Medications To Manage Symptoms
Some drugs can help relieve symptoms and slow the diseases progression.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are available from pharmacies over the counter . Examples include Motrin, Advil, and Aleve. Long-term use and high doses can lead to side effects, including:
- high blood pressure
- kidney and liver problems
Corticosteroids reduce pain and inflammation and may help slow joint damage, but they cannot cure RA. If NSAIDs do not work, a doctor may inject a steroid into the joint. Relief is usually rapid, but the effect is variable. It can last a few weeks or months, depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Corticosteroids can help with acute symptoms or short-term flare-ups. However, a doctor will limit these injections to no more than three times per year because of their impact on the soft tissue structures around the joints. More frequent injections can potentially damage these structures or cause them to tear off from where they attach to bone.
Learn more about steroid injections here.
Preclinical Autoimmune Disease: A Comparison Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Multiple Sclerosis And Type 1 Diabetes
- 1Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Amsterdam Rheumatology and Immunology Centre, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 2Department of Experimental Immunology, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 3Amsterdam Rheumatology Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 4Department of Neurology, MS Center Amsterdam, Amsterdam University Medical Center , Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam Neuroscience, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 5Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 6Amsterdam Rheumatology and Immunology Center, Reade, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Rheumatic Symptoms And Primary Immunodeficiencies
Autoantibodies occur more often in patients with primary immunodeficiencies than in healthy people, and autoimmune illness can occur. This is most common in CVID, affecting approximately 20 percent of patients. A range of autoimmune disorders can occur, including thyroid disease, hematological disease, polyarthritis resembling rheumatoid
ARTHRITIS, SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS, and SJOGREN’S syndrome. The arthritis associated with CVID is usually chronic and affects knees, wrists, ankles, and fingers but unlike rheumatoid arthritis does not cause erosions of bone. In the primary immunodeficiencies there is an increased risk of developing lymphoma.
The treatment for the primary immunodeficiencies associated with severe T cell or enzyme defects is bone marrow transplantation. In patients with defective antibody production immunoglobulin replacement therapy with intravenous immunoglobulin decreases the risk of infections.
inclusion body myositis This form of inflammatory muscle disease was discovered just over 30 years ago. Since then it has been increasingly recognized and is now the most common muscle disease in people over the age of 50 years. It occurs mostly in older people and is more frequent in men.
Cause
Recommended Reading: What Do You Do For Arthritis In Your Fingers
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated
Joint damage generally occurs within the first two years of diagnosis, so its important to see your provider if you notice symptoms. Treating rheumatoid arthritis in this window of opportunity can help prevent long-term consequences.
Treatments for rheumatoid arthritis include lifestyle changes, therapies, medicine and surgery. Your provider considers your age, health, medical history and how bad your symptoms are when deciding on a treatment.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, which means that your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake, causing inflammation in the affected parts of the body.
RA mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees. In a joint with RA, the lining of the joint becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. This tissue damage can cause long-lasting or chronic pain, unsteadiness , and deformity .
RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
Read Also: Does Stelara Help Psoriatic Arthritis
What Are The Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA generally develops in 4 stages:
Stage 1: An X-ray will not show any bone or joint destruction.
Stage 2: An X-ray will show the impact on the bone.
Stage 3: An X-ray will show a particular kind of erosion of the cartilage and bone that a doctor can recognize as resulting from RA and deformities in the affected joints.
Stage 4: The person will experience ankylosis, which is when a joint becomes stiff and fuses with the bone.
What Are The Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis affects everyone differently. In some people, joint symptoms develop over several years. In other people, rheumatoid arthritis symptoms progress rapidly. Many people have time with symptoms and then time with no symptoms .
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Pain, swelling, stiffness and tenderness in more than one joint.
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods.
- Pain and stiffness in the same joints on both sides of your body.
Also Check: How Serious Is Psoriatic Arthritis
What Are The Symptoms Of Autoimmune Diseases
The symptoms of an autoimmune disease depend on the part of your body that’s affected. Many types of autoimmune diseases cause redness, swelling, heat, and pain, which are the signs and symptoms of inflammation. But other illnesses can cause the same symptoms.
The symptoms of autoimmune diseases can come and go. During a flare-up, your symptoms may get severe for a while. Later on, you may have a remission, which means that your symptoms get better or disappear for a period of time.
Make Your Diet As Anti
Dr. Singh is telling his patients to stick to a Mediterranean diet pattern to possibly help reduce inflammation and boost mood. This means loading up on fruits and vegetables, beans, nuts, white meat, fish, and whole grains, and avoiding red meat and high-sugar, processed food. Of course, this is easier said than done when fresh, healthy food may be hard to come by or too expensive.
Check out these anti-inflammatory meals made with mostly shelf-stable ingredients for inspiration.
You May Like: What Pills Are Good For Arthritis
Fatigue Is As Daunting As Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain
Most people are aware that RA is a chronic pain condition. Managing the pain and learning to live with pain become the focus after being diagnosed with RA. Most people dont realize that, with RA, fatigue is as big of a problem as pain. Research published in the journal RMD Open suggests that fatigue in RA is a persistent problem and an unmet need. Even with improved treatment strategies, fatigue persists.
RELATED: Does the Autoimmune Protocol Diet Help Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis And Thrombocytopenic Purpura Associated With Common Variable Immunodeficiency
ABSTRACT
REFERENCES
Abbott JK, Gelfand EW. Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2015 35:637-58.
Hammarström L, Vorechovsky I, Webster D. Selective IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency . Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 120:225-31.
Saifi M, Wysocki CA. Autoimmune Disease in Primary Immunodeficiency: At the Crossroads of Anti-Infective Immunity and Self-Tolerance. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2015 35:731-52.
Conley ME, Notarangelo LD, Etzioni A. Diagnostic criteria for primary immunodeficiencies. Representing PAGID and ESID . Clin Immunol. 1999 93:190-7.
Bonilla FA, Bernstein I, Khan D, Ballas ZK, Chimen J, Frank MM, et al. Practice parameter for diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005 94:S1-64.
Gathmann B, Grimbacher B, BeautéJ, Dudoit Y, Mahlaoui N, Fischer A, et al. The European internet-based patient and research database for primary immunodeficiencies: results 2006-2008. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 157:3-11.
Ameratunga R, Brewerton M, Slade C, Jordan A, Gillis D, Steele R, Koopmans W, Woon ST. Comparison of diagnostic criteria for common variable immunodeficiency disorder. Front Immunol. 2014 15:415
Seidel MG. Autoimmune and other cytopenias in primary immunodeficiencies: pathomechanisms, novel differential diagnoses, and treatment. Blood. 2014 124:2337-44.
Read Also: How Can You Get Arthritis In Your Knee
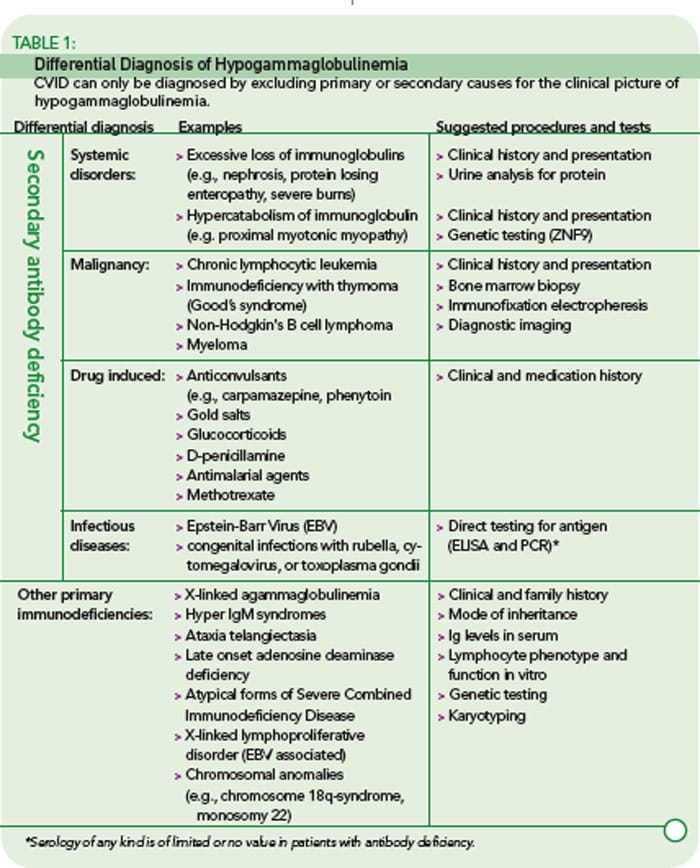
Diagnosis Of Immunodeficiency Disorders
-
Sometimes genetic testing
Doctors must first suspect that an immunodeficiency exists. Then they do tests to identify the specific immune system abnormality.
Doctors suspect immunodeficiency when one or more of the following occur:
-
A person has many recurrent infections .
-
Infections are severe or unusual.
-
A severe infection is caused by an organism that normally does not cause severe infection .
-
Recurring infections do not respond to treatment.
-
Family members also have frequent and severe recurring infections.
E How Do We Document And Evaluate Immune Deficiency Disorders Excluding Hiv Infection
1. General.
a. Immune deficiency disorders can be classified as:
Primary for example, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, thymic hypoplasia , severe combined immunodeficiency , chronic granulomatous disease , C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency.
Acquired for example, medication-related.
b. Primary immune deficiency disorders are seen mainly in children. However, recent advances in the treatment of these disorders have allowed many affected children to survive well into adulthood. Occasionally, these disorders are first diagnosed in adolescence or adulthood.
2. Documentation of immune deficiency disorders. The medical evidence must include documentation of the specific type of immune deficiency. Documentation may be by laboratory evidence or by other generally acceptable methods consistent with the prevailing state of medical knowledge and clinical practice.
3. Immune deficiency disorders treated by stem cell transplantation.
a. Evaluation in the first 12 months. If you undergo stem cell transplantation for your immune deficiency disorder, we will consider you disabled until at least 12 months from the date of the transplant.
b. Evaluation after the 12-month period has elapsed. After the 12-month period has elapsed, we will consider any residuals of your immune deficiency disorder as well as any residual impairment resulting from the treatment, such as complications arising from:
Graft-versus-host disease.
Immunosuppressant therapy, such as frequent infections.
You May Like: Does Popping Your Bones Cause Arthritis
Follow Public Health Guidance
Its important to continue to follow recommendations from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for people who may be at a higher risk of complications, even as economies begin to reopen. This includes:
- Stay home as much as possible
- Follow social distancing when near others
- Wear a face covering in public
- Wash hands thoroughly and often
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces
What Are The Goals Of Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
The most important goal of treating rheumatoid arthritis is to reduce joint pain and swelling. Doing so should help maintain or improve joint function. The long-term goal of treatment is to slow or stop joint damage. Controlling joint inflammation reduces your pain and improves your quality of life.
Also Check: Do Tomatoes Make Arthritis Worse
Activation Of The Immune System
RA, SLE, MS, and T1D all have a latent phase that precedes formal clinical diagnosis . The length of this phase can vary between diseases and within individuals at risk for the same disease, but a common feature is the activation of the immune system, which is visible to a varying degree in the different diseases and precedes the onset of symptoms.
Figure 2 This illustration shows an overview of the transition from at-risk to disease diagnosis. In purple is represented RA, in orange SLE, in blue MS, and in green T1D. *Also known as incomplete Lupus. ACPA, Anti-citrullinated protein antibody RF, Rheumatoid factor anti-CarP, anti-carbamylated ANA, antinuclear antibody anti-dsDNA, anti-double strand DNA anti-RNP, anti-nuclear ribonucleoprotein IAA, autoantibodies against insulin IA-2, autoantibodies against insulinoma-associated antigen-2 GAD or GADA, autoantibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase anti-ZnT8, autoantibodies against zinc-transporter 8 ICA, islet cell antibodies.
Humoral Immunity
As described above, the majority of RA patients is seropositive, and these antibodies develop over many years before the clinical disease, with increasing concentrations as well as specificities . In particular ACPA are thought to be involved in the development of synovitis and bony erosions.
So far, in MS no specific autoantibody has been found, however, autoantibodies against several CNS cells have been reported in this disease .
Cellular Immunity
Soluble Factors
What Triggers Autoimmune Diseases
That’s still not clear. But researchers are making progress.
As with other life-long conditions like heart disease, itâs probably not just one thing that causes these disorders. Many things work together to raise your risk, like your genes, environment, and lifestyle choices, says John A. Peyman, PhD, program officer in the autoimmunity branch of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases .
For starters, it seems that you can be more likely to get an autoimmune disease if other members of your family have one. Your parents can pass down genes that make it more likely.
One gene has been linked with most autoimmune diseases, Peyman says. Itâs called human leukocyte antigen .
â200 other genes contribute a tiny bit to the chance of getting RA,â he says.
So what happens if you inherit one of the genes?
You may be more likely than the average person to get an autoimmune disorder. While another person might get an infection and get better, the same infection might trigger the inflammation inside your body that leads to the disease, Peyman says.
For example, researchers are studying super-tiny living things called microbes in your gut, mouth, and on your skin. They may work more closely with the immune system than people thought, Ladd says. If they’re out of balance, it may trigger your immune system and make more inflammation.
