Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Spine
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the immune system turns on itself. It attacks synovium the lining of the joints. Although rheumatoid arthritis is more common in other joints, it can also affect the spine, specifically the cervical region . Rheumatoid arthritis of the spine is not caused by wear and tear, so its considered an inflammatory arthritis. It may cause back pain even when these joints are not in use. It tends to affect women more than men.
How Is Arthritis In Feet Treated
A diagnosis of arthritis does not necessarily mean that your quality of life will decrease. By seeking treatment early and taking an active role in the management of your arthritis, you can control the pain and limit damage to your joints.
Left untreated, however, arthritis can eventually lead to foot and ankle deformities.
A treatment regimen for arthritis in the foot or feet may include nonsurgical therapies and/or surgery. There are many nonsurgical treatment options, and they are often used in combination with one another. These can be divided into three categories:
Medical therapy
- A brace or a cane
Physical and complementary medicine
- Physical therapy and gentle exercises
- Acupuncture or massage at and around affected joints
- Application of a heating pad or a damp, warm towel to affected joints
- Weight control
For many types of arthritis, aspirin is used as the first-line treatment, and its success or failure can help guide other therapeutic interventions. Treatment can control inflammation and preserve or restore joint function.
Surgical intervention may be considered as a last resort if the arthritis does not respond to nonsurgical interventions.
The choice of surgery depends on the type of arthritis you have, its impact on the joints, and its location. More than one surgery may be needed. Surgeries used to treat arthritis in the feet include:
- Arthroscopic debridement
- Arthrodesis or fusion
- Arthroplasty or joint replacement
Foods That Trigger Inflammation In Arthritis
Arthritis is a disease of the musculoskeletal system that specifically affects the joints, and is mainly caused by a combination of external factors such as foods, physically demanding jobs, allergies or previous injuries. There are various types of arthritis, but the most common forms are rheumatoid arthritis and infectious arthritis. Arthritis is also one of the major reasons of physical disability among older adults over the age of 55 years. Although there is no known cure for arthritis, the symptoms can be kept under control and joint mobility and range of motion can be enhanced with the help of physical and occupational therapy. Consuming more anti-inflammatory foods and avoiding inflammation causing foods can also help in alleviating the symptoms of arthritis.
You May Like: Signs Of Arthritis In Arm
What Are The Prognosis For Arthritis And What Are Arthritis Complications
The outlook for patients with arthritis depends on its severity, complications, and whether or not there are non-joint manifestations of the disease. For example, rheumatoid arthritis can affect the lungs, kidneys, eyes, etc. Chronic joint inflammation can lead to permanent damage to the joint and loss of joint function, making movement difficult or impossible.
Effects On Your Daily Life
- See a doctor or other relevant healthcare professional if youre unable to do everyday tasks due to joint or muscle pain.
- If youve lifted something heavy and hurt your back, for example, take some painkillers, apply some heat and try to stay active. If the pain doesnt ease after a couple of weeks or so, see a doctor.
Its important to see a doctor if you get any new symptoms or if you have any trouble with drugs youre taking.
If you have an appointment with a doctor, to help make sure you get the most out of it, you could take a list of questions with you and tick them off as they are discussed.
You could also keep a symptoms diary with details of how youre feeling in between appointments. Some people find that taking a friend or relative with them to an appointment can provide support and ensure that all important points are discussed.
Also Check: How You Get Arthritis
Degenerative Or Mechanical Arthritis
Degenerative or mechanical arthritis refers to a group of conditions that mainly involve damage to the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones.
The main job of the smooth, slippery cartilage is to help the joints glide and move smoothly. This type of arthritis causes the cartilage to become thinner and rougher.
To compensate for the loss of cartilage and changes in joint function, the body begins to remodel the bone in an attempt to restore stability. This can cause undesirable bony growths to develop, called osteophytes. The joint can become misshapen. This condition is commonly called osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis can also result from previous damage to the joint such as a fracture or previous inflammation in the joint.
