It Is Precisely These Similarities That Sometimes Lead To Confusion Between Arthrosis And Arthritis Which Are Sometimes Mistaken For Each Other
Yet they are two very different diseases that differ on several points.
First and foremost, the nature of the disease and the age of those affected: arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease of autoimmune origin that can develop in people of any age, including children, while arthrosis is a degenerative disease that mainly occurs after the age of 50.
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is based on a combination of factors, including:
- Morning stiffness that lasts at least one hour and has been present for at least six weeks
- Swelling of three or more joints for at least six weeks
- Swelling of the wrist, hand, or finger joints for at least six weeks
- Swelling of the same joints on both sides of the body
- Changes in hand x-rays that are hallmarks of rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatoid nodules of the skin
- Blood test that is positive for rheumatoid factor* and/or anti-citrullinated peptide/protein antibodies
* The rheumatoid factor may be present in people who do not have rheumatoid arthritis. Other diseases can also cause the rheumatoid factor to be produced in the blood. A test called CCP antibody can sometimes help to determine whether the rheumatoid factor antibody is due to rheumatoid arthritis or some other disease. This is why the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is based on a combination of several factors and NOT just the presence of the rheumatoid factor in the blood.
It is also important to note that not all of these features are present in people with early rheumatoid arthritis, and these problems may be present in some people with other rheumatic conditions.
In some cases, it may be necessary to monitor the condition over time before a definitive diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis can be made.
Measures To Reduce Bone Loss
Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can cause bone loss, which can lead to osteoporosis. The use of prednisone further increases the risk of bone loss, especially in postmenopausal women.
You can do the following to help minimize the bone loss associated with steroid therapy:
- Use the lowest possible dose of glucocorticoids for the shortest possible time, when possible, to minimize bone loss.
- Get an adequate amount of calcium and vitamin D, either in the diet or by taking supplements.
- Use medications that can reduce bone loss, including that which is caused by glucocorticoids.
- Control rheumatoid arthritis itself with appropriate medications prescribed by your doctor.
Don’t Miss: Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
Osteoarthritis: Elaine Reveals Her Experience Of The Condition
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
In the UK, more than 10 million people have arthritis or similar conditions. There are many types of arthritis with the two most common kinds being osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can develop gradually but also come on quickly. Heres one sign affecting your lungs, causing you to cough.
What Are The Signs That Ra Is Progressing
Signs Your RA Is Progressing
Flares that are intense or last a long time. Diagnosis at a young age, which means the disease has more time to become active in your body. Rheumatoid nodules bumps under your skin, often around your elbows. Active inflammation that shows up in tests of joint fluid or blood.
Recommended Reading: Are Bananas Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Immunomodulatory Cytotoxic And Immunosuppressive Drugs
Treatment with azathioprine or cyclosporine provides efficacy similar to DMARDs. However, these drugs are more toxic. Thus, they are used only for patients in whom treatment with DMARDs has failed or to decrease the need for corticosteroids. They are used infrequently unless there are extra-articular complications. For maintenance therapy with azathioprine, the lowest effective dose should be used. Low-dose cyclosporine may be effective alone or when combined with methotrexate but is rarely used anymore. It may be less toxic than azathioprine. Cyclophosphamide is no longer recommended due to its toxicity.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
