People With Seronegative Ra Often Have Different Symptoms
The conventional wisdom is that seropositive patients have more severe symptoms, but recent studies suggest that the difference between the two forms of the disease may have more to do with the joints affected than with the severity of the RA symptoms. And a report published in June 2016 in BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders found that further research is needed to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients with seronegative RA. My experience has been that while the symptoms are similar, seronegative patients are more difficult to treat, says Vinicius Domingues, MD, a rheumatologist in Daytona Beach, Florida, and a medical adviser to CreakyJoints.
Family & Personal Medical History
The patients medical history and family history are important factors in helping to reach a RA diagnosis. Studies have shown that the average risk of someone in the general population developing RA is about 1%. However, if there is a family history of the disease, the risk of another family member developing RA increases.
When diagnosing RA doctors ask about the following:
- Patients family members who have or had RA
- Patients existing or past autoimmune disorders
- Patients family members with other autoimmune disorders
- Other medical conditions, illnesses or complications
Depending on each patients unique set of answers, it can help doctors identify factors that lead to a RA diagnosis.
Heart And Blood Vessels
People with RA are more prone to atherosclerosis, and risk of myocardial infarction and stroke is markedly increased.Other possible complications that may arise include: pericarditis, endocarditis, left ventricular failure, valvulitis and fibrosis. Many people with RA do not experience the same chest pain that others feel when they have angina or myocardial infarction. To reduce cardiovascular risk, it is crucial to maintain optimal control of the inflammation caused by RA , and to use exercise and medications appropriately to reduce other cardiovascular risk factors such as blood lipids and blood pressure. Doctors who treat people with RA should be sensitive to cardiovascular risk when prescribing anti-inflammatory medications, and may want to consider prescribing routine use of low doses of aspirin if the gastrointestinal effects are tolerable.
Read Also: What Can You Take To Relieve Arthritis Pain
What Is A Rheumatoid Factor Test
A rheumatoid factor test measures the amount of rheumatoid factor in your blood. Rheumatoid factors are proteins produced by the immune system. Normally, the immune system attacks disease-causing substances like viruses and bacteria. Rheumatoid factors attack healthy joints, glands, or other normal cells by mistake.
An RF test is most often used to help diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of autoimmune disorder that causes pain, swelling, and stiffness of the joints. Rheumatoid factors may also be a sign of other autoimmune disorders, such as juvenile arthritis, certain infections, and some types of cancer.
Other names: RF Blood Test
Why Are Rest And Exercise Important For Ra
You need to be active, but you also have to pace yourself. During flare-ups, when inflammation gets worse, its best to rest your joints. Using a cane or joint splints can help.
When the inflammation eases, its a good idea to exercise. Itll keep your joints flexible and strengthen the muscles that surround them. Low-impact activities, like brisk walking or swimming, and gentle stretching can help. You may want to work with a physical therapist at first.
Recommended Reading: Is Heat Good For Arthritis In The Knee
What If Your Bloodwork Is Normal
Often patients with PsA will have normal CRP and ESR levels. Similarly, while anti-CCP is typically an RA indicator, anti-CCP can be both negative or positive in PsA.
While bloodwork is certainly part of the diagnostic process, patient history and a physical examination are the most important factors to correctly diagnose PsA.4,9
ByAlan King Jr | Submitted On June 24, 2009
There is a wealth of information available out there about rheumatoid arthritis and you can start you search online or go through medical books. You can find all sorts of helpful information about how this ailment is treated and even find alternative treatments. You can even go as far as diagnosing yourself to check if you are showing the symptoms of RA. But its always safe to check for accuracy and validity which is why getting a blood test for rheumatoid arthritis is necessary.
Getting Tested
There are different kinds of blood tests for RA and the results can give you information that can be very useful for diagnostic evaluation and especially recommendations on how it can be treated. What the blood test does is that it finds the disease in your system and affirms if you do in fact have rheumatoid arthritis. Through these blood tests you can get an accurate diagnosis because having these tests are crucial indicators to find out about a patients condition.
Blood Test Types
Dont Miss: What To Give Dogs With Arthritis In Hips
Treatment Of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis
Just like seropositive rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative rheumatoid arthritis cannot be reversed.
Treatment of this disorder is focused on alleviating pain and discomfort associated with inflammation around the body. Treatment can also slow the progression of this disease, or stop the progression altogether.
Its important to listen to your body and be aware of the signs and symptoms of RA, because the earlier we can detect this disorder, the greater our chances are of slowing its progression. Seronegative RA causes serious damage to the joints and bones because the body attacks the synovial tissues that cushion the bones. When the synovial tissue and supporting cartilage deteriorate, the bones no longer have the padding they need, and they start to rub against each other, which deteriorates the bones over time.
Medications
The symptoms of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis can be treated with NSAIDs medications, like ibuprofen. NSAIDs are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with joint swelling. These medications can increase range of motion, as they reduce the swelling that causes stiffness and inhibits movement.
Other medications, specifically disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs , can be taken to slow joint damage caused by seronegative RA. Sulfasalazine is a common DMARD used to slow the progression of seronegative RA and psoriatic arthritis.
Intra-articular Injections
Herbal Remedies
Therapy
Surgery
Read Also: Is Flaxseed Good For Arthritis
Difference Between Lupus And Rheumatoid Arthritis
These two diseases are almost similar in nature. But a closer look displays some distinct differences. Lupus attacks joints and any other part of the body, including the internal organs. It can manifest with skin rashes, fever, and pain. Rheumatoid arthritis primarily attacks the joints. Unlike lupus, it attacks corresponding joints in the body. While rheumatoid arthritis deforms the joints, lupus does not.
Dont Miss: What Is The Best Medicine For Degenerative Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis Blood Tests
The rheumatoid arthritis blood tests that doctors perform to help diagnose the disease include:
- Rheumatoid factor
- C-Reactive Protein
- Antinuclear Antibody
None of these tests can singularly conclude that a patient has rheumatoid arthritis. Rather, doctors look at the combined results from all, alongside a number of other criteria including physical symptoms and genetics, in order to reach a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
You May Like: Can You Test For Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Similar to other autoimmune conditions, rheumatoid arthritis causes your immune system to attack the healthy tissues and cells in your body. Although RA usually damages the joints, it can affect other parts of the body, such as the eyes, heart, or lungs. RA can cause inflammation in joints located in the wrists, hands, knees, and ankles.
Symptoms can vary from person to person, but some early signs of RA include pain and tenderness in the joints. Over time, symptoms may get worse and progress to redness, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. Some people also have a low-grade fever and fatigue.
The exact cause of RA is not known, but several factors increase the risk of having this disease. It occurs more often in older adults and women. Smoking and being overweight also raise the risk of having RA. Certain genes have been linked to a higher chance of developing RA.
Illustration by Verywell
What Do Rheumatoid Factor Test Results Mean
Testing positive for rheumatoid does not necessarily mean the patient has rheumatoid arthritis. A positive for rheumatoid factor test results means that it can lead to or is the cause of inflammatory symptoms from an autoimmune disorder.
In certain cases, however, patients may test positive for rheumatoid factor, yet remain healthy and never experience any obvious symptoms.
Rheumatoid factor can be present in patients several months or even years before clinical rheumatoid arthritis symptoms develop. Depending on the level of symptoms a patient exhibits, the rheumatoid factor test results can assist doctors in reaching a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
Positive rheumatoid factor results in someone who has been clinically diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis may also indicate the potential for a more aggressive disease course. This is possible in both children and adult patients.
Patients who test negative for rheumatoid factor but still exhibit symptoms and meet other diagnostic criteria may still be diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Arthritis In Shoulder
Getting A Referral For A Diagnosis
If your GP suspects you have RA or another inflammatory health condition, they will usually refer you to a specialist rheumatologist for a proper diagnosis. GPs dont have access to the specialist diagnostic tests and equipment that rheumatologists have, so the first step to getting a formal diagnosis for RA is usually through a referral from your GP.
However, if you are experiencing symptoms of RA and want to get a fast and accurate diagnosis of your condition, it can help to book a private consultation directly with a qualified rheumatologist. While there isnt one definitive test that will confirm you have RA, your specialist rheumatologist will conduct a series of diagnostic tests, including blood tests, to either rule out or confirm RA.
Many other inflammatory health conditions can mimic RA symptoms, so having a comprehensive set of diagnostic tests will help clarify the cause of your symptoms and lead to the most appropriate short and long-term treatment plan to help manage your condition.
There are six most commonly used blood tests to help rheumatologists diagnose RA. These are:
You May Like: Whats Wbc In Blood Test
What Causes Rheumatoid Factor
It is not exactly known what causes rheumatoid factor to develop in the blood. However, it is thought to be a combination of genetics and other external risk factors. The uncertainty may be because certain people have low levels of rheumatoid factor, which may not ever be enough to trigger a significant autoimmune response.
On the other hand, people who have high levels of rheumatoid factor may go on to develop autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, while others with elevated rheumatoid factor may not develop an autoimmune disorder. It isnt completely known what triggers the autoimmune response that causes rheumatoid arthritis.
Don’t Miss: Is Drinking Water Good For Arthritis
Lab And Blood Tests For Ra
Here are some of the things you can expect to happen at your appointment if the doctor thinks you have RA.
Personal and family medical history: Your doctor will ask about your past and your relativesâ. If someone in your family tree has RA, you may be more likely to have the disease.
Physical exam: The doctor will check your joints for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion. RA tends to strike several joints.
Antibody blood tests: Doctors look for certain proteins that show up in your blood when you have RA. These proteins mistakenly target healthy cells and kick off the inflammation process. So a high or positive test result means inflammation is in your body.
- Rheumatoid factor : high levels
- Anti-CCP : high levels
- ANA, or antinuclear antibodies: the results are positive or negative
Not all people with RA have these proteins.
Other blood tests: Besides RF and anti-CCP, other blood tests could include:
Complete blood count: It helps your doctor find anemia , which is common in RA. It looks for four things:
- White blood cells 4.8-10.8
- Hematocrit 42-52
- Platelets 150-450
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate: This measures how fast your red blood cells clump and fall to the bottom of a glass tube within an hour. Your doctor might call it a sed rate.
Normal ranges are:
- Men younger than 50: 0-15 mm/h
- Men older than 50: 0-20 mm/h
- Women younger than 50: 0-20 mm/h
- Women older than 50: 0-30 mm/h
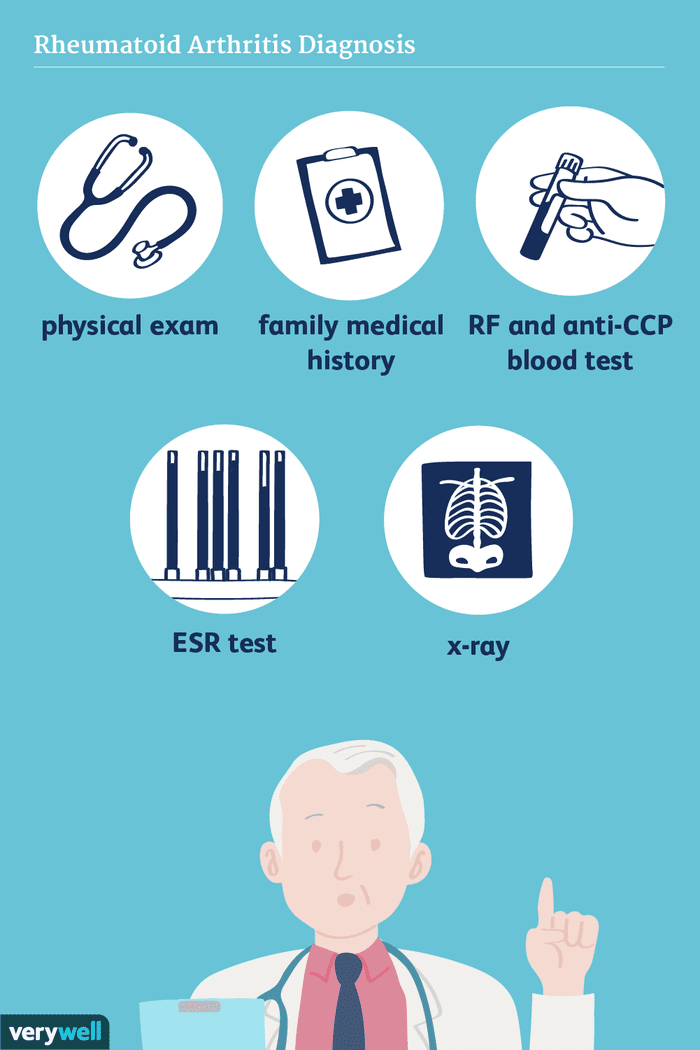
The Diagnostic Criteria For Rheumatoid Arthritis
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis cant be established with just one test. Instead, rheumatologists rely on a combination of your medical history, a physical exam, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging tests to pinpoint the disease.
They also try to rule out the possibility of other conditions that may resemble RA, such as lupus, psoriatic arthritis, gout, or osteoarthritis. This is called a differential diagnosis.
To begin the diagnostic process, a rheumatologist will take your medical history, which includes asking questions about your current symptoms particularly pain, swelling, and stiffness and their location, duration, and severity.
Theyll also ask about your familys medical history as it pertains to RA and other autoimmune conditions. Conditions like RA can be more common in families with RA or other immune system-related health problems. For example, research recently published in the journal Arthritis Care & Research found that people who have a first-degree relative with RA are more than twice as likely as the general population to develop RA. A family history of lupus, scleroderma, thyroid disease, or inflammatory bowel disease also substantially increased the risk of RA.
