Prostaglandins Leukotrienes And Other Lipid Mediators
The enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 is upregulated in inflamed joint tissues and is responsible for elevated production of lipid mediators including prostaglandins such as PGE2 in the OA joint . Studies have suggested that overexpression of COX-2 is likely induced by proinflammatory mediators such as IL-1, TNF, and IL-6, as well as via TLR4 stimulation . There is in fact an extensive literature beyond the scope of this review suggesting that PGE2 is involved in inflammation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and possibly structural changes that characterize arthritic diseases, which is well reviewed elsewhere by Martel-Pelletier and colleagues .
The biosynthetic pathway producing prostaglandin begins with production of arachidonic acid by the enzyme phospholipase A2. In addition to the generation of prostaglandins by COX enzymes, arachadonic acid can be converted to another class of lipid mediators known as leukotrienes through the action of the lipoxygenase family of enzymes. These mediators, primarily leukotriene B4 and its metabolite LTC4, are produced by OA synovium and to a lesser extent OA bone and cartilage . In addition to its role as a powerful leukocyte chemoattractant , LTB4 has been demonstrated to stimulate TNF and IL-1 production from human OA synovial explants .
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
