Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means your immune system attacks the cells that line your joints by mistake, making the joints swollen, stiff and painful.
Over time, this can damage the joints, cartilage and nearby bone.
It’s not clear what triggers this problem with the immune system, although you’re at an increased risk if:
- you are a woman
- you have a family history of rheumatoid arthritis
Find out more about the causes of rheumatoid arthritis.
How Does Seronegativity Affect Treatment And Prognosis
Generally, the available treatments for RA can be used to treat both seronegative and seropositive cases. The types of medication you receive will depend on how long you have had RA and how severe your symptoms are. RA treatments work by targeting the source of inflammation or treating symptoms and may include:
People with seronegative RA may respond better to traditional RA medications. People with seronegative RA may also have a milder disease course than those with seropositive RA. However, this may not always be the case and depends on other factors such as underlying conditions and genetics.
Seronegative Ra: What Are The Symptoms Of Seronegative Ra
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis is the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis without the presence of certain antibodies in the patients blood. It is one of two main types of rheumatoid arthritis diagnoses.
In most cases of rheumatoid arthritis, the patient tests positive for rheumatoid factor and/or anti-citrullinated peptides antibodies. These indicate that the patient is seropositive and that they possess the antibodies that cause an attack on joints and lead to inflammation. These patients tend to have a more severe disease course with more joint deformities, x-ray damage, disability and inflammation outside of the joints.
You May Like: What Helps Arthritis Pain In Feet
What Is Seronegative Spondyloarthritis
Seronegative spondyloarthritis is a group of inflammatory rheumatic diseases with common clinical and aetiological features, including axial and peripheral inflammatory arthritis, enthesitis, extra-articular manifestations and a close link to the presence of the human leucocyte antigen -B27 epitope.
Associations Of Od With Clinical And Laboratory Parameters And Od Quartile Distribution Of Ra Patients Taking Or Not Corticosteroid Therapy
Within the group of seronegative RA patients there was no difference in O.D. values between females and males or between subjects with or without joint erosions . There was no correlation between O.D. levels and age at enrollment, age at diagnosis, disease duration, ESR, CRP, DAS28, tender and swollen joint counts . There was no difference in O.D. values among patients receiving different disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs , while treatment with corticosteroids was associated with lower O.D. levels .
Finally, we stratified the whole study sample according the O.D. quartile distribution. Considering the potential influence of corticosteroid therapy, these analyses were performed in subgroups of subjects taking or not corticosteroids . As expected, healthy donors were strictly prevalent in the lowest quartile while seropositive RA or seronegative RA patients were more frequent in the higher quartiles in both the subgroups. A progressive increase of prevalence of RA+/RA- patients by increasing O.D. values, from the lowest to the highest quartile, was particularly evident among subjects not taking corticosteroids , while the trend although significant appeared milder in those taking corticosteroids .
Also Check: How To Ease Arthritis Pain In Fingers
Can Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis Become Seropositive
People who test negative for RF and ACPA may become positive later on. Up to 80 percent of people with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis will eventually become seropositive.
Doctors say that this change typically happens within two years of receiving a diagnosis.
Some cases initially diagnosed as seronegative rheumatoid arthritis will later be diagnosed with other autoimmune disorders, such as psoriatic arthritis or chronic gout.
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis is more likely to be incorrectly diagnosed than seropositive arthritis. Its symptoms can bear a resemblance to those associated with osteoarthritis.
In other cases in which seronegative rheumatoid arthritis is diagnosed, it may not respond to conventional treatments.
That may be a sign that the patient doesnt actually have seronegative rheumatoid arthritis, but another condition altogether.
Other types of arthritis, including spondyloarthritis, which affects the spine, can be mistaken for rheumatoid arthritis.
Why Does The Distinction Matter
The distinction between seropositive and seronegative RA is important because it can help doctors rule out other rheumatic diseases during diagnosis. People who have anti-CCP antibodies and other relevant symptoms can easily be diagnosed with RA.
However, seronegative individuals may have a more difficult time getting an accurate diagnosis. For example, if a seronegative person develops a skin rash, they may be diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis. Osteoarthritis can also be mistaken for seronegative RA because both conditions cause joint pain and other similar symptoms.
