Age Of Onset For Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is often thought to be a condition related to old age, but this is not the case.
According to the Arthritis Foundation, the average onset of RA is between the ages of 30 and 60 years old, and children can also get it.
Women tend to be diagnosed slightly earlier than men, potentially due to hormonal changes in the mid-30s and then again after the mid-40s.
RA is a chronic condition that can progress over time with periods of increased disease activity, called flares, and periods of remission.
Symptoms of RA vary from person to person depending on the severity of their condition.
An older study on a small group of middle-aged women with RA found that they reported fewer joint symptoms during post-ovulation in their menstrual cycles and also during pregnancy. This is when levels of estrogen and progesterone are higher.
Medical experts tend to agree that the effect of sex hormones combined with environmental and genetic factors could explain the higher prevalence of women diagnosed with RA.
Research continues to seek more answers.
As mentioned, RA isnt only a disease for older people.
According to the , the diagnoses in the United States of all types of arthritis from 2013 to 2015 are as follows:
| Age range |
|---|
- unintentional weight loss
These signs can precede the painful joint symptoms commonly associated with RA.
Recurrent bouts of fatigue along with a general sense of not feeling well may occur weeks or months before other symptoms.
You May Like: How To Deal With Arthritis
What Are The Four Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stage 1: In early stage rheumatoid arthritis, the tissue around your joint is inflamed. You may have some pain and stiffness. If your provider ordered X-rays, they wouldnt see destructive changes in your bones.
- Stage 2: The inflammation has begun to damage the cartilage in your joints. You might notice stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
- Stage 3: The inflammation is so severe that it damages your bones. Youll have more pain, stiffness and even less range of motion than in stage 2, and you may start to see physical changes.
- Stage 4: In this stage, the inflammation stops but your joints keep getting worse. Youll have severe pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of mobility.
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Go Away
No, rheumatoid arthritis doesnt go away. Its a condition youll have for the rest of your life. But you may have periods where you dont notice symptoms. These times of feeling better may come and go.
That said, the damage RA causes in your joints is here to stay. If you dont see a provider for RA treatment, the disease can cause permanent damage to your cartilage and, eventually, your joints. RA can also harm organs like your lung and heart.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have rheumatoid arthritis, you may feel like youre on a lifelong roller coaster of pain and fatigue. Its important to share these feelings and your symptoms with your healthcare provider. Along with X-rays and blood tests, what you say about your quality of life will help inform your treatment. Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms and recommend the right treatment plan for your needs. Most people can manage rheumatoid arthritis and still do the activities they care about.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/18/2022.
References
Also Check: Is Colchicine Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Is Jia Treated
When JIA is diagnosed early and treated appropriately, it can usually be managed effectively. Theres no cure, but theres a lot doctors can do to ease the symptoms of JIA and prevent or limit damage to joints.
For some people, taking medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation. Some patients need to take a weekly medication called methotrexate. Newer medications such as etanercept, adalimumab, abatacept, and tocilizumab can keep the immune system in check and control the disease far better than was possible a few years ago. For arthritis flare-ups, doctors may also use medicines called corticosteroids , but they try to limit these to avoid side effects.
Physical therapy exercises that improve flexibility and the use of heat can help people with JIA control symptoms. Its rare that joints get damaged in a persons teens, but surgery can repair damaged joints if needed.
Heres Why The Disease Progresses What To Expect And How To Stop It

Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition for which there is no cure. But even though the disease is progressive, newer disease-modifying drugs may actually be able to slow or even halt it getting worse. We have many effective treatments for RA that help control the symptoms of joint pain and stiffness, but also prevent progression of the disease and the development of permanent damage, says Lindsay Lally, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City.
Early treatment for RA is key, because whatever joint damage has already occurred cant be reversed. Find out how to recognize the symptoms at each stage of RA, and what can be done to treat it.
Also Check: What Does Arthritis Look Like In Your Hands
What Do Doctors Do
Its not always easy for doctors to diagnose JIA right away. JIA itself can have lots of different symptoms, and some infections, like Lyme disease, have similar symptoms to JIA. So doctors will want to rule out any other possibilities before deciding something is JIA.
If a doctor suspects a patient has JIA, he or she will ask about the persons symptoms, find out if others in the family have had arthritis, and do a complete physical examination to look for joint swelling, eye problems, and rashes. A doctor may do blood tests and X-rays. In some cases, doctors may use a needle to take a sample of synovial fluid from a persons joint.
Sometimes, a doctor might need to see a patient for several months to determine the particular type of JIA the person has.
What Causes Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Like adult rheumatoid arthritis, JIA is an autoimmune disease. This means the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy cells and tissues. JIA is caused by several things. These include genes and the environment. This means the disease can run in families, but can also be triggered by exposure to certain things. JIA is linked to part of a gene called HLA antigen DR4. A person with this antigen may be more likely to have the disease.
Also Check: How To Reduce Knee Swelling From Rheumatoid Arthritis
At What Age Does Osteoarthritis Begin
Osteoarthritis is usually is seen in the elderly age group above the age of 50 years. It is very rarely seen below 50 years because the capacity of the body to compensate for damage occurring at the joint is not reached at its maximum. According to a radiological survey, nearly 50 % of the patients above the age of 65 years has radiological evidence of osteoarthritis.
Also Check: How To Treat Lower Back Arthritis
General Joint Pain And Stiffness
In addition to morning joint stiffness, you may also experience general joint stiffness throughout the day, especially after a period of inactivity.
Some of the first areas RA stiffness typically affects are the wrists and certain joints in the hands and feet, but its also possible to experience pain and stiffness in your knees or shoulders. Usually, both sides of your body will be affected.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If You Have Arthritis
What Are The Treatment Options For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Medications to treat rheumatoid arthritis can be very effective when the disease is caught early and managed properly.
We can hope to put people in remission so they can get back to doing whatever they enjoy, without a lot of limitations, says Dr. Brunet.
These medications include:
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: These drugs can slow rheumatoid arthritis progression by suppressing the bodys immune system. They include methotrexate , leflunomide , hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine .
- Biologics: This subset of DMARDs target specific proteins in the body, so they tend to have less of an effect on the immune system as a whole. They also work by suppressing the immune system and include abatacept , adalimumab , anakinra , certolizumab , etanercept , golimumab Simponi, infliximab , rituximab , tocilizumab and tofacitinib .
- Corticosteroids: These drugs, such as prednisone, reduce inflammation and may be given on a short-term basis to relieve joint pain and swelling. They usually arent recommended for long-term use, because they can cause side effects including high blood glucose levels and bone thinning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs : These medicines can be given by prescription or over-the-counter to reduce pain and inflammation. Examples include ibuprofen and naproxen sodium.
Part of a patients treatment for rheumatoid arthritis may also include physical or occupational therapy to learn exercises that can help keep joints flexible and muscles strong.
An Overview Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
This is due to inflammation of the synovial lining . This can cause the diseaseâs characteristic swelling, pain, limited range of motion, and decreased function, but also joint damage and deformity as the synovium begins to thicken and inflamed cells release enzymes that digest bone and cartilage.
RA typically has a symmetrical pattern of joint damage. For example, both of your knees are usually affected rather than just one. Signs and symptoms can differ slightly depending on the part of the body thatâs affected.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
Can Imaging Exams Detect Arthritis
Imaging exams can help your healthcare provider get a clear picture of your bones, joints and soft tissues. An X-ray, MRI or ultrasound can reveal:
- Bone fractures or dislocations that may be causing you joint pain.
- Cartilage breakdown around your joints.
- Muscle, ligament or tendon injuries near your joints.
- Soft tissue inflammation.
Rheumatoid Factor And Anti
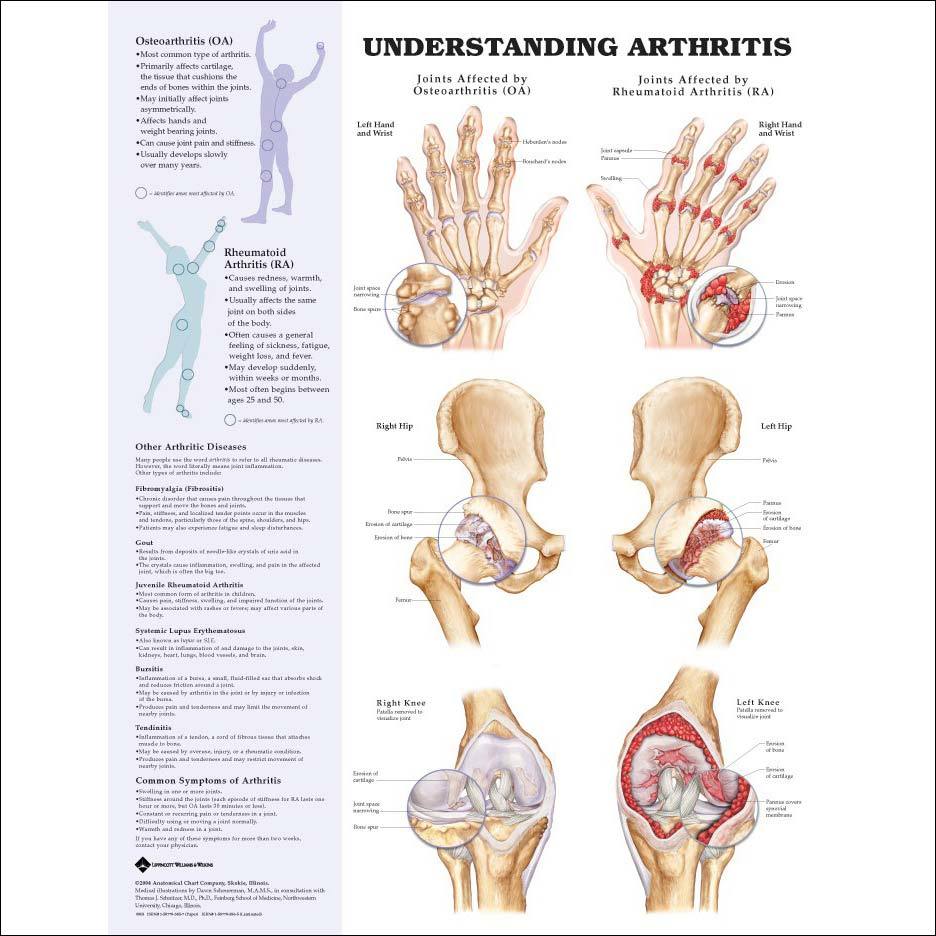
Specific blood tests can help to diagnosis rheumatoid arthritis, but are not accurate in every person. About half of all people with rheumatoid arthritis have a positive rheumatoid factor present in their blood when the disease starts, but about one in every 20 people without rheumatoid arthritis also tests positive for this.
Another antibody test known as anti-CCP is also available. People who test positive for anti-CCP are very likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis, but not everybody found to have rheumatoid arthritis has this antibody.
Those who test positive for both rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP may be more likely to have severe rheumatoid arthritis requiring higher levels of treatment.
You May Like: How To Cure Rheumatoid Arthritis Naturally
Joint Subluxation And Dislocation
Joint erosions, which are visible on X-ray, are associated with limited joint mobility and function. As the joint becomes eroded and cartilage is damaged, bone-on-bone contact can be the painful end result.
Severe damage to cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and bone can cause joints to become unstable. Joint instability can lead to subluxation or, less often, dislocation.
While many joints can become deformed or subluxed due to RA, toes are among the more common ones. The associated pain, damage, and functional limitations often lead to a loss of mobility.
People whoâve had RA for more than a decade are at risk of developing a condition called cervical myelopathy, in which joints of the spine can dislocate and put pressure on the brain stem, spinal cord, and spinal nerve roots. This is an uncommon but serious problem that needs to be corrected with surgery to avoid permanent damage.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Healthcare Provider Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next healthcare providerâs appointment to help you ask the right questions.
Read Also: Is Eating Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
How Is Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Treated
The goal of treatment is to reduce pain and stiffness, and help your child keep as normal a lifestyle as possible.
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Treatment may include medicines such as:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines , to reduce pain and inflammation
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines , such as methotrexate, to ease inflammation and control JIA
- Corticosteroid medicines, to reduce inflammation and severe symptoms
- Medicines called biologics that interfere with the body’s inflammatory response. They are used if other treatment isnt working.
Talk with your childs healthcare provider about the risks, benefits, and possible side effects of all medicines.
Other treatments and lifestyle changes may include:
- Physical therapy, to improve and maintain muscle and joint function
- Occupational therapy, to improve ability to do activities of daily living
- Nutrition counseling
- Regular eye exams to find early eye changes from inflammation
- Regular exercise and weight control
- Getting enough rest
- Learning to use large joints instead of small joints to move or carry things
Don’t Miss: Can Arthritis Be Cured Permanently
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
Osteoarthritis Of The Hip
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease, which means it causes gradual damage to the joint. It is the most common form of hip arthritis and can affect other joints. Hip osteoarthritis is typically caused by wear and tear related to aging and worsens over time. The breakdown of cartilage leads to pain and inflammation.
Hip osteoarthritis may develop faster in some people due to irregular shape of the bones forming the hip joint. For example, if the ball and the socket parts of the hip joint dont perfectly fit together , they may rub against each other, eventually leading to osteoarthritis. This may also happen in people with hip dysplasia, who have a hip socket that is too shallow to support the ball of the femur. This places abnormal stress on the cartilage, causing it to wear away prematurely.
Stages of Osteoarthritis of the Hip
Don’t Miss: Is Biofreeze Good For Arthritis
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means your immune system attacks the cells that line your joints by mistake, making the joints swollen, stiff and painful.
Over time, this can damage the joints, cartilage and nearby bone.
It’s not clear what triggers this problem with the immune system, although you’re at an increased risk if:
- you are a woman
- you have a family history of rheumatoid arthritis
Find out more about the causes of rheumatoid arthritis.
Joint Damage Pain Deformities Loss Of Function: Late
It is important for people with these symptoms to be diagnosed as soon as possible, because if RA isnt diagnosed and treated early the synovial lining can become so inflamed that it damages and erodes the cartilage this makes bone loss more likely.
Moving joints becomes more difficult, and flare-ups can occur with greater frequency. These joint changes are called erosions, and they can lead to deformities of the bone, such as crooked fingers, says Daniel Solomon, MD, MPH, chief of the section of clinical sciences in the division of rheumatology at Brigham and Womens Hospital in Boston. In severe cases, bones may eventually fuse together. All of this further contributes to pain and loss of function.
Read Also: Does Collagen Help With Arthritis
Read Also: What Can I Use For Arthritis
What Is Arthritis In Dogs
In healthy joints, the slippery tissue called cartilage cushions the ends of the bones in the joints. Unhealthy joints show something different. It is osteoarthritis or arthritis in dogs, no matter the term, the results are the same: cartilage that breaks down, causes pain and swelling. As it gets worse, bone spurs can form, causing more pain and joint damage.
These illustrations show the difference between healthy and unhealthy cartilage. The healthy joint looks like this:
An unhealthy joint looks like this:
Unfortunately, we cannot see this with our own eye, but rather need some sort of X-Ray or MRI to see it.
How would you know if your dog had unhealthy cartilage or healthy cartilage?
Some think the key symptom of dog arthritis is limping, but dogs are pretty good at hiding pain and may never limp. For some dogs, when this happens, your dog may simply become less active or show signs of stiffness when getting up. There may be some visible signs of arthritis in your dogs legs.
Arthritis can be difficult to recognize and your dog may not show any signs.
Thats why its important to talk to your veterinarian today about keeping your dog active and youthful. The earlier you start the better chance you have of bringing out the puppy inside him.
The Impact Of Ra Symptoms
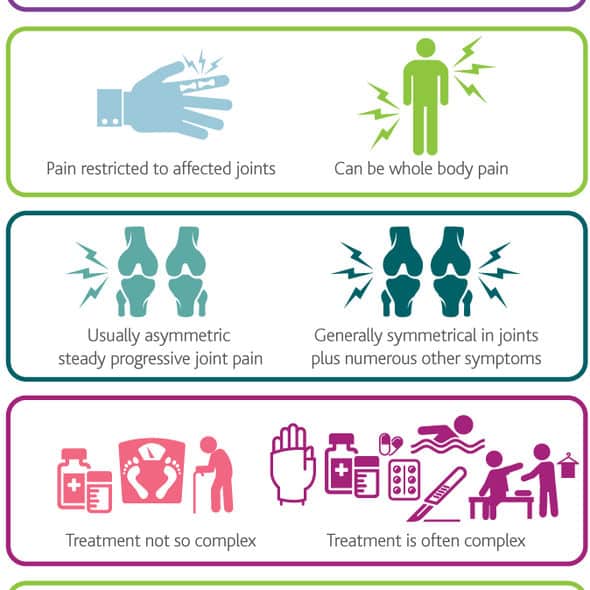
Once it develops, RA is a lifelong condition. Living with RA can take a toll over time. Physically, joint symptoms can impact your ability to perform everyday activities and care for your family, while emotionally, you may not feel like participating in social activities or like you’re to do your best at work. Talking to your rheumatologist can help you achieve better results in managing RA symptoms.
To help manage your RA diagnosis, download our Doctor Discussion Guide to inform your next appointment with your rheumatologist. Through open conversation with your doctor about how symptoms are affecting you physically and emotionally, together you can decide your best plan for treatment.
There are so many different faces for RA, and its not relegated to one age group. If you are scared because of the information that youve read… have a conversation with your doctor. Take that opportunity dont let it pass you by. Because you have one life.
– Meg, CIMZIA patientIndividual results may vary.
Don’t Miss: Can Gout Cause Rheumatoid Arthritis