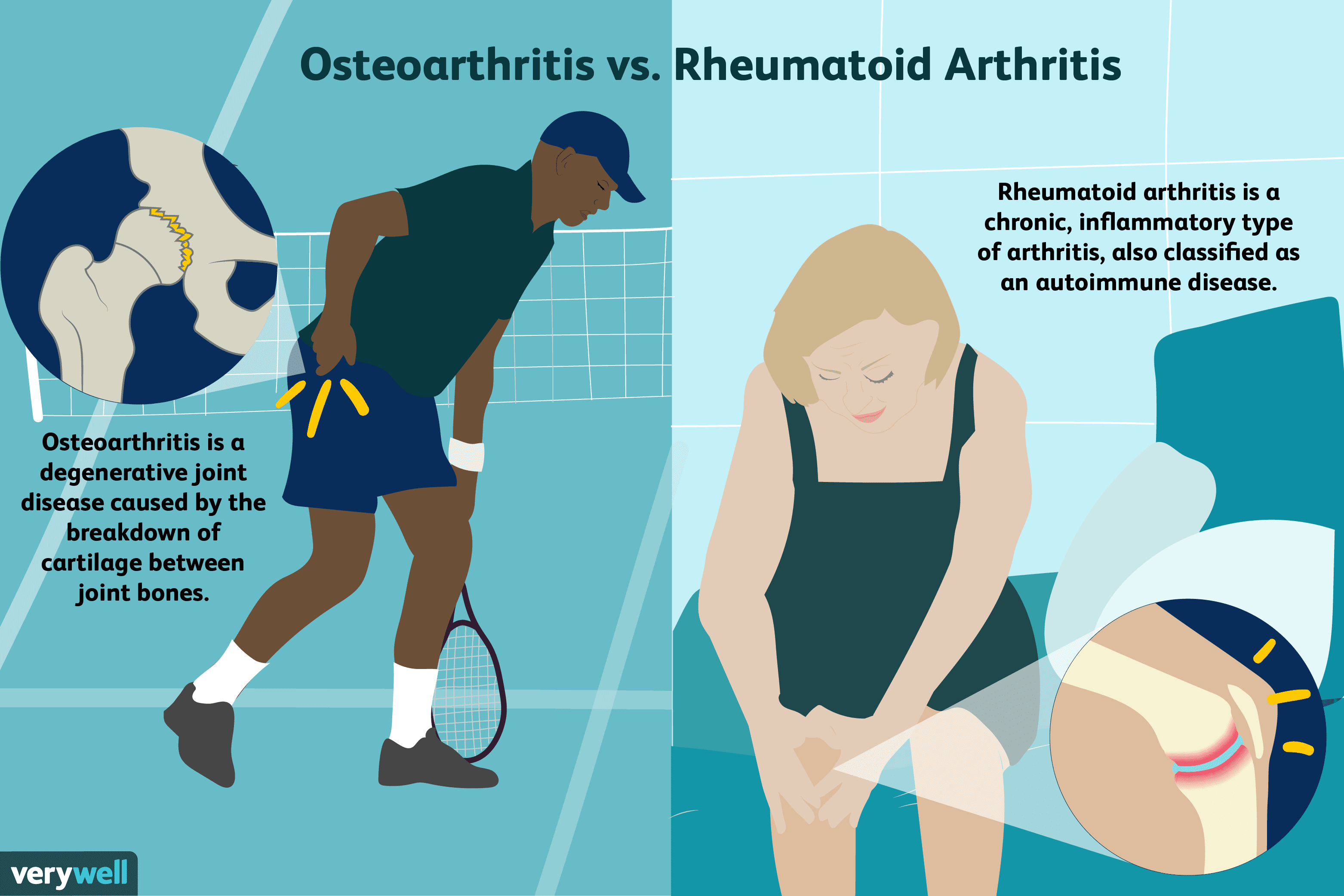
Whats The Difference Between Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis is more common than you might think. For example, more than 46 million Americans1 or 1 in every 6 have some form of arthritis.
There are more than 200 different types of arthritis including little known diseases like Kawasaki disease, and Sweets syndrome 2 Two of the most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
< Extract>
Researchers also believe that skeletal remains from humans living around 4500 B.C. show signs of the disease.
www.arthritis.org
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the breakdown of cartilage the flexible tissue that protects bone ends from rubbing against each other. Osteoarthritis is further characterized by the creation of bony spurs or growths due to bone wear and tear.3
Osteoarthritis affects only the joints and can affect many different joints,3 including the hand, knee, spine and hip.3 As well as causing pain and stiffness, osteoarthritis can also limit movement, as inflamed joints do not bend as far or as easily.3
Age is a major risk factor for this type of arthritis. Around 8 out of 10 adults over the age of 50 are affected in the UK.3 Other contributing factors are being overweight, stress to a joint from overuse or injury, and a family history of osteoarthritis.3
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an auto-immune disease. This basically means that the bodys immune system attacks its own healthy tissues, joints, and organs and treats them like invaders.
< illustration joint>
Read Also: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause A Rash
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis
The first step in finding relief from joint pain, swelling, and stiffness is working with your doctor to determine if you could be having symptoms of certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis . The sooner you know, the sooner you can begin treatment and find relief from your symptoms.
Weve put together a quick guide to help you understand the differences between RA and OA. While RA and OA can both lead to joint pain and stiffness, there are important differences that can help you have a conversation with your doctor to assist in identifying which type of arthritis you might haveand ultimatelyhow to treat it. Use the chart below to learn more about RA and OA.
Differences Between Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis is the inflammation of joints. It is not a single disease. There are over 100 types of arthritis. Some similar symptoms of arthritis in general include joint stiffness and joint pain. These symptoms make it difficult to move around and perform everyday tasks. Lets take a look at the two most common types of arthritis, their differences, and how arthritis doctors treat them.
Read Also: High Rheumatoid Factor Causes
What Are The Risk Factors For Oa
- Joint injury or overuseInjury or overuse, such as knee bending and repetitive stress on a joint, can damage a joint and increase the risk of OA in that joint.
- AgeThe risk of developing OA increases with age.
- GenderWomen are more likely to develop OA than men, especially after age 50.
- ObesityExtra weight puts more stress on joints, particularly weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees. This stress increases the risk of OA in that joint. Obesity may also have metabolic effects that increase the risk of OA.
- GeneticsPeople who have family members with OA are more likely to develop OA. People who have hand OA are more likely to develop knee OA.
- Race Some Asian populations have lower risk for OA.
What Are The Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis
Pain is the most common symptom of OA, followed by stiffness. Pain usually increases during activity and decreases with rest. However, in the morning or after other long periods of inactivity, some people with OA may experience a feeling of stiffness. This symptom is caused by a temporary thickening of natural fluids inside the joint. It usually lasts for less than 20 minutes in the affected joint once a person begins moving again.
Pain felt during movement of the joint is often accompanied by a crackling or grinding sound called “crepitus.” Some people with OA may feel little or no pain for unknown reasons. The level of pain each person with OA experiences can depend on many factors including: the stage of the disease, the way a person’s brain processes pain messages, cultural, gender and psychological differences.
Osteoarthritis is not associated with the following symptoms. If you have these are symptoms, you have some form of :
- swelling, redness or warmth in the joints where you feel pain
- fevers
- symptoms on both sides of the body
Also Check: Inflammatory Polyarthritis Symptoms
Hss Research Enhances Arthritis Treatment Options
Hospital for Special Surgerys pace-setting medical research contributes essential knowledge to researching the prevention and treatment of osteoarthritis and inflammatory arthritis. HSS musculoskeletal medicine research is organized into five main programs: