What Are Common Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease
Between taking care of yourself and family members and trying to manage a social life and career, its common for women to feel tired and achy. But are these symptoms of a stressful life, or could they be tied to an underlying condition like autoimmune disease?
Ana-Maria Orbai, M.D., M.H.S., is a rheumatologist at the Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center. Rheumatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal diseases and autoimmune conditions . Orbai talks about how to recognize common autoimmune disease symptoms and when you should see a doctor.
What Hip Symptoms Of Ra Feel Like
Hip pain doesnt always indicate rheumatoid arthritis. It may be from another kind of arthritis, like psoriatic arthritis, or from a pinched nerve, tight muscles around the hips and buttocks, or simple overuse.
When your hip pain is due to inflammation caused by RA, you may experience other symptoms as well.
Here are some of the signs of hip pain from RA:
- dull ache around the groin, buttocks, or thighs
- heat or warmth to the touch around the hips, buttocks, thighs, and groin
- pain or stiffness in the morning, which may reduce with movement or activity
- difficulty standing or walking, due to pain in the hip joint
- limping, often after RA progression leads to further joint damage
As RA can affect your whole body, you may also experience generalized symptoms like:
- high temperature
- sweating
RA can affect both hips, as the condition often creates symptoms in the same joint on both sides of the body.
Ra Facts: What Are The Latest Statistics On Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex disease that affects each patient differently. People from all ethnic backgrounds are at risk of developing RA. It is the third most common type of arthritis behind osteoarthritis and gout.
Below are some RA facts and statistics provided by ongoing disease research.
Recommended Reading: What To Do For Arthritis Pain In Hands
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated
There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. But there are treatment options your doctor can prescribe to help manage your pain and stop further damage to your joints. Your doctor may recommend a combination of medicines, including:
- Pain relief medicines, such as paracetamol.
- Omega-3 supplements. This is a type of fat naturally found in foods such as certain fish that you can take as a food supplement to help with pain and stiffness.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or cyclo-oxygenase-2 selective inhibitors. These are pain relief medicines that your doctor might prescribe when paracetamol and supplements do not relieve your pain and stiffness.
- Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs , such as methotrexate. These are a group of medicines that reduce your symptoms and the damage to your joints, including medicines known as biologic DMARDS .
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisolone. These are medicines that can help manage your pain and stiffness during flare ups. Corticosteroids are available as tablets, or it might be injected by your doctor into a joint to reduce pain.
Other complementary treatments such as massage, acupuncture or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation can help reduce your pain. But they will not reduce the damage to your joints and should not replace your prescribed medications.
Tripterygium wilfordii is a Chinese herb that is not recommended to treat rheumatoid arthritis as it can have dangerous side effects.
What Are The Different Types Of Inflammatory Arthritis
The major types of inflammatory arthritis include:
When detected and treated in its early stages, the effects of inflammatory arthritis can be greatly diminished, or the condition may even disappear completely. The importance of proper diagnosis, particularly in the early stages of the disease, may prevent serious, lifelong arthritic complications.
The Early Arthritis Initiative of the connects patients quickly and efficiently with a rheumatologist who can evaluate their joint pain and get each patient started on an appropriate course of treatment. HSS also offers specialized patient for conditions such as and .
Don’t Miss: Arthritis Attack Symptoms
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are many effective methods for decreasing the pain and inflammation and slowing down the disease process. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are very important.
Extensive research is being done to learn the cause of rheumatoid arthritis and the best methods of treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/17/2017.
References
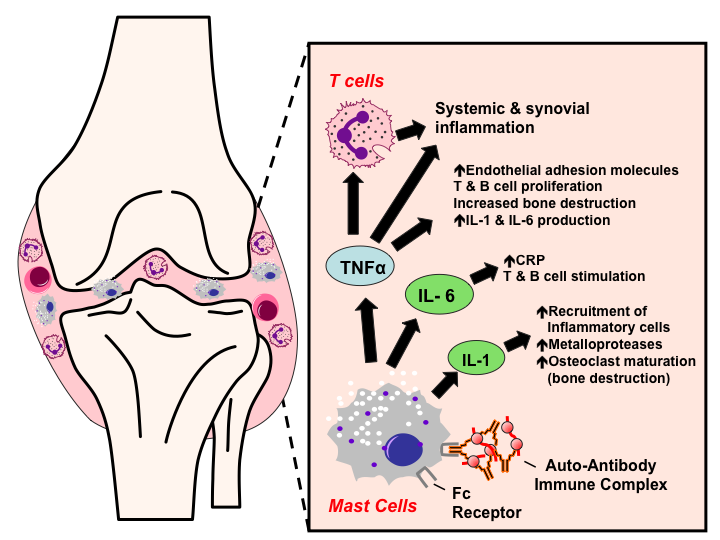
Amplification In The Synovium
Once the generalized abnormal immune response has become established which may take several years before any symptoms occur plasma cells derived from B lymphocytes produce rheumatoid factors and ACPA of the IgG and IgM classes in large quantities. These activate macrophages through Fc receptor and complement binding, which is part of the intense inflammation in RA. Binding of an autoreactive antibody to the Fc receptors is mediated through the antibody’s N-glycans, which are altered to promote inflammation in people with RA.
This contributes to local inflammation in a joint, specifically the synovium with edema, vasodilation and entry of activated T-cells, mainly CD4 in microscopically nodular aggregates and CD8 in microscopically diffuse infiltrates. Synovial macrophages and dendritic cells function as antigen-presenting cells by expressing MHC class II molecules, which establishes the immune reaction in the tissue.
Also Check: How Can I Relieve Arthritis Pain In My Hands
Treatment Options For Ra In The Hip
Theres no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but treatment is available to reduce inflammation and stop the progression of the disease.
The goal of treatment is to help you achieve remission, which is a period when symptoms disappear. Your treatment will depend on the nature and severity of your symptoms.
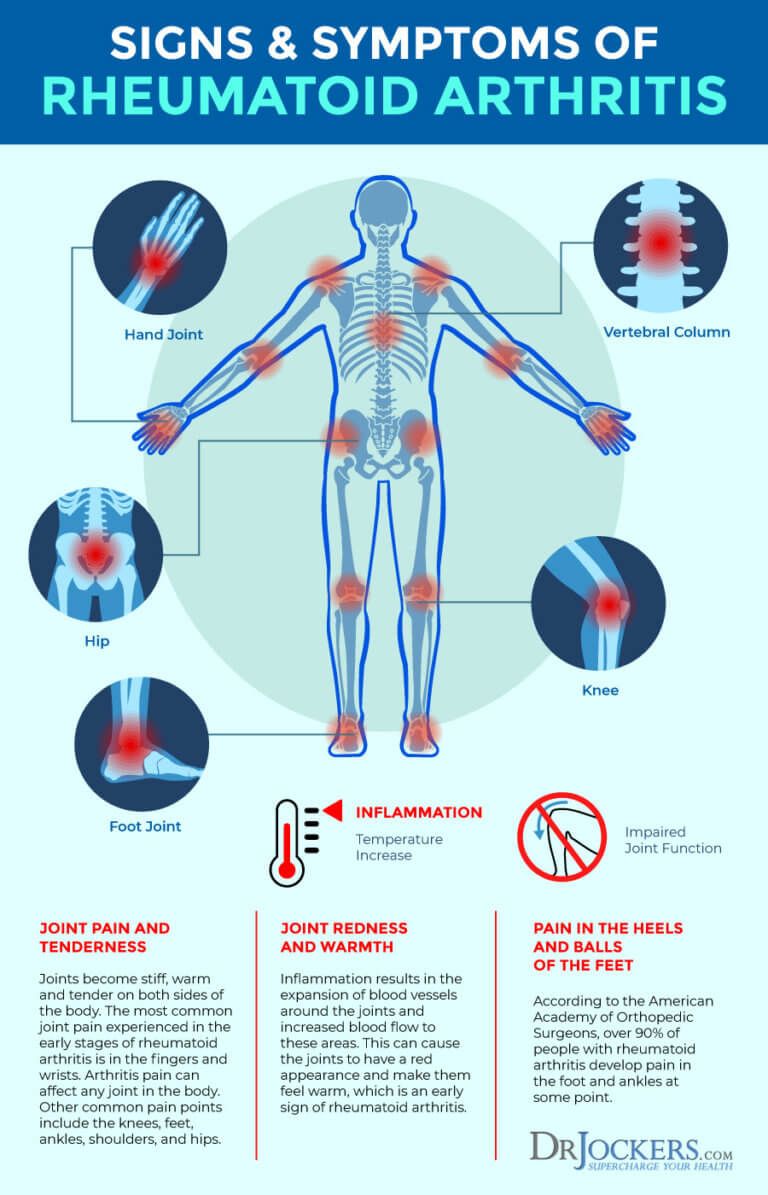
Facts And Statistics About Ra Symptoms
RA has a very specific set of clinical symptoms that indicate the onset of the disease. The most common initial clinical symptoms of RA include:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Symptoms affecting multiple joints including the hands and fingers
- Symmetrical symptoms affecting both the left and right sides of the body
- Morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes
- Symptoms lasting longer than six consecutive months
Doctors will perform a physical examination, blood tests, as well as imaging tests in order to consider all possible diagnoses. Doctors will also look for additional symptoms which indicate increased inflammation such as:
- Chronic fatigue
- Illness and malaise
- Depression
There are four main stages of RA progression beginning with the onset of clinical symptoms to the end stage, which will be reached if appropriate treatment is not applied.
Also Check: Does Arthritis Cause Swelling
Raynaud’s Came Years After My Ra Diagnosis
Interestingly, I developed Raynaud’s myself a couple years after being diagnosed with RA. I was probably around age 20-21, I think. And while my Raynaud’s “attacks” have always been fairly mild, my younger sister gets pretty severe ones. She does not have RA, yet she has an autoimmune thyroid condition and developed Raynaud’s around age 19. This makes me assume that we both have the primary form of Raynaud’s, despite also living with autoimmune diseases.
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means your immune system attacks the cells that line your joints by mistake, making the joints swollen, stiff and painful.
Over time, this can damage the joints, cartilage and nearby bone.
It’s not clear what triggers this problem with the immune system, although you’re at an increased risk if:
- you are a woman
Find out more about the causes of rheumatoid arthritis.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Arthritis In Legs And Knees
Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Hereditary
Rheumatoid arthritis isnt considered a hereditary disease, but it does run in some families. This may be due to environmental causes, genetic causes, or a combination of both.
If you have family members who have or have had RA, talk to your healthcare provider, especially if you have any symptoms of persistent joint pain, swelling, and stiffness unrelated to overuse or trauma.
Having a family history of RA increases your risk of getting the disease, and early diagnosis can make a big difference in how effective treatment will be.
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by a problem with the immune system, which mistakes your own body tissue as if it were an outside harmful invader . The immune system attacks your own joints, causing inflammation.
The precise cause of the immune system problems that lead to RA is unknown, but it is thought that they are triggered by environmental factors such as infections with viruses or bacteria in people who have some genetic predisposition to the disease. However, although some patients do remember having viral-type illness when their RA symptoms first started, most do not. No specific infectious agent has been found that triggers the immune system’s response. Some evidence points to cigarette smoking and oral inflammation as triggers for the early development of rheumatoid arthritis.
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of RA. Genetic factors means that a person has genes that place him or her at risk for RA, and that those genes have been turned on . But it is the contact with an environmental agent in the genetically predisposed person that seems to initiates the self-perpetuating inflammation characteristic of RA. While it is clear that genetics are important, if you have RA, this does not at all mean that your child or grandchildren will develop it. Actually, the risk is very small.
Read Also: Finger Arthritis Relief
Diseases That Mimic Rheumatoid Arthritis
A number of diseases can be similar to rheumatoid arthritis . There is notable overlap between symptoms of RAjoint pain, stiffness, fatigueand those of RA-like rheumatic or autoimmune diseases, other types of arthritis, and some viral and bacterial infections.
Ruling out other conditions that mimic RA, such as Lyme disease, lupus, and fibromyalgia is part of diagnosing RA. This process relies on a combination of your physical examination, medical history, laboratory test results, and imaging studies.
Even after you’ve been diagnosed with RA, your healthcare providers may consider other conditions if your symptoms are still not improving, despite treatment with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs .
Research published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases found that more than 40% of people who were diagnosed with RA actually had a different condition.
It’s also possible that you could have RA and another condition.
Verywell Health / Hilary Allison
What Is Raynaud’s Disease
According to the Mayo Clinic, “Raynaud’s disease causes some areas of your bodysuch as your fingers and toesto feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. In Raynaud’s disease, smaller arteries that supply blood to your skin narrow, limiting blood circulation to affected areas .”1
Recommended Reading: Arthritis Triggers
What Are The Treatments For Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is usually treated with a combination of medications to relieve swelling and pain while regulating the immune system. Joint surgery to relieve pain and disability, including joint replacement, may also be considered when these nonsurgical methods have failed to provide lasting benefit.
With early detection and intervention, RA and other forms of inflammatory arthritis can be treated very effectively. The connects patients quickly and efficiently with a rheumatologist who can evaluate their joint pain and get each patient started on an appropriate course of treatment. HSS also offers specialized for people with RA.
Today, we are blessed with a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis and characteristics of RA and the availability of safe and effective medications that can alter the natural history of RA and improve function. We start with the premise that RA is eminently controllable, and the goal of our therapies is “no evidence of disease.” That means no signs of redness, warmth, swelling or tenderness and normal function. Since we would not accept uncontrolled illness in angina, chronic obstructive lung disease, hypertension or diabetes, we should similarly not accept it in RA. Luckily, today, we have the therapeutic tools to make this happen.
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
Recommended Reading: Ra Hand Pain Relief
Scientists Discover Link Between Rheumatoid Arthritis And Other Serious Disease
- Date:
- University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
- Summary:
- Researchers have discovered that having one kind of autoimmune disease can lead to another.
Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have discovered that having one kind of autoimmune disease can lead to another.
The scientists serendipitously found that mice with antibody-induced rheumatoid arthritis in their joints went on to develop spinal lesions similar to those in axial spondyloarthritis which causes fusion of the vertebrate and curvature, or bending, of the backbone.
The study was published today in the journal Immune Network.
“Our results suggest that one autoimmune disease, such as inflammatory arthritis, may also lead to a secondary autoimmune disease such as AxSpA,” said the study’s lead author Nirmal Banda, PhD, professor in the division of rheumatology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. “This interesting disease association may be due to the binding of anti-collagen autoantibodies to the spine, or to some alteration of the immune system that requires further investigation.”
These same anti-collagen antibodies are also present in humans with arthritis. They directly attack joint cartilage resulting in inflammation and pain.
Banda noted that every mouse injected with collagen antibody-induced arthritis developed arthritis and then curvature of the spine consistent with axial spondyloarthritis.
“I believe we are the first to make this link,” he said.
Story Source:
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, which means that your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake, causing inflammation in the affected parts of the body.
RA mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees. In a joint with RA, the lining of the joint becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. This tissue damage can cause long-lasting or chronic pain, unsteadiness , and deformity .
RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
Also Check: How To Help Someone With Arthritis
Learn More About Raynaud’s Disease
If you have Raynaud’s or you just want to read more about it, the two sources I used for this article, from The Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins, have even more detailed information on their websites . There are other great sources online too, of course.
Most of the time, I forget that I even have Raynaud’s disease, except when it decides to randomly attack my fingers and toes. And now that it’s been happening again lately, I wonder: Who else with RA has this condition? I’m curious to know! What’s yours like? Mild, moderate, severe? Do you get what I mean when I mention the “ghostly toes” and the strange, numb feeling?
If you are struggling with this irritating cold-weather condition, hang in there, because I’m dealing with it too. You’re not alone. And make sure that you stock up on plenty of gloves and warm socks this winter!
Most Common Autoimmune Diseases
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammation of the lining of the joints, leading to pain and swelling typically in the hands and feet. It can affect anyone, but is most prevalent in women over 40. Rheumatoid arthritis can sometimes affect other organs as well, such as skin, eyes, lungs and blood vessels. As with all autoimmune disorders, treatment focuses on managing pain and minimizing bone erosion and joint damage.
We have more in-depth information on Rheumatoid Arthritis here.
2. Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of arthritis in children under 16. Symptoms usually include pain and swelling in the joints, and can vary from moderate to severe. In some cases, symptoms will subside over time while others can persist well into adulthood.
We have more in-depth information on juvenile rheumatoid arthritis here.
3. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Lupus can be difficult to diagnose because it shares symptoms with many other disorders. The inflammation resulting from lupus can affect many different areas of the body, from the lungs, heart, joints, skin, kidneys, and brain. Like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus is more prevalent in women and can sometimes be identified by a butterfly-shaped rash on the face, along with photosensitivity, fatigue and fever, joint pain, and other skin lesions that worsen under sun exposure.
We have more in-depth information on lupus here.
You May Like: Ra In Hand Symptoms