Your rheumatologist will also perform a physical examination, testing each of your joints for things like swelling, tenderness, and limited range of motion. The location of affected joints is important to diagnosis.
You May Like: What Drugs Are Used To Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis
Read Also: What To Do For Arthritis Pain In Thumb
Take This Test: Do You Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
Related Article
The most common cause for a swollen knee in a young woman?
A swollen knee in a young woman needs a reason. Whats the most common cause? Actually, I dont know the answer to that exactly. But when a 30-something year-old presents to her doctor with a swollen knee thats stiff and
Like this article? Share the love!
Take this test: Do you have Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Lots of people have joint pain or other joint problems. Most of the time, there are not due to rheumatoid arthritis .
There is no single test to diagnose RA. The diagnosis is made from a combination of clinical symptoms and findings, supported by various blood tests .
However, you can try this arthritis screen to determine the likelihood of having the disease by this series of questions which may act as a rheumatoid arthritis test.
Recommended Reading: What Does The Rash From Psoriatic Arthritis Look Like
The Role Of Blood Tests
Blood tests dont provide a simple yes-or-no answer to whether you have RA. But they can help your doctor steer toward a diagnosis. Blood tests narrow down options and suggest how your disease might progress.
After you receive a diagnosis of RA, continued blood tests will monitor the side effects of drugs used in treatment. They can also help track the progression of the disorder.
Also Check: Does Alcohol Consumption Affect Arthritis
Ra Diagnosis: What Criteria Are Used To Diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis
If a patient is showing early signs and symptoms of RA, a doctor can refer the patient to a rheumatologist a physician who specializes in arthritis and other diseases of the joints, muscles and bones. The rheumatologist will work with the patient and the patients primary care physician to reach a RA diagnosis and provide treatment.
Because there is no exact known cause of RA, doctors look at a number of different factors before reaching a diagnosis. To reach a diagnosis, physicians follow a set procedure looking for multiple criteria, rather than one individual test. This includes examining physical symptoms, looking at family and personal medical history, and performing blood and other diagnostic tests .
Some cases may be easier to diagnose than others, especially in the early stages of developing symptoms when symptoms may be less clear. Doctors work hard to ensure theyve looked at all possibilities and that their examination and testing results are consistent with most cases of RA.
Blood Tests For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Finally, there are that can indicate whether or not you have rheumatoid arthritis. Since RA cannot be officially diagnosed with just one blood test, that means once the ACR/EULAR Classification has been met , your doctor will likely ask you to take additional tests to confirm an RA diagnosis. In general, doctors are looking for specific inflammatory markers and/or proteins in your blood that signal you have this condition.
Don’t Miss: What Is Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis
Quick Answers For Clinicians
The symptoms for rheumatoid arthritis are often nonspecific. Therefore, multiple conditions must be considered in the differential diagnosis of RA. Some of these conditions are , gout, and systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease, and Sjögren syndrome. Careful evaluation is necessary for proper diagnosis and medical management of these conditions.
Autoantibodies such as rheumatoid factor , anticitrullinated protein antibodies , and anticarbamylated protein antibodies are a distinctive feature of rheumatoid arthritis . Additionally, their presence often precedes the onset of disease symptoms, making them useful tests for RA diagnosis. Autoantibody testing may also be useful in predicting the severity of disease course. As such, autoantibody testing leads to more accurate diagnosis and prognosis and often contributes to better disease management.
How Is Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis is diagnosed through a series of tests, including blood tests, X-rays, and physical examinations.
Blood tests arent always accurate, because every person is different, so the level of antibodies that each person possesses is likely to differ. The antibody count also depends on the severity of the disorder. In early RA, antibodies are produced at a much slower rate than in the more progressed stages of RA. Some tests wont pick up on these low levels of antibodies and will return negative results.
To diagnose seronegative rheumatoid arthritis, a rheumatoid factor test and an anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides test are performed on the blood. If these tests show positive results, X-rays and physical examinations are also completed to accurately diagnose RA.
If these blood tests show negative results, X-rays and physical examinations are still performed, because seronegative RA could still be present. If X-ray results show inflamed or damaged joints, and a physical examination indicates numerous symptoms of RA, a person will be diagnosed with seronegative RA.
These are some of the common signs and symptoms that your rheumatologist will look for when diagnosing seronegative RA:
- Exposure to certain chemicals, minerals, and air pollutants
Seronegative RA and seropositive RA share most of the same risk factors. Although, studies have shown that obesity and smoking have a considerable impact on the development of seronegative RA.
Also Check: Is There Anything You Can Do To Prevent Arthritis