Read Also: Is Arthritis In The Knee Curable
Symptoms Of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis patients must possess a distinct set of symptoms in order to be diagnosed. This is because the lack of antibodies in the blood makes it more difficult to reach a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
Some of the most important symptoms in diagnosing seronegative rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Joint pain, stiffness specifically in the hands but also in knees, elbows, hips, feet and ankles
- Joint swelling and redness
- Morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes
- Eye redness
Though this is not an exhaustive list, the majority of these will support a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis. If we compare these symptoms to seropositive rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, there are many similarities. However, many patients see these symptoms evolve and change over time.
It is thought that seropositive patients experience a more severe disease course than seronegative patients. But studies have also shown that in some patient cases, the progression is comparable and sometimes is there is little difference. This is where it becomes complicated in trying to classify rheumatoid arthritis into sub-types and to reach a solid diagnosis.
There are some symptoms that are thought to be rheumatoid arthritis in seronegative patients, but later turn out to be other conditions. These cases mainly involve differences in the types of joints and areas affected as well as the levels of inflammation.
What Do The Test Results Mean
The presence of either of these tests may indicate that RA is present. However, seropositivity is only one criterion of several that makes the diagnosis of RA likely . If the other criteria for the diagnosis are present, then seropositivity is an additional clinching factor. A positive anti-CCP test is marginally stronger than positive RF test for the diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Help Arthritis In Your Hands
People With Seronegative Ra Often Have Different Symptoms
The conventional wisdom is that seropositive patients have more severe symptoms, but recent studies suggest that the difference between the two forms of the disease may have more to do with the joints affected than with the severity of the RA symptoms. And a report published in June 2016 in BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders found that further research is needed to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients with seronegative RA. My experience has been that while the symptoms are similar, seronegative patients are more difficult to treat, says Vinicius Domingues, MD, a rheumatologist in Daytona Beach, Florida, and a medical adviser to CreakyJoints.
What Is Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
When a patient tests negative for RF and anti-CCP antibodies, yet they still display strong symptoms consistent with rheumatoid arthritis, they are given a diagnosis of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis.
The term seronegative means they dont possess the antibodies that seropositive patients do. In other words, seronegative patients may also simply possess extremely low levels of the antibodies not enough for the test to detect.
Many seronegative rheumatoid arthritis patients go on to develop antibodies years after their initial diagnosis, which then changes their diagnosis to seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. This is one of the many reasons that a patient can still be diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis even if they are seronegative.
You May Like: Can Arthritis Affect The Heart
The Presence Or Absence Of Rf Or Acpa Doesnt Make Or Break An Ra Diagnosis
Testing for rheumatoid factor in people suspected of having RA was popularized in the 1960s, and experts still dont fully understand the exact link between these factors and the development of the disease. RF can be positive in multiple diseases, such as hepatitis C, endocarditis, and multiple myeloma.
Rheumatoid factor clearly plays a role in how serious rheumatoid arthritis can be, says John J. Cush, MD, a professor of internal medicine and rheumatology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. A different blood test checks for ACPA, which may be more closely linked to the development of the disease than RF. A study published in the journal Autoimmunity Reviews in July 2016 found that ACPA antibodies represent an independent risk factor for developing RA. Having ACPA suggests theres a genetic risk factor for the disease, but its not necessary for either antibody to be present in the blood for a diagnosis of seronegative RA.
RELATED:6 Things About Rheumatoid Arthritis That Are Difficult to Explain or Understand
How Are Blood Tests Used To Help Diagnose Ra
RF and anti-CCP tests dont definitively point to RA because some healthy people without RA test positive for these antibodies, while other people who do have autoimmune problems test negative, says Umbreen Hasan, MD, consultant rheumatologist for Allina Health in Minnesota.
Thats why doctors will also consider RA symptoms, inflammation levels, and the amount of joint swelling with the help of X-rays and ultrasounds.
Although blood tests for inflammatory arthritis can help in the diagnosis of the condition, a good history and physical examination is more important, says Dr. Hasan. The diagnosis should not be solely based on blood tests.