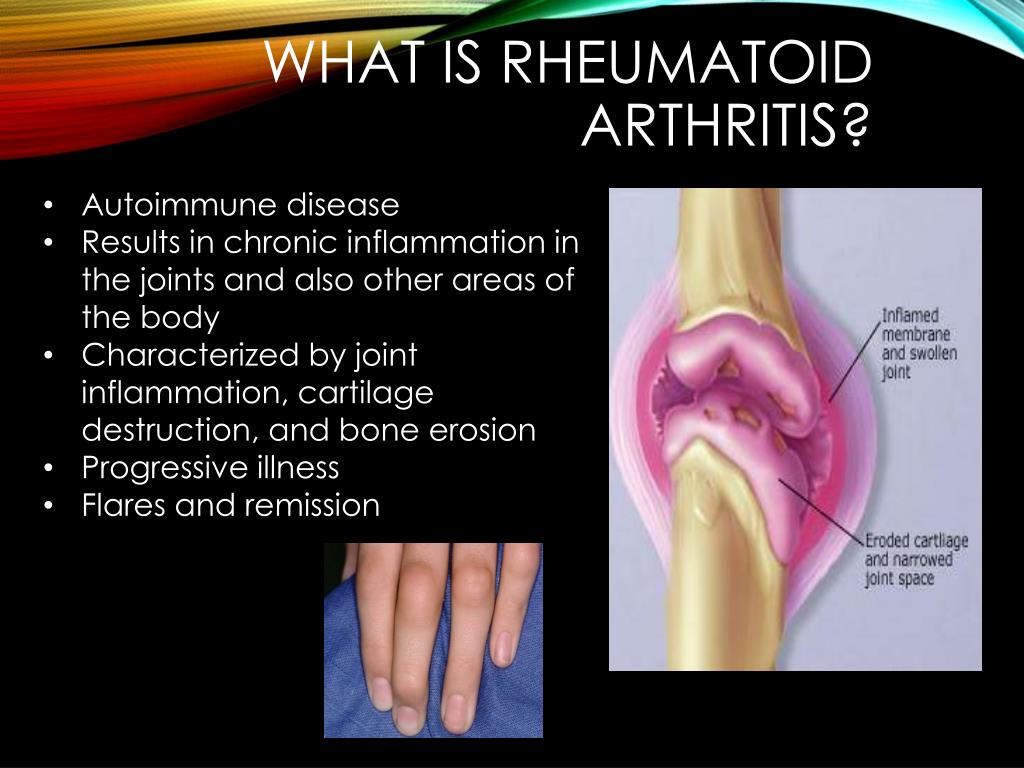
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the joints. Within the body, joints are the points where bones come together and allow for movement. Most of these joints those called synovial joints also provide shock absorption.
RA is an autoimmune condition, in which your immune system mistakes the linings of your joints as “foreign” and attacks and damages them, resulting in inflammation and pain.
You May Like: Bee Pollen For Arthritis
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, which means that your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake, causing inflammation in the affected parts of the body.
RA mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees. In a joint with RA, the lining of the joint becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. This tissue damage can cause long-lasting or chronic pain, unsteadiness , and deformity .
RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are many effective methods for decreasing the pain and inflammation and slowing down the disease process. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are very important.
Extensive research is being done to learn the cause of rheumatoid arthritis and the best methods of treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/17/2017.
References
Also Check: What Helps Lower Back Arthritis
What Are The Mortality Rates Among Canadians With Or Without Rheumatoid Arthritis
Between 20072008 and 20162017, age-standardized all-cause mortality rates decreased among females with diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis and among males with diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis . Mortality rates were consistently higher among males compared to females.
Over the surveillance period, the age-standardized all-cause mortality rate ratios were relatively stable ranging from 1.7 to 1.6 in females and from 1.5 to 1.7 in males. While rate ratios were similar among females and males, they showed an increase in mortality risk among those with diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis.
Figure 4: Age-standardizedFootnote e all-cause mortality rates and rate ratios among Canadians aged 16 years and older with and without diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis , Canada,Footnote f from 20072008 to 20162017
- Footnote e
| 1.7 |
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City
EDUCATION 113
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City
EDUCATION 113
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City
EDUCATION 113
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City
EDUCATION 113
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City EDUCATION 113
Pelvic organ prolapse.docx
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City EDUCATION 113
Cold War.docx
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City EDUCATION 113
Osteopathic medicine.docx
Wesleyan University-Philippines in Cabanatuan City EDUCATION 113
Notes and formulae mathematics.docx
Read Also: Is Eating Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
Medical Imaging In The Cloud
There has been growing trend to migrate from on-premise to a PACS. A recent article by Applied Radiology said, “As the digital-imaging realm is embraced across the healthcare enterprise, the swift transition from terabytes to petabytes of data has put radiology on the brink of . Cloud computing offers the imaging department of the future the tools to manage data much more intelligently.”
What Are Newer Rheumatoid Arthritis Medications And Side Effects
![What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? [Infographic] What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? [Infographic]](https://www.arthritisdaily.net/wp-content/uploads/what-is-rheumatoid-arthritis-infographic-avail.png)
Newer “second-line” drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis include the following:
Each of these medicines can increase the risk for infections, and the development of any infections should be reported to the doctor when taking these newer second-line drugs.
While biologic drugs are often combined with DMARDs in the treatment of RA, they are generally not used with other biologics due to the risk of serious infections. Similarly, JAK inhibitor medication is not used with traditional biologic medicines.
Recommended Reading: Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis Sufferers
Drugs For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The goal is to reduce inflammation as a means of preventing erosions, progressive deformity, and loss of joint function. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are used early, often in combination. Other drug classes, including biologic agents such as tumor necrosis factor -alpha antagonists, an interleukin -1 receptor inhibitor, IL-6 blockers, B-cell depleters, T-cell costimulatory molecule modulators, and Janus kinase inhibitors, seem to slow the progression of RA. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are of some help for the pain of RA but do not prevent erosions or disease progression, may increase cardiovascular risk, and thus should be used only as adjunctive therapy. Low-dose systemic corticosteroids may be added to control severe polyarticular symptoms, usually with the objective of replacement with a DMARD. Intra-articular depot corticosteroids can control severe monarticular or even oligoarticular symptoms but with chronic use may have adverse metabolic effects, even in low doses.
The optimal combinations of drugs are not yet clear. However, some data suggest that certain combinations of drugs from different classes are more effective than using DMARDs alone sequentially or in combination with other DMARDs. In general, biologic agents are not given in combination with each other due to increased frequency of infections. An example of initial therapy is
Other Treatment Options For Chronic Rheumatoid Arthritis: Steroids Nsaids And Pain Relievers
DMARDs and biologic response modifiers are important agents used to treat chronic rheumatoid arthritis. But they arenât the only options. Several other medications can be used to treat severe RA, including the following:
- Steroid medications, such as prednisone. Steroids can quickly reduce RA pain and swelling and slow damage to the joints. They arenât recommended for long-term use. Thatâs because they become less effective over time, and they can have serious side effects, including cataracts, diabetes, and thinning bones.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDS. NSAIDS such as ibuprofen and naproxen sodium help relieve pain and inflammation, and are often used together with DMARDs.
- Pain relievers such as acetaminophen . These medications are another option for relieving pain. They donât, however, affect joint inflammation.
You May Like: Is Banana Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Are The Symptoms Of Inflammatory Arthritis
The most common symptoms of inflammatory arthritis are:
- Joint pain and stiffness after periods of rest or inactivity, particularly in the morning
- Swelling, redness and/or a feeling of warmth in the affected joints
- Inflammation of other areas in the body, such as the skin or internal organs like the lungs and heart
People with inflammatory arthritis generally experience alternating periods of “flares” of highly intense symptoms with periods of inactivity.
How Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Managed
The specific causes of rheumatoid arthritis are unknown, but there are a number of factors associated with an increased risk of developing the disease including family history, smoking, increased age and occupational exposures.Footnote 4Footnote 5 While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are treatment options which aim to alleviate joint symptoms and improve function. Individuals often work with a rheumatologist to develop a treatment plan to prevent further joint damage. Medication is often prescribed as a first line of therapy and is key to controlling disease and preventing damage. Other ways to manage include physical therapy, occupational therapy and education.Footnote 6 Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis who are diagnosed and treated early are less likely to experience long-term joint damage and functional impairments.
Read Also: What Helps Lower Back Arthritis
Living With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong disease. When its treated, it may go away for a little while, but it usually comes back. Its important to see your doctor as soon as symptoms begin. The earlier you start treatment, the better your outcome. Some of the damage from RA is irreversible, so finding the disease and treating it early is very important.
If left untreated, RA can cause other health problems. Your hands may become bent or twisted. Other joints can become deformed. Inflammation will affect your cartilage and bones. Lung and heart problems also can occur. Talk to your doctor if you notice any new symptoms or problems.
What Joints Does Ra Affect
RA usually starts in your hands. The most common affected areas on your body are:
- Elbows
- The knuckle where each finger meets your hand
- The first joint in your fingers
But RA can appear anywhere on your body, including:
- Toes
- Shoulders
- Finger joint closest to the thumbnail
Your symptoms usually are symmetrical, meaning that they show up in the same joints on both sides of your body.
It doesnât happen often, but RA can also affect joints in your voice box called the cricoarytenoid joints. It can make your voice hoarse. Rarely, you may lose your voice.
Also Check: Is Banana Bad For Arthritis
Is There A Cure For Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis. However, with early, aggressive treatment with DMARDs, many patients are able to achieve remission, meaning the symptoms of RA are quiet. Sometimes, the dose of medications may be reduced when remission is achieved. It is unusual for rheumatoid arthritis to remain in remission if medications are stopped, and when this does occur , symptoms and signs usually come back over time. For this reason, it is not advisable to stop rheumatoid arthritis medications unless advised to do so by a rheumatologist.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis
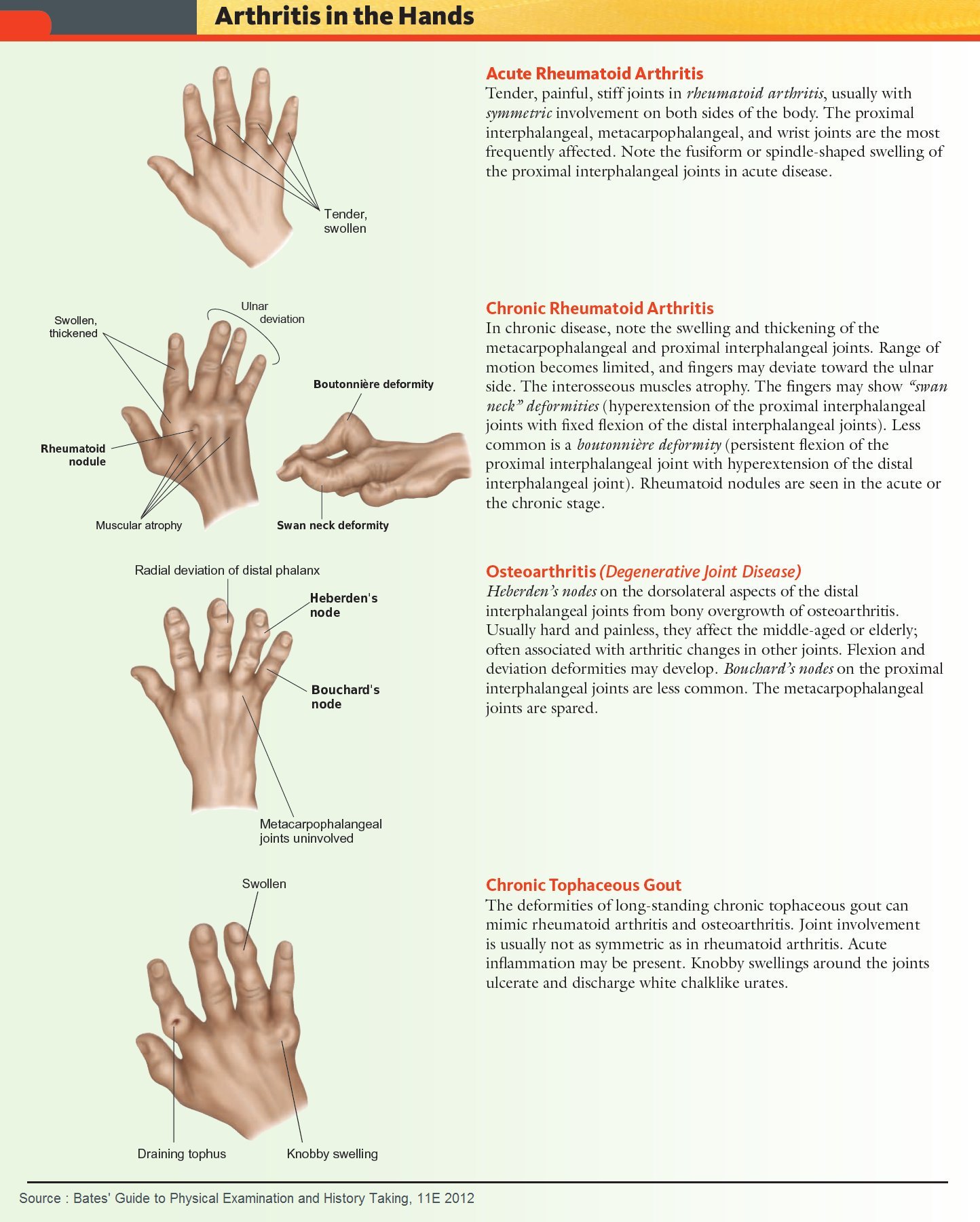
Many people confuse rheumatoid arthritis with osteoarthritis due to their similar symptoms, but the two diseases are caused by different factors.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Whereas rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes joint malfunction due to inflammation, osteoarthritis is a mechanical disease brought on by the destruction of joints through wear and tear.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, with approximately 27 million Americans over the age of 25 having been diagnosed with it. Osteoarthritis is also most commonly seen in people middle-aged to elderly and is the top cause of disability in those age groups, though it can also appear in younger people who have sustained joint injuries.
With osteoarthritis, the cartilage, joint lining, ligaments, and bone are all affected by deterioration and inflammation. When the cartilage begins to break down due to stress or changes in the body, the surrounding bones slowly get bigger and begin to fail.
Osteoarthritis is a slowly progressing disease and occurs in the joints of the hand, spine, hips, knees, and toes. Furthermore, risk factors of this disease most often stem from lifestyle or biological causes, such as:
- Obesity
Osteoarthritis sometimes occurs alongside rheumatoid arthritis or other disease, such as gout.
Recommended Reading: Remedy For Arthritis In Lower Back
Treatment And Medication Options For Rheumatoid Arthritis
To treat RA, doctors aim to stop the progression of the disease by reducing symptoms, controlling inflammation, minimizing joint and organ damage, and improving physical function.
Proven treatments include medication and physical therapy. Early, aggressive measures can help control symptoms and complications before the disease significantly worsens, by reducing or altogether stopping inflammation as quickly as possible.
How Is Inflammatory Arthritis Treated
Inflammatory arthritis is usually treated with a combination of medications that relieve swelling and pain along with others, such as steroids or immunosuppressive drugs, that regulate the immune system. To prevent loss of mobility and joint function, it is essential that patients strive to balance between periods of rest and activity .
As with osteoarthritis, joint replacement surgery may need to be considered when these nonsurgical methods have failed to provide lasting benefit.
Learn more about IA from the articles below or find the best arthritis doctor at HSS for your condition and insurance by selecting treating physicians.
Also Check: Is Tomato Bad For Arthritis
Prognosis For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis decreases life expectancy by 3 to 7 years, with heart disease, infection, and gastrointestinal bleeding accounting for most excess mortality drug treatment, cancer, as well as the underlying disease may be responsible. Disease activity should be controlled to lower cardiovascular disease risk in all patients with RA. recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with RA and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders.)
At least 10% of patients are eventually severely disabled despite full treatment. Whites and women have a poorer prognosis, as do patients with subcutaneous nodules, advanced age at disease onset, inflammation in 20 joints, early erosions, cigarette smoking, high erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and high levels of RF or anticyclic citrullinated peptide .
Compression Of Medical Images
Medical imaging techniques produce very large amounts of data, especially from CT, MRI and PET modalities. As a result, storage and communications of electronic image data are prohibitive without the use of compression. image compression is used by the standard for storage and transmission of medical images. The cost and feasibility of accessing large image data sets over low or various bandwidths are further addressed by use of another DICOM standard, called , to enable efficient streaming of the compressed image data.
Don’t Miss: Is Banana Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The Difference Between Rheumatoid Arthritis And Osteoarthritis
Like RA, people with osteoarthritis can experience painful and stiff joints that make moving around difficult.
People with OA may have joint swelling after extended activity, but OA doesnt cause any significant inflammatory reaction that typically results in redness of the affected joints.
Unlike RA, OA isnt an autoimmune disease. Its related to the natural wear and tear of the joints as you age, or it can develop as a result of trauma.
OA is most often seen in older adults. However, it can sometimes be seen in younger adults who overuse a particular joint such as tennis players and other athletes or those whove experienced a severe injury.
RA is an autoimmune disease. The joint damage from RA isnt caused by normal wear and tear. Its caused by your body attacking itself.
How To Understand Chronic Pain Vs Acute Pain
Acute pain is pain that lasts for a specific time, has a specific cause, and has a protective function. Chronic pain is long-lasting and its cause may be elusive, making it harder to treat.
For the purpose of guiding treatment, doctors will usually categorize the pain as either acute or chronic.
Acute pain is generally defined as being caused by an identifiable source that is associated with some type of tissue damage, inflammation or disease process. Acute pain has a relatively brief duration, usually a few days or weeks, and most often serves a protective function. For example:
- Wrist joint pain while unscrewing a jar top indicates that there is too much stress on the joint, so the person stops trying to unscrew the cap.
- A person who touches a hot stove feels pain and pulls his or her hand away to prevent a serious burn.
- A person recovering from an illness feels pain, signaling the need for rest.
Chronic pain is defined as pain that lasts beyond the expected period of healing.1 Chronic pain is often described as pain lasting longer than 3 to 6 months, but this time period is a rule of thumb normal healing time should be the primary consideration. For example:
The source of chronic pain will affect how it is treated:
Don’t Miss: Are Eggs Bad For Psoriatic Arthritis