The Role Of Cytokines And Other Inflammatory Mediators
Evidence from in-vivo and in-vitro studies indicates that synoviocytes, chondrocytes, and cells from other joint tissues can produce and/or respond to a number of cytokines and chemokines that may also be detected in osteoarthritis synovial fluid. Although the mechanism by which the inflammatory process is initiated in osteoarthritis is unclear, abnormal mechanical and oxidative stresses are probably involved. Chondrocytes in osteoarthritis cartilage, especially those in clonal clusters, express IL-1, IL-1-converting enzyme , and type 1 IL-1 receptor . IL-1 is synthesized by chondrocytes at concentrations that are capable of inducing the expression of MMPs and other catabolic genes, and it colocalizes with TNF-, MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-8, and MMP-13, and type II collagen cleavage epitopes in regions of matrix depletion in osteoarthritis cartilage. The expression of MMPs is tightly regulated in chondrocytes under physiological conditions, wherein its expression pattern is restricted and the MMPs play essential roles in the low-turnover ECM remodeling.
Read Also: What Is Considered A High Rheumatoid Factor Level
Lifestyle And Trigger Factors
Arthritis is also known to develop suddenly without a known cause, and at any age. In some instances, something in your medical history or lifestyle or just a combination of both of these could be responsible for your arthritis.
*All individuals are unique. Your results can and will vary.
There are a number of factors that could be responsible for your arthritis if youre susceptible to it:
- Physically demanding jobs can increase your risk of osteoarthritis, more so if it involves heavy and repetitive activity.
- the Previous injury to a joint can also increase your risk of osteoarthritis.
- Infections, illness or an allergic reaction can cause short-lived arthritis.
- Some diets may appear to make your arthritis worse.
Read More:TriFlex Review Is This Product Safe To Use?
Whats The Outlook For Someone Living With Arthritis
Since theres no cure for arthritis, most people need to manage arthritis for the rest of their lives. Your healthcare provider can help you find the right combination of treatments to reduce symptoms. One of the biggest health risks associated with arthritis is inactivity. If you become sedentary from joint pain, you may face a greater risk for cancer, heart disease, diabetes and other serious conditions.
Recommended Reading: Edema Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Is Inflammatory Arthritis Treated
There are no cures for any of the inflammatory arthritis conditions. Thus, the goals of treatment are to treat the pain, as well as to reduce inflammation, maintain joint movement and overall strength, as well as the muscular strength, to decrease stress on the joint, and to overall, treat the underlying joint disease.
Thus, treatment of inflammatory arthritis is multifaceted and tailored to each persons needs. It also may change as the disease process changes. A typically plan includes medications, rest, exercise, and in some cases, surgery to repair joint.
The plan incorporates all of these treatment modalities, but is also dependent on the type of disease, the person’s age, type of medications he or she is taking, overall health, medical history, and severity of symptoms.
Many drugs are used to treat inflammatory arthritic conditions. Pain reduction is important the drugs that are often used treat not only pain but also reduce inflammation. Examples include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and Celebrex. Occasionally, stronger medications called opioids are used as well.
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are used to treat inflammation. Often, they are used on a short-term basis due to side effects.
Medications can also be prescribed to slow the progression of the disease. Examples include certain chemotherapy medications , disease-modifying treatments, and biologic therapy.
Spinal Arthritis May Contribute To Other Issues In The Spine
Spinal arthritis may cause bone spurs overgrowths on the edges of the bones. In the spine, bone spurs particularly affect facet joints, making them grow larger. This condition is called facet joint hypertrophy. Although bone spurs on their own are not harmful, they may narrow the passages for the spinal cord and the nerves exiting the spine. This may lead to two painful conditions:
-
Spinal stenosis compression of the spinal cord inside the spinal canal
-
Radiculopathy pinching of the peripheral nerves as they exit the spine
Ankylosing spondylitis may also cause additional problems such as:
-
Stress fractures in places where new bone has formed
-
Collapsed vertebrae
-
A spinal deformity called kyphosis
Recommended Reading: Does Arthritis Cause Redness
How Does A Doctor Diagnose Arthritis
There are three different types of tests used to diagnose arthritis inpatients. Based on the symptoms the diagnose differs.
Osteoarthritis Of The Spine
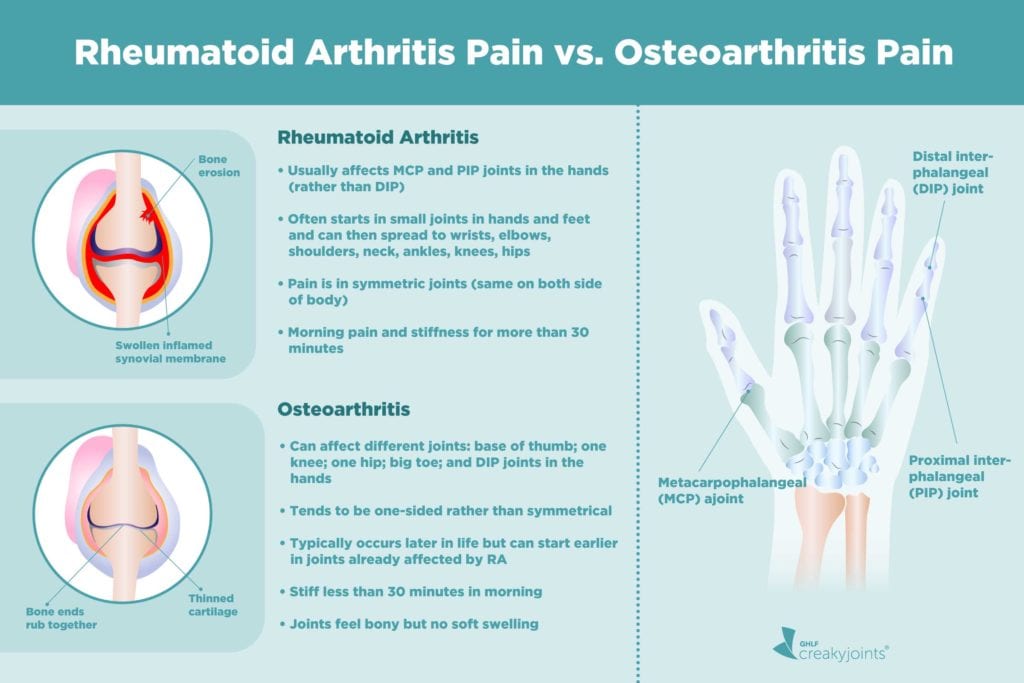
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of spinal arthritis. It usually affects the lower back and develops through wear and tear. As the cartilage between the joints slowly breaks down, it leads to inflammation and pain. Because the pain is from mechanical damage, it is typically more noticeable when you bend or twist your back. Past back injuries may also contribute to the development of degenerative arthritis of the spine.
Osteoarthritis of the spine usually affects the facet joints between the vertebrae. It is also known as facet joint arthritis, facet joint syndrome and facet disease. In some cases, degeneration of the spinal discs may contribute to facet joint arthritis. As discs between the vertebrae become thinner, more pressure is transferred to the facet joints. This leads to more friction and more damage to the cartilage.
When these degenerative changes occur in the neck, this condition is called cervical spondylosis. Arthritis in the neck doesnt always cause pain, and many people have no noticeable symptoms.
Also Check: Mayo Clinic Arthritis Treatment
The Role Of Synovitis In Osteoarthritis
Inflammation is a major factor associated with the risk of both progression of cartilage loss and signs and symptoms of disease, including joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, indicators of synovitis . Synovitis, involving infiltration of mononuclear cells into the synovial membrane and production of proinflammatory mediators, including interleukin 1 , tumor necrosis factor- , and chemokines, is common in early-stage and late-stage disease . MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 and cysteine cathepsins B and S, as well as IL-6, can be detected in osteoarthritis synovial fluid samples, although at significantly lower levels than in rheumatoid arthritis patients, reflecting the enhanced inflammatory processes in the RA joint . The synovial effusions may be visualized in the joint by magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound . The association between meniscal damage and synovial effusion has been noted by MRI. In patients with traumatic meniscal injury, but no radiographic evidence of osteoarthritis, the synovium retrieved during arthroscopic meniscectomy is frequently inflamed and increased inflammation scores are associated with increased pain and dysfunction and a unique chemokine profile .
How Are Inflammatory Diseases Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask about your medical history and do a physical exam, focusing on:
- The pattern of painful joints and whether there are signs of inflammation
- Whether your joints are stiff in the morning
- Any other symptoms
Theyll also look at the results of X-rays and blood tests for biomarkers such as:
- C-reactive protein
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Don’t Miss: Is Vicks Vaporub Good For Knee Pain
Early Osteoarthritis: Synovial Inflammation Precedes Structural Change
The field of clinical rheumatology often considers OA to be the condition manifest by significant cartilage loss and joint space narrowing. In fact, the current American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for OA require the presence of radiographic changes of bony enlargement or osteophyte formation . It is now clear that inflammation is present in OA joints well before the development of significant radiographic change. The combination of sensitive imaging modalities as well as direct arthroscopic visualization has suggested that, even at its earliest stages, before visible cartilage degeneration has occurred, OA is already an inflammatory disease. In one study, serial arthroscopies performed on knees with symptomatic but preradiographic OA revealed a clear association between the presence of synovitis and the future development of medial cartilage loss . Studies using magnetic resonance imaging with or without contrast enhancement have similarly suggested an association between the presence of synovitis and OA progression .
What Is The Patient’s Role In Treating Or Managing Arthritis
The patient is the most important member of the health care team.
The patient plays an important role in his or her medical care. The patient can contribute to the success of a treatment plan by:
- learning about arthritis
- reporting progress and setbacks to health team
- keeping a positive attitude
- developing relationships with the rest of the health care team
Keeping a positive attitude, though sometimes difficult, is an important ingredient in overcoming arthritis. Asking questions and finding out as much as you can about of arthritis and its treatment is important. So talk over your concerns with your doctor. If you still need more information , ask the nurse, physical therapist, social worker, occupational therapist to help you find answers to your questions.
Read Also: Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Get Worse With Age
Should I See A Doctor
Its common to have aches and pains in your muscles and joints from time to time. This may especially be true if you take part in unusual or strenuous physical activities.
So, how can you tell the difference between the early signs of arthritis and normal pain and stiffness? And, how do you know when you should see a doctor about your symptoms?
If you have swelling or stiffness that you cant explain and that doesn’t go away in a few days, or if it becomes painful to touch your joints, you should see a doctor. The earlier you get a diagnosis and start the right type of treatment, the better the outcome will be.
Here are some other things to think about that might help you decide whether you need to see a doctor:
Advanced Glycation End Products
When you grill or fry your food or consume foods that have been cooked at high temperatures, including pasteurized foods, your body produces toxins called AGEs. These toxins can damage proteins in your body, which triggers your immune system to destroy the AGEs with cytokines. Cytokines cause inflammation.
You May Like: Vicks Vapor Rub For Arthritis
What Is A Rheumatologist
Rheumatologists are expert physicians who specialize in diagnosing and treating inflammatory arthritis and autoimmune diseases where joints can be involved. They also care for people with other diseases of the connective tissue and those with osteoporosis. As needed, the rheumatologist coordinates the care his or her patients receive from surgeons and other specialists, as well as from other health care professionals.
In many, but not all cases, people become aware that they have inflammatory arthritis when they develop symptoms of inflammation in one or more joints. On a simple level, joints are where two bones are attached. A joint can be fibrous and a simple connection without movement, such as joints in the pelvis. However, most joints are “ball and socket joints”, which are covered with a smooth layer of specialized tissue called cartilage – allowing for a gliding motion examples are the knees, elbows, shoulders, hips or elbows. Other structures that attach the bones to each other and to muscles include the tendons, tissue that attaches muscles to bones and the ligaments, tissues that attach bone to bone. These can also be targets of inflammation in inflammatory arthritis. Furthermore, the joints are held together by a capsule, a kind of protective container that is lined with a membrane called the synovium. In inflammatory arthritis inflammation of the synovium is what usually causes pain, stiffness and swelling. This is called “synovitis”.
Contributions Of Aging And Obesity To Inflammatory Processes In Osteoarthritis

Although osteoarthritis is not inevitable as we grow old, aging is one of the most prominent risk factors for osteoarthritis onset and development. Chondrocytes in aging cartilage have impaired activity compared with normal chondrocytes, with evidence of a senescent secretory phenotype . The increased accumulation and expression of both advanced glycation end-products and the AGE receptor, RAGE, that occur in aging chondrocytes are associated with dysregulated signaling pathways, altered synthetic activity, and increased synthesis of and enhanced sensitivity to cytokines and chemokines, which trigger the expression of MMPs and other inflammatory mediators . The aging-related loss of autophagy, a protective mechanism for normal chondrocytes that protects cells during stress responses, is associated with cell death and osteoarthritis development . An earlier study showed that decreased HIF-2 expression is associated with autophagy in osteoarthritis tissues and aging cartilage, and with elevated HIF-1 as a possible compensatory mechanism.
Don’t Miss: Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain At Night