Heres Why The Disease Progresses What To Expect And How To Stop It
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition for which there is no cure. But even though the disease is progressive, newer disease-modifying drugs may actually be able to slow or even halt it getting worse. We have many effective treatments for RA that help control the symptoms of joint pain and stiffness, but also prevent progression of the disease and the development of permanent damage, says Lindsay Lally, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City.
Early treatment for RA is key, because whatever joint damage has already occurred cant be reversed. Find out how to recognize the symptoms at each stage of RA, and what can be done to treat it.
How Is Ra Treated
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs biological response modifiers are medications that are an effective second-line treatment. In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
You May Like: Pain Relief For Rheumatoid Arthritis In Hands
Clinical Characteristics Of Patients And Controls
Fifty RA patients and 50 healthy controls were included. One patient withdrew for personal reasons subsequently, the matched control was excluded from analysis. Characteristics of patients and controls, including traditional cardiovascular risk factors, are shown in Table . RA patients had a less favorable cardiovascular risk profile: hypertension was more frequent in RA patients compared to HC. Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure were higher in patients. Furthermore, BMI and the percentage of active smokers were higher in the RA group. Although the proportion of individuals with dyslipidemia did not differ between RA and HC, absolute levels of HDL were lower and triglycerides were higher in RA patients .
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of patients and controls
What Are The First

The American College of Rheumatology has updated guidelines on the treatment of RA and continues to recommend methotrexate as the first-line treatment, unless contraindications are present.16 Methotrexate may not be appropriate in patients with increased risk of hepatotoxicity, such as those with frequent alcohol use or with preexisting liver disease. Other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs can be considered for first-line treatment, including leflunomide , hydroxychloroquine , and sulfasalazine . If disease activity is high, glucocorticoids may also be added.16 Typically, 5 to 10 mg of prednisone daily for four to six weeks is sufficient, but the lowest possible dosage for the shortest possible duration should be used as a bridge until DMARD therapy is effective.
Biologic and Nonbiologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs
NA = not available TB = tuberculosis TNF = tumor necrosis factor.
*Estimated retail price of one month’s treatment based on information obtained at . Generic price listed first brand price listed in parentheses.
Nonbiologic drugs listed in approximate order of priority.
Cost of a single dose typically infused in a hospital setting.
Adapted with permission from Wasserman AM. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Am Fam Physician. 2011 84:1249.
Biologic and Nonbiologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs
NA = not available TB = tuberculosis TNF = tumor necrosis factor.
Don’t Miss: Can You Stop Arthritis
Treatment For Advanced Stage Rheumatoid Arthritis
Advanced cases of rheumatoid arthritis are difficult to treat. The involved joints are structurally damaged. The joint is partially or completely deformed. The aim of treatment is to reduce inflammation, pain, and preserve function of the joint.
Drugs play important role in controlling pain and stiffening of the joint. Corticosteroids and anti inflammatory medicines help in alleviating the symptoms to an extent. But mobility of joint is difficult to deal with if the joints are completely damaged and deformed as in advanced stage. In such cases physical therapy, lifestyle changes such as reducing weight, change in diet, nutritional supplements, may be useful.
Surgical treatment can be thought of if there is significant deformity, joint damage and loss of function. Joint replacement surgery for knee and hip joint helps the patient to live comfortable life.
How To Know If Advanced Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy Is Right For You
For those with rheumatoid arthritis , nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are often the first-line treatment option.
NSAIDs help pain by reducing inflammation in your joints. And while theyve been in use for decades and provide a certain level of comfort, they do nothing to prevent joint damage.
Read on to find out more about these RA medications along with advanced therapies that you may want to consider.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Arthritis
Factors That Influence Disease Course
Several factors can influence the course of your disease. The more factors you have, the more likely it is that you’ll have a progressive and destructive form of rheumatoid arthritis and a severe disease course.
Known influencing factors include:
- Positive for rheumatoid factor or anti-CCP
Remember, though, that even people with severe, progressive disease can achieve remission with proper treatment.
What Are The 5 Worst Foods To Eat If You Have Arthritis
- Trans-fat and fatty foods such as baked foods, cakes, doughnuts, cookies, pizza, and fried chicken
- Foods that contain gluten such as bread, bulgur, wheat, cakes, pies, candies, cereals, communion wafers, cookies and crackers.
- White sugar and refined carbohydrates such as white flour, white bread, white rice, pastries, sodas, snacks, pasta, sweets, and cereals.
- Processed and fried foods such as french fries, fried chicken, cereal, cheese, cookies, chips, etc.
- Grilled, boiled, or fried red meat.
Read Also: What Can You Do To Help Arthritis In Your Hands
Measurement Of Disease Activity
Disease activity was assessed using the Disease Activity Score for 28 joints . Ranges of DAS-28 correspond with disease activity. DAS-28 score < 2.6 indicates remission. DAS-28 score 2.6 to 3.2 indicates low disease activity. DAS-28 score 3.2 to 5.1 indicates moderate disease activity. DAS-28 score above 5.1 is considered high disease activity. Besides the DAS-28, for each patient the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria for remission were determined. In these criteria patients are considered to be in remission if they have a maximum of 1 for each of the following: 28-joint count for swollen joints and tender joints , CRP and patient’s global assessment .
What Is Advanced Arthritis
Advanced arthritis is a term used to describe later-stage arthritis. Affecting multiple joints simultaneously, advanced arthritis is considered a degenerative condition that requires long-term treatment to manage symptoms. Individuals with severe arthritis are placed on a multi-faceted treatment program that can include drug and physical therapies. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair joint damage.
Unfortunately, there is no single test for detecting arthritis. A physical examination of the affected area is initially performed. Subsequent testing can include blood and urine tests to check for markers indicative of inflammation. Imaging tests are conducted to evaluate the extent of inflammation and condition of the affected joint. If there is fluid buildup around the affected joint, a sample of the fluid may be collected for laboratory analysis.
There are several causes of arthritis. The most common trigger for arthritic symptoms is age-related wear and tear on the joints. The bones are naturally cushioned by cartilage, which allows the joints to move freely. Arthritis occurs when cartilage breaks down and the affected bones are allowed to grind against one another. This grinding in the joints causes soft tissue inflammation and fluid accumulation and impairs joint flexibility.
Don’t Miss: What Does Ra Feel Like
Symptoms Of Advanced Stage Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms begin insidiously and rarely with acute onset.
The joint damage is gradual. Mainly hands, ankles, finger, elbow, shoulder and knee joint are involved. Generally the joint involvement is bilateral. In advanced stage of disease fibrous tissue forms in the joint and the bones fuse together.
Patient has joint pain, morning stiffness, swelling of joint, loss of joint motility, development of nodes over the bony prominences. Many patients with advanced stage of rheumatoid arthritis have muscle atrophy. The joints are deformed.
How Your Treatment Changes As Ra Progresses

Early stage. A key focus is to control the inflammation. Thatâs especially critical in the early phase of the disease to prevent joint damage. You may get:
- A disease-modifying antirheumatic drug , such as methotrexate
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , such as aspirin and ibuprofen, for pain
Quitting smoking and losing any extra weight also can help slow your RA.
Moderate stage. This is when you may have trouble with regular daily activities because of pain. You also may tire more easily. There are several options. Your doctor may have you try combining methotrexate with two other DMARD medications, sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine. Another option is a stronger form of DMARDs, called biologic DMARDs, including:
- Tofacitinib
- Upadacitinib
If a certain joint is particularly inflamed, your doctor may give the joint steroid shots. Once your pain is under control, itâs important to exercise to keep ahead of your RA. You also may need physical therapy.
Severe stage. If a TNF inhibitor fails to improve your symptoms, your doctor may recommend you try a different TNF inhibitor or a different class of biologic. If you donât respond to one, you may respond to another.
Surgery is a last-resort treatment for very severe RA. That includes when your joints are deformed and damaged and limit your mobility. The three most common surgeries for RA are:
You May Like: Can You Get A Rash With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Impact Of Disease In The Last Week
Responses to all seven RAID domains were completed in the majority of cases , with one domain missing in 24 additional cases. The missing domain was emotional well-being in all 24 cases and was substituted with the mean of the submitted responses to the other six domains. A total RAID score was therefore calculated for 611 respondents. The mean was 4.79 . A RAID score < 2, deemed a patient acceptable state , was recorded in 12.4% of participants.
shows, for each domain, the proportion of respondents scoring low range , high range , mild and severe scores. In each of the seven RAID domains, > 50% of respondents recorded a score in the high range in the last week. Sleep and fatigue were the domains with the highest proportion of respondent scores in the high range and severe categories, with 74.3%/40.8% and 72%/38.7% of respondents scoring in these categories, respectively. Ability to cope was the lowest scoring domain, with least disability among respondents however, even here 51.2% scored in the high range and only 28.9% in the mild range.
About The Contrast Program
The contRAst Program is a way for patients with rheumatoid arthritis to contribute to a treatment option. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of autoimmune arthritis. In fact, 1.3 million Americans are affected by this condition. It occurs when the immune system attacks healthy tissue. The tissue targeted will be hit with inflammation, and in the instance of RA, the joints are commonly affected.
RA primarily affects smaller joints in the hands and feet. However, it is capable of affecting organs. Women between the ages of 30 and 50 are the primary demographic with this condition. Rheumatoid arthritis was commonly recognized as a disabling illness, but recent treatments have made living with RA easier.
Rheumatoid arthritis does not have a cure, so most treatment options are targeted toward the symptoms. Fortunately, there are research studies looking at investigational drugs to slow the progression of this condition. Currently, many patients with RA do not respond well to treatment options. The contRAst Program is aiming to change that for the better.
You May Like: Arthritis And Skin Rash
Survey Design And Dissemination
Patients with RA were invited by NRAS to complete a survey . This was hosted using the NRAS Health-Unlocked online peer support forum and shared more widely through NRAS social media channels, including Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn and Twitter. A landing page explained the rationale behind the survey, emphasizing the aim to understand the experiences of patients of living with RA. This was followed by screening questions to identify the target population based on current therapies.
What Are The 4 Stages Of Progression Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
To determine the progression of RA, patients are categorized by clinical and radiologic criteria into 4 stages, as follows:
-
Stage I No destructive changes observed upon radiographic examination radiographic evidence of osteoporosis is possible
-
Stage II Radiographic evidence of periarticular osteoporosis, with or without slight subchondral bone destruction slight cartilage destruction is possible joint mobility is possibly limited, but no joint deformities are observed adjacent muscle atrophy is present extra-articular soft tissue lesions are possible
-
Stage III Radiographic evidence of cartilage and bone destruction in addition to periarticular osteoporosis joint deformity without fibrous or bony ankylosis muscle atrophy is extensive extra-articular soft tissue lesions are possible
-
Stage IV Presence of fibrous or bony ankylosis, along with criteria of stage III
Read Also: Is Arthritis Acute Or Chronic
Measurement Of Joint Damage And Cumulative Crp
To determine the amount of joint damage, we used the van der Heijde modification of the Sharp score. The maximum erosion score for the hands is 160 and for the feet 120 the maximum score for joint space narrowing is 120 for the hands and 48 for the feet, resulting in a maximum total score of 448 . Radiography of the hands and feet were performed when recent radiographs, taken within one year, were not available. Cumulative CRP was calculated by calculating the area under the curve by using the trapezoid model .
What Are The Types Of Arthritis
There are several types of arthritis. Common ones include:
- Ankylosing Spondylitis is arthritis that affects the spine. It often involves redness, heat, swelling, and pain in the spine or in the joint where the bottom of the spine joins the pelvic bone.
- Gout is caused by crystals that build up in the joints. It usually affects the big toe, but many other joints may be affected.
- Juvenile Arthritis is the term used to describe arthritis in children. Arthritis is caused by inflammation of the joints.
- Osteoarthritis usually comes with age and most often affects the fingers, knees, and hips. Sometimes osteoarthritis follows a joint injury. For example, you might have badly injured your knee when young and develop arthritis in your knee joint years later.
- Psoriatic Arthritis can occur in people who have psoriasis . It affects the skin, joints, and areas where tissues attach to bone.
- Reactive Arthritis is pain or swelling in a joint that is caused by an infection in your body. You may also have red, swollen eyes and a swollen urinary tract.
- Rheumatoid arthritis happens when the bodys own defense system doesnt work properly. It affects joints and bones , and may also affect internal organs and systems. You may feel sick or tired, and you may have a fever.
Arthritis is seen with other conditions. These include:
You May Like: Rheumatoid Arthritis Thigh Pain
What Tissues Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Attack
Woman with pain from Rheumatoid Arthritis
In simple terms, RA affects the joints of the body. Specifically, RA targets the synovium, which is the lining of the membranes that surrounds the joint capsule. This membrane is a layer of tissue that covers the joints. This synovium becomes hardened from the inflammation process of RA. This change actually results in the destruction of the cartilage and bone at the joint.
The Number Of Swollen Painful Joints You Have Is An Indicator Of Disease Severity
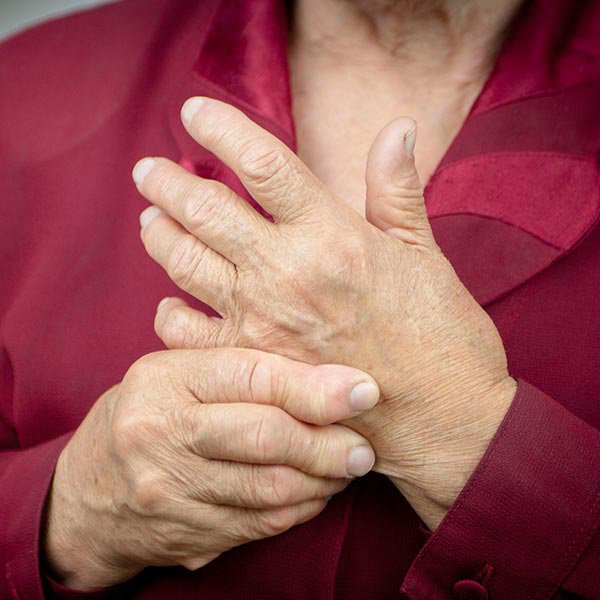
The more joints that are painful and swollen, the more severe the disease may be, says Dr. Cush. Joint pain and swelling are characteristic signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatologists consider this a very important way to measure disease severity.
Your doctor should examine joints in your hands, feet, shoulders, hips, elbows, and other spots to see how many are causing problems. Symmetrical symptoms, such as having the same swollen joints on both sides of the body, are also hallmark symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, Cush says.
Dr. Domingues adds that the traditional morning stiffness and joint swelling that are characteristic symptoms of RA should be discussed with a rheumatologist as soon as possible. Those are signs of active rheumatoid arthritis, and when it presents like that, it gives doctors an opportunity to be aggressive in early treatment or to switch to another class of drugs if symptoms are worsening.
RELATED: People With Rheumatoid Arthritis Develop Resilience by Dealing With Disease Challenges
Recommended Reading: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause A Rash