You May Like: What Foods Flare Up Arthritis
What Are The Four Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stage 1: In early stage rheumatoid arthritis, the tissue around your joint is inflamed. You may have some pain and stiffness. If your provider ordered X-rays, they wouldnt see destructive changes in your bones.
- Stage 2: The inflammation has begun to damage the cartilage in your joints. You might notice stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
- Stage 3: The inflammation is so severe that it damages your bones. Youll have more pain, stiffness and even less range of motion than in stage 2, and you may start to see physical changes.
- Stage 4: In this stage, the inflammation stops but your joints keep getting worse. Youll have severe pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of mobility.
Work Disability Is Common With Rheumatoid Arthritis
According to the CDC, RA can make work difficult. In fact, adults with RA are less likely to be employed than those who do not have RA, research shows. As the disease progresses and worsens, many people with RA find they cannot work at the level they once did. Work loss among people with RA is highest among people whose jobs are physically demanding, and less so among those with jobs that are less physical or where they have influence over the job pace and job activities.
While some studies suggest work disability rates with RA are somewhat variable, prospective studies show that the rate is about 30 to 40 percent five years after diagnosis, according to research published in the journal Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
It has been theorized that better treatment options, such as biologic drugs, would have a positive impact on RA and lower work disability rates. While there may be improvement in individual cases, research suggests that overall work disability remains a problem with RA.
It can be difficult to determine when it is the right time to stop working, but you must consider your physical limitations and the demands of your current job, as well as the demands of any type of work. Social Security Disability defines disability for their purposes of determination as the inability to engage in any substantial gainful activity by reason of any medically determinable physical or mental impairment that has lasted or is expected to last for 12 months or result in death.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Arthritis In Your Fingers
What Are The Risk Factors For Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are several risk factors for developing rheumatoid arthritis. These include:
- Family history: Youre more likely to develop RA if you have a close relative who also has it.
- Sex: Women and people designated female at birth are two to three times more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
- Smoking:Smoking increases a persons risk of rheumatoid arthritis and makes the disease worse.
- Obesity: Your chances of developing RA are higher if you have obesity.
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. Researchers think its caused by a combination of genetics, hormones and environmental factors.
Normally, your immune system protects your body from disease. With rheumatoid arthritis, something triggers your immune system to attack your joints. An infection, smoking or physical or emotional stress may be triggering.
Is rheumatoid arthritis genetic?
Scientists have studied many genes as potential risk factors for RA. Certain genetic variations and non-genetic factors contribute to your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Non-genetic factors include sex and exposure to irritants and pollutants.
People born with variations in the human leukocyte antigen genes are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis. HLA genes help your immune system tell the difference between proteins your body makes and proteins from invaders like viruses and bacteria.
Also Check: How To Tell If You Have Osteoarthritis Or Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Is A Common Variable Immune Deficiency
Common Variable Immune Deficiency is the dysfunction of the immune system typically caused due to a mutation in a gene or genes. It can cause recurrent bacterial and rarely viral infections and is characterized by low protective antibodies and a higher risk of infections. People who have a common variable immune deficiency cannot make antibodies against agents that can cause infection.
In the vast majority of common variable immune deficiency cases, the causes are unknown. But it has been identified that genetic mutation is the cause for 10 % of people with CVID. Therefore it is believed to occur due to the combination of both environmental and genetic factors. But the ecological factors are unclear.
Common symptoms of common variable immunodeficiency are:
-
Swollen glands or lymph nodes.
-
Cough with yellow, green, or brown phlegm or mucus.
-
Wheezing or other breathing issues.
Common variable immunodeficiency is the most commonly occurring primary immunodeficiency in adulthood. It presents a wide range of clinical manifestations that often include non-infectious complications and heightened susceptibility to infections.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis
RA is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. Osteoarthritis leads to many of the same symptoms as RA but is due to the typical wear and tear of the joints.
While RA usually affects the same joints on both sides of the body, osteoarthritis may only affect one side.
Although other symptoms can help a person figure out if they are experiencing RA or osteoarthritis, only a doctor can diagnose these conditions.
It may be difficult for a doctor to diagnose RA in its early stages, as it can resemble other conditions.
The CDC recommends getting a diagnosis within 6 months of the onset of symptoms so that treatment can begin as soon as possible.
A doctor will look at the persons clinical signs of inflammation and ask how long the person has experienced them and how severe their symptoms are. They will also perform a physical examination to check for swelling, functional limitations, or other unusual presentations.
They also may recommend some tests, including:
Read Also: Is Vitamin D Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis