What Are The Potential Complications Of Osteoarthritis
In some cases, osteoarthritis can lead to serious complications. It is important to understand that osteoarthritis and its symptoms are not a normal part of the aging process and can be treated. You can minimize discomfort and reduce your risk of complications by following the treatment plan you and your healthcare provider develop specifically for you. Complications of osteoarthritis include:
-
Adverse effects of osteoarthritis treatment
Symptoms Of Oa And Ra
Because OA and RA are caused by different factors, they elicit different symptoms.
A person who has rheumatoid arthritis may experience fatigue, malaise, and depression, preceding other symptoms by weeks to months. These are common symptoms of systemic diseases, as critical body systems, like the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, are under attack. These systems have key responsibilities in the body, and any damage to these systems can throw neurological, physiological, and physical functions off track.
Other symptoms of RA include:
- Low-grade fever
- Morning stiffness of the joints
- Swelling of the joints
- Cracking and popping of the joints
Are There Alternative Treatments For Osteoarthritis
While recent research has questioned their usefulness, some medical research has shown that the supplementsglucosamine and chondroitin may relieve pain in some people with osteoarthritis, especially in the knee. There is no evidence that glucosamine can help rebuild cartilage. SAMe is another supplement with potential benefits for osteoarthritis. In fact, some research has shown it may be as effective an anti-inflammatory drugs. Remember to always let your doctor know about any supplements you’re taking, because they can have side effects and interact with medications.
Acupuncture has also been shown to provide significant and immediate pain relief in some people with osteoarthritis.
Also Check: How To Test For Arthritis In Knee
Reducing Inflammation And Preventing Damage
A balanced, nutritious diet will give the body the tools it needs to prevent further damage to the joints, which is essential for people with osteoarthritis.
Some foods are known to reduce inflammation in the body, and following an anti-inflammatory diet can improve symptoms. Eating enough antioxidants, including vitamins A, C, and E, may help to prevent further damage to the joints.
What Are Some Conditions Related To Osteoarthritis
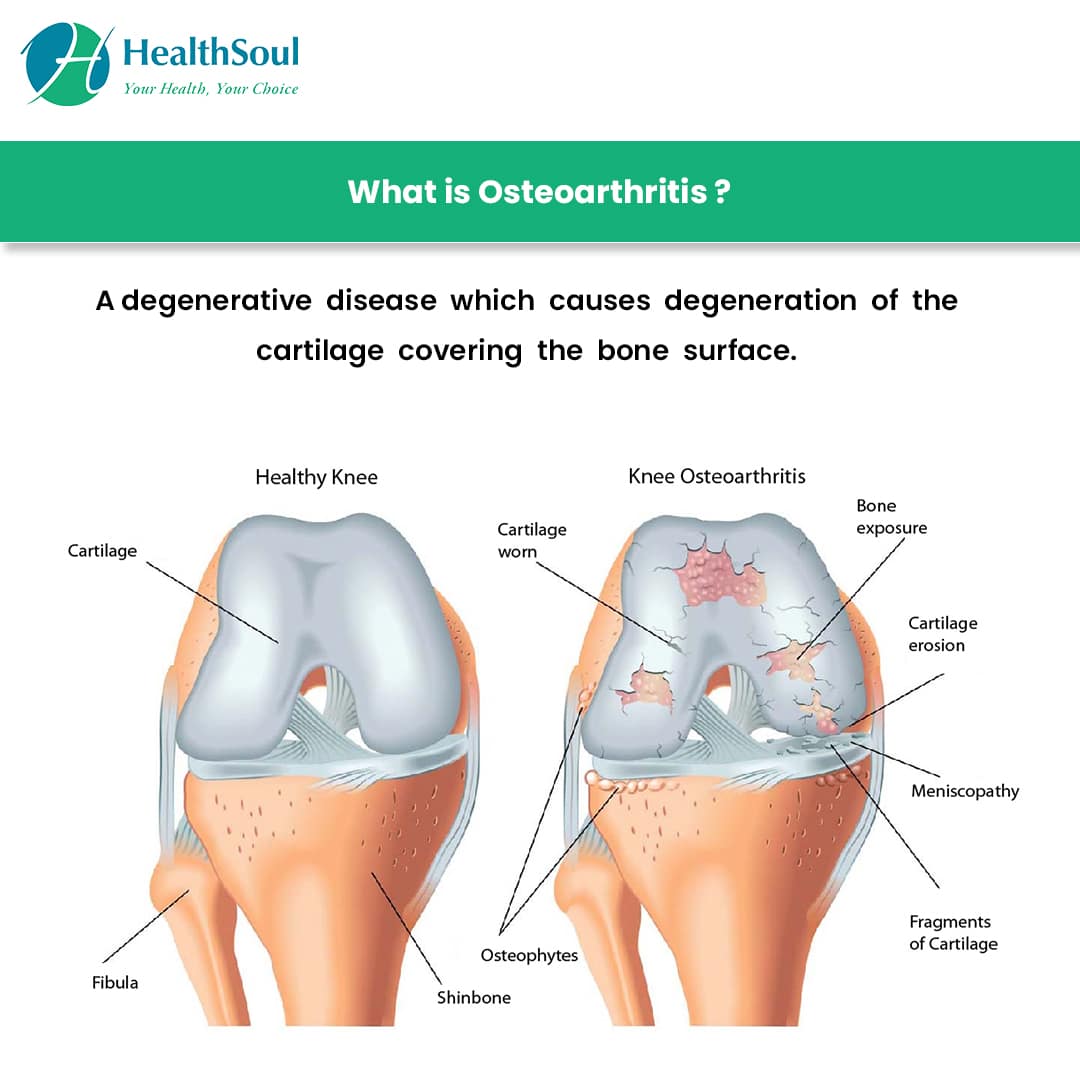
Osteoarthritis is the most common of the more than 100 types of arthritis. Other common types of arthritis include:
-
Gout, a form of arthritis caused by uric acid crystals lodging in the joint space
-
Juvenile arthritis, any type of arthritis affecting the pediatric population
-
Psoriatic arthritis, an autoimmune disease that affects the joints and possibly the skin
-
Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease that affects the joints and other parts of the body
Recommended Reading: What Are Biologics For Rheumatoid Arthritis
What About The Mediterranean Diet
Studies have suggested that the Mediterranean diet can reduce the inflammation that contributes to the symptoms of osteoarthritis.
As well as helping to reduce the pain associated with osteoarthritis, eating a Mediterranean-style diet offers many other health benefits, including weight loss.
Following a Mediterranean diet may also reduce the risk of:
When someone is living with osteoarthritis, their body is in an inflammatory state.
While foods with anti-inflammatory properties may reduce symptoms, some foods contain substances that actively contribute to this inflammation. It is best to avoid or restrict these dietary choices.
The types of food to avoid are those that include the following:
Other Pain Relief Treatments
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
A TENS machine sends electrical pulses to your nerve endings through pads placed on your skin. It produces a tingling sensation and is thought to relieve pain by altering pain signals sent to the brain. The research evidence on the effectiveness of TENS is mixed, but some people do find it helpful. A physiotherapist will be able to advise on the types of TENS machine available and how to use them. Or they may be able to loan you one to try before you buy.
Hyaluronic acid injections
Hyaluronic acid, or hyaluronan, is a lubricant and shock absorber thats found naturally in the fluid in your joints. Injections of hyaluronic acid have sometimes been used as a treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee. The treatment isnt currently available on the NHS because research evidence on its long-term effectiveness is mixed. The treatment is, however, available privately.
You May Like: How Can You Prevent Arthritis In Your Fingers
What Are The Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis affects people in different ways, and not everyone has pain. The most common symptoms are:
- Pain when you move, which often gets better with rest
- Stiffness, especially for the first 30 minutes after you get up from resting
- Swollen joints, especially after using the joint a lot
- Less movement in the joint than normal
- A joint that feels loose or unstable
Watch Our Video About What Osteoarthritis Is
Osteoarthritis is a very common condition which can affect any joint in the body. Its most likely to affect the joints that bear most of our weight, such as the knees and feet. Joints that we use a lot in everyday life, such as the joints of the hand, are also commonly affected.
In a healthy joint, a coating of tough but smooth and slippery tissue, called cartilage, covers the surface of the bones and helps the bones to move freely against each other. When a joint develops osteoarthritis, part of the cartilage thins and the surface becomes rougher. This means the joint doesnt move as smoothly as it should.
When cartilage becomes worn or damaged, all the tissues within the joint become more active than normal as the body tries to repair the damage. The repair processes may change the structure of the joint, but will often allow the joint to work normally and without any pain and stiffness. Almost all of us will develop osteoarthritis in some of our joints as we get older, though we may not even be aware of it.
However, the repair processes dont always work so well and changes to the joint structure can sometimes cause or contribute to symptoms such as pain, swelling or difficulty in moving the joint normally.
For example:
For most joints, osteoarthritis is more common and more severe in women.
Recommended Reading: How To Make Arthritis Pain Go Away
What Are The Risk Factors For Osteoarthritis
In addition to age and secondary causes such as inflammatory arthritis and prior injury/ trauma, several other risk factors increase the chance of developing osteoarthritis including obesity, diabetes, elevated cholesterol, sex, and genetics.
- Obesity is a risk factor for osteoarthritis, particularly of the knee. In addition to overloading the weight-bearing mechanisms of the body, the metabolic and pro-inflammatory effects of obesity have been studied as contributory to osteoarthritis. Maintaining ideal body weight or losing extra weight is important for those at risk.
- Both diabetes and hyperlipidemia contribute to the inflammatory response within the body, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis. Oxidation of lipids can also create deposits in cartilage which affects affecting blood flow of subchondral bone in the same way that blood vessels are affected by atherosclerosis. Elevated blood sugars, as well as elevated cholesterol/lipids, increase free radicals within the body, this oxidative stress exceeds the resilience of cartilage on the cellular level. Controlling diabetes and hyperlipidemia is important for bone health in addition to general health.
- Heredity can play a role in osteoarthritis, as individuals born with other bone diseases or genetic traits may be more likely to develop osteoarthritis. For example, Ehlers-Danlos, which is characterized by joint laxity or hypermobility, can contribute to osteoarthritis.
What Causes Osteoarthritis
Primary osteoarthritis is a heterogeneous disease meaning it has many different causes, it is not only âwear and tearâ arthritis. Some contributing factors to OA are modifiable and others are non-modifiable . Age is a contributing factor, although not all older adults develop osteoarthritis and for those who do, not all develop associated pain. As discussed above, there can also be inflammatory and metabolic risks that can increase the incidence of osteoarthritis, particularly in the setting of diabetes and/or elevated cholesterol.
Osteoarthritis can be genetic both as primary such as nodular OA of the hands as well as secondary related to other genetic disorders, such as hypermobility of joints. Inflammatory and infectious arthritis can contribute to the development of secondary osteoarthritis due to chronic inflammation and joint destruction. Previous injuries or traumas including sports-related and repetitive motions can also contribute to osteoarthritis.
Although the exact mechanisms of cartilage loss and bone changes are unknown, advancements have been made in recent years. It is suspected that complex signaling processes, during joint inflammation and defective repair mechanisms in response to injury, gradually wear down cartilage within the joints. Other changes cause the joint to lose mobility and function, resulting in joint pain with activity.
Read Also: Are Potatoes Bad For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Should I See A Specialist
Its unlikely that youll need to see a specialist to get a diagnosis of osteoarthritis, although your doctor may refer you if theres some doubt about the diagnosis or if they think there might be additional problems.
Your doctor may refer you if specialist help is needed to manage your osteoarthritis this might be for physiotherapy, podiatry for foot problems, or occupational therapy, which can help if youre having difficulty with everyday activities.
If your arthritis becomes severe and is causing long-term problems, your GP may refer you to an orthopaedic surgeon to consider joint surgery or to a pain management programme.
- supplements and complementary treatments.
Common Types Of Arthritis
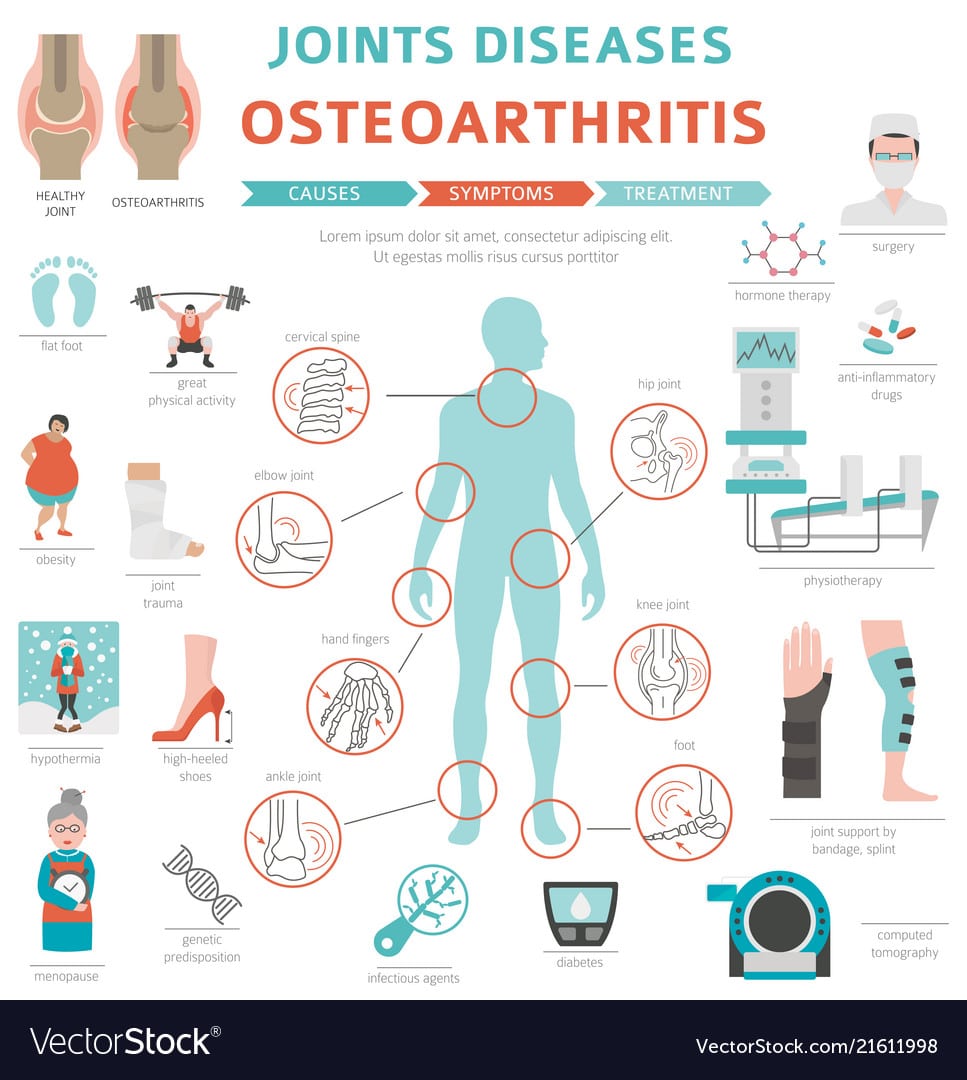
Posted June 17, 2019 by Vivek Bhalla, MD
Commonly associated with older age, arthritis affects more than 50 million Americans, including more than 300,000 children each year. There are over 100 different forms of arthritis. Depending on the type, it can be extremely painful and affect everyday activities or go relatively unnoticed and be easily managed for years.
Simply put, arthritis is the inflammation of one or more joints. Most individuals experience common symptoms like joint pain, swelling, stiffness and/or decreased range of motion.
Here are 5 of the most common types of arthritis:
Read Also: What Can An Orthopedic Doctor Do For Arthritis
Osteoarthritis Of The Spine
If you have back pain, it may indicate that you have spinal OA. This condition affects the facet joints located throughout the spine.
Age and trauma to the spine are both potential risk factors for spinal OA. A person who is overweight, or whose job requires squatting and sitting, may also be at increased risk.
Spinal OAs symptoms can vary in severity. They include:
- stiffness or tenderness in the joints in your back
- weakness, numbness, or tingling in your arms or legs
- reduced range of motion
Its important to pay attention to these symptoms. Without treatment, spinal OA can worsen, causing more severe symptoms and disability. Get the facts on OA of the spine.
You may have risk factors for OA that you cant change, such as heredity and age. However, other risk factors can be controlled. Managing them can help reduce your risk of OA.
The following tips can help you manage the risk factors under your control:
- Support your body. If youre an athlete or an avid exerciser, make sure you care for your body. Wear athletic supports and shoes that reduce impact on your knees. Also make sure to vary your sports, so that all of your muscles get a workout, not just the same muscles every time.
- Maintain a moderate weight. Keep your body mass index in the appropriate range for your height and sex.
- Eat a nutritious diet. Reach for a range of healthy foods, with a focus on fruits and vegetables.
- Get enough rest. Give your body ample opportunities to rest and sleep.
How Is Osteoarthritis Diagnosed
There is no specific test for osteoarthritis. To find out if you have osteoarthritis, your provider:
- Will ask about your symptoms and medical history
- Will do a physical exam
- May use x-rays or other imaging tests to look at your joints
- May order lab tests to make sure that a different problem isn’t causing your symptoms
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Diet For Arthritis
Is There A Surgery For Osteoarthritis
When osteoarthritis pain is not controlled with other treatments, or when the pain prevents you from participating in your normal activities, you may want to consider surgery.
There are several types of surgery for osteoarthritis. They include:
- Arthroscopy to clean out the damaged cartilage or repair tissues. It is most commonly performed on the knee and shoulder. Recent evidence has questioned its effectiveness for osteoarthritis.
- Joint replacement surgery to replace the damaged joint with an artificial one. Joint replacement surgery should be considered when the severity of the joint pain significantly interferes with a personâs function and quality of life. Even under the best of circumstances, surgery cannot return the joint to its normal state , but movement and function are significantly improved. In addition, an artificial joint will greatly diminish pain. The two joints most often replaced are the hip and the knee. Artificial joints are now also available to replace shoulders, fingers, elbows, and ankles to treat severe pain that has not responded to other treatments.
- Joint fusion to remove the damaged joint and fuse the two bones on each side of the joint. This is done more often in areas in which joint replacement is not effective.
Talk to your doctor to determine if any of these treatment options are right for you.
Osteoarthritis: Causes Risk Factors And Treatment
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis in the United States, affecting roughly 12 percent of Americans aged 25 74. Its a chronic joint disease that breaks down cartilage in the neck, lower back, knees, hips, shoulders, and/or fingers. Common symptoms are pain, stiffness, and limited joint movement.
Recommended Reading: What Is Good To Take For Arthritis Pain
How Is Osteoarthritis Managed
There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but most people with osteoarthritis can manage their symptoms, continue with daily activities and live healthy and enjoyable lives. Be careful of any products or treatments that claim to cure osteoarthritis completely your doctor will help to find the right treatment for you.
The Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care has developed a guide to help you discuss the main treatment options for osteoarthritis of the knee with your doctor.
Difference Between Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are several different types of arthritis. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are two of the most common forms. Although the symptoms of these two types of arthritis can be similar, it’s very important to distinguish between them in order to determine the proper treatment.
At the University of Michigan Health System, our experienced rheumatologists will do appropriate tests to determine which type of arthritis you have. Then we will develop an effective treatment plan and will explain your options.
Osteoarthritis occurs when the smooth cartilage joint surface wears out. Osteoarthritis usually begins in an isolated joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system malfunctions and attacks the body instead of intruders. In this case, it attacks the synovial membrane that encases and protects the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis often targets several joints at one time. The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- the symmetrical nature of the disease ,
Read Also: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Psoriatic Arthritis
Knee Brace For Osteoarthritis
Wearing a brace around your knee can be an excellent nonsurgical treatment for knee OA. Braces can lower swelling and pressure. They can also increase stability in your knee by shifting your weight away from the damaged part of your knee. This allows for greater mobility.
There are several types of knee braces. Some may be custom fitted for you, and others are available OTC. Your doctor may recommend that you try different kinds of braces for different activities. Find out whats the best type of brace for your OA.
Diagnosis Of Oa And Ra
The causes, symptoms, and treatment methods differ for OA and RA, so its important that we determine the type of arthritis a patient has in order for us to develop an effective treatment plan.
How Osteoarthritis is Diagnosed
Osteoarthritis is generally diagnosed through a series of tests, along with a physical examination and an assessment of past medical history.
Common tests used to diagnose OA include:
- Ultrasound to evaluate the ligaments and tendons around the affected joint
- Analysis of synovial fluid to determine whether degeneration is present
- Closed synovial biopsy to remove a piece of synovial tissue and assess its condition
- Arthroscopy examination of the joints through a small camera
- Arthrocentesis examination to remove joint fluid and assess its condition
How Rheumatoid Arthritis is Diagnosed
Rheumatoid arthritis is generally diagnosed through a series of tests, including physical examinations, blood tests, and x-rays.
If our rheumatology doctor, Dr. Maria Farooq, suspects rheumatoid arthritis, she will assess the affected joints to determine whether they are swollen, red, or warm, as these signs are indicative of RA. This physical exam may be followed by any of the following tests:
Read Also: Does Icy Hot Work For Arthritis