However, if you have symptoms that are consistent with rheumatoid arthritis and you do test positive for these antibodies, your doctor will feel pretty confident being able to diagnose you with RA.
Don’t Miss: What Blood Tests Can Detect Rheumatoid Arthritis
New Symptoms May Change The Diagnosis
Eventually, people with seronegative disease may be diagnosed with a different disease altogether, according to the Arthritis Foundation. If, say, a person diagnosed with seronegative RA develops a skin rash, her diagnosis might change to psoriatic arthritis. Other changes or new test results could lead to a new diagnosis of chronic gout or osteoarthritis. The most important thing at the time you see a rheumatologist is determining whether you have inflammatory arthritis or mechanical arthritis, where there is less that can be done to treat it, says Domingues.
What Is Seronegative Ra
Unlike seropositive RA, seronegative RA means that there are no detectable anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides present in your bloodstream. Anti-CCP antibodies are also known as anti-citrullinated protein antibodies . They recognize proteins that have undergone citrullination, a type of molecular change in structure.
Seronegative RA is less common than seropositive RA, accounting for around 20 percent of cases. In some cases, a person will be diagnosed with seronegative RA if the antibodies are present but the levels are so low that they cannot be detected by a blood test. Seronegativity makes it more difficult to diagnose RA.
Don’t Miss: When Is Arthritis Pain The Worst
Antibody Detection: Multiplex Microarray And Elisa
High-throughput IgG screening was performed on sera from 2755 RA cases and 370 controls using a custom-made microarray chip , as previously described . Antigens included 19 citrullinated peptides from filaggrin, fibrinogen, vimentin, -enolase, collagen type II , and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-A3 , and 17 non-citrullinated antigens reported as autoantibody targets in other rheumatic/autoimmune disorders . Cutoff was set based on reactivity among controls and correspond to the highest 98th percentile found in 20 randomly selected subsets comprising 80% of the control population.
Anti-CCP2 IgG was measured using Immunoscan CCPlus® ELISA , according to the manufacturers instructions, with a cutoff of 25U/mL. IgM, IgG, and IgA RF were analysed using EliA immunoassay on Phadia 2500 , using cutoff values as stated in the manufacturers instructions. Anti-carbamylated fibrinogen antibodies were measured in a subset of patients , as previously reported , with cutoff set at the 98th percentile among 316 EIRA controls.
Clinical And Laboratory Features And Treatment Of Ra Patients
The main clinical features, biochemical characteristics and treatment of all seronegative RA patients included in the study are summarized in Table 1. Supplementary Table 1 shows the data related to patients with seropositive RA, used as control. The RA patients were predominantly female and the gender percentage in the two seronegative RA groups were equally balanced.
Table 1 Clinical and laboratory features and treatment of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis patients from the Perugia and Verona cohorts.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do For Arthritis In The Shoulder
How Being Seronegative Affects Ra
As with people who are seropositive, RA isnt predictable for those who are seronegative. But because it can be harder to diagnose seronegative RA, it can take longer to get treated for it. That delay might make it less likely that youll go into remission, which is when you have very few signs of the disease.
People who start treatment within the first 2 years of symptoms are more likely to go into remission than those who dont.
Other Conditions Associated With Seronegative Patients
A seronegative result along with what are thought to be rheumatoid arthritis symptoms could potentially indicate other conditions altogether. Often times when inflammation is present or consistent it means that the seronegative patient may have osteoarthritis instead of rheumatoid arthritis. This is a common confusion.
Spondyloarthritis conditions are sometimes associated with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis because they are inflammatory. These are conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, as well as psoriatic arthritis.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Rheumatoid Arthritis In Fingers
Blood Tests: Rheumatoid Factor
I was diagnosed seronegative when I was 27. For 30 years I wondered if a mistake was made. Mary
Rheumatoid Factor measures the level of rheumatoid factors in your blood proteins that can attack the healthy tissues in your body. This test is negative in 20 to 30 percent of people with RA. When it is positive, you may have RA, but it can also indicate a number of other conditions. It is also positive in a small percentage of healthy individuals.
Some Symptoms Of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
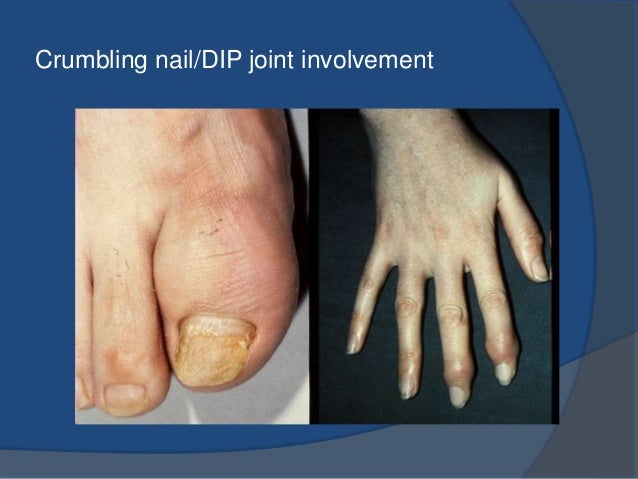
In case a patient tested seronegative, the patient must possess some distinctive symptoms, which can conclude that the patient has rheumatoid arthritis. Some signs of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis are:
- Tenderness, swelling, and redness in the joints
- Pain and stiffness in the palm of the hands, knees, elbows, hips, feet, and ankles
- Inflammation
- Eye redness
These are not the only signs of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. If you compare these signs to seropositive rheumatoid arthritis patients, their symptoms have similarities, but these symptoms evolve and change over time.
Read Also: Is Lemon Water Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Does This Affect The Medications That Will Work For Me
Whilst the efficacy of most medications for RA is not affected by whether someone is seropositive or seronegative, evidence suggests that patients who are seronegative for both RF and anti-CCP do not respond as well to rituximab as patients who are seropositive for one or both.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis is an auto-immune disease, meaning that the symptoms such as pain and inflammation are caused by the immune system attacking the joints.
Information
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you think you have symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, so they can try to identify the underlying cause.
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis quickly is important, because early treatment can prevent it getting worse and reduce the risk of joint damage.
Find out more about diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis.
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Arthritis Pain In Fingers
Seronegative Vs Seropositive Ra: Are There Other Differences
Past studies seemed to indicate that seropositive RA patients had a worse prognosis and more severe disease progression than seronegative RA patients, according to MedPage Today. This has created a certain stigma around seronegative RA that it is a less severe disease and perhaps even requires less aggressive treatment.
However, the thinking here is changing based on newer research. For example, a Dutch study found that seronegative RA patients had significantly greater disease activity and worse functional ability than seropositive patients on the other hand, seropositive patients had greater joint damage.
A Canadian study found that measures of RA disease activity was higher in seronegative patients than in seropositive patients when the study began. Both seronegative and seropositive patients received similar treatment. When measured again after two years, the seronegative RA patients had a significantly greater improvement in several measures of disease activity and less erosion than those with seropositive disease.
Part of the problem may be the delay in diagnosis. Because people with seronegative RA take longer to get diagnosed and start disease-modifying medication, they may be missing a crucial window to prevent progression and enter remission.
What You Can Do
It leaves doubt in your mind and makes you feel like there has been a misdiagnosis, like maybe you have something curable. Amy
If you have problems getting diagnosed or treated due to negative blood tests, advocate for yourself. Ask your doctor to order both RF and anti-CCP tests. If negative, find information to show your doctor. Ask for a referral to a rheumatologist regardless of test results. If a rheumatologist wont diagnose without positive blood tests, get a second opinion.
You May Like: Can Yoga Help Arthritis Joint Pain
Seronegative Ra May Not Be The Correct Diagnosis
According to Cush and Domingues, a small percentage of people with the seronegative form of RA will do very well on therapy and go into remission, and others will experience severe disease and require medication. And still others will not respond to conventional treatment, which may be because they dont have RA at all. Spondyloarthritis conditions, which often affect the spine, are sometimes mistaken for seronegative rheumatoid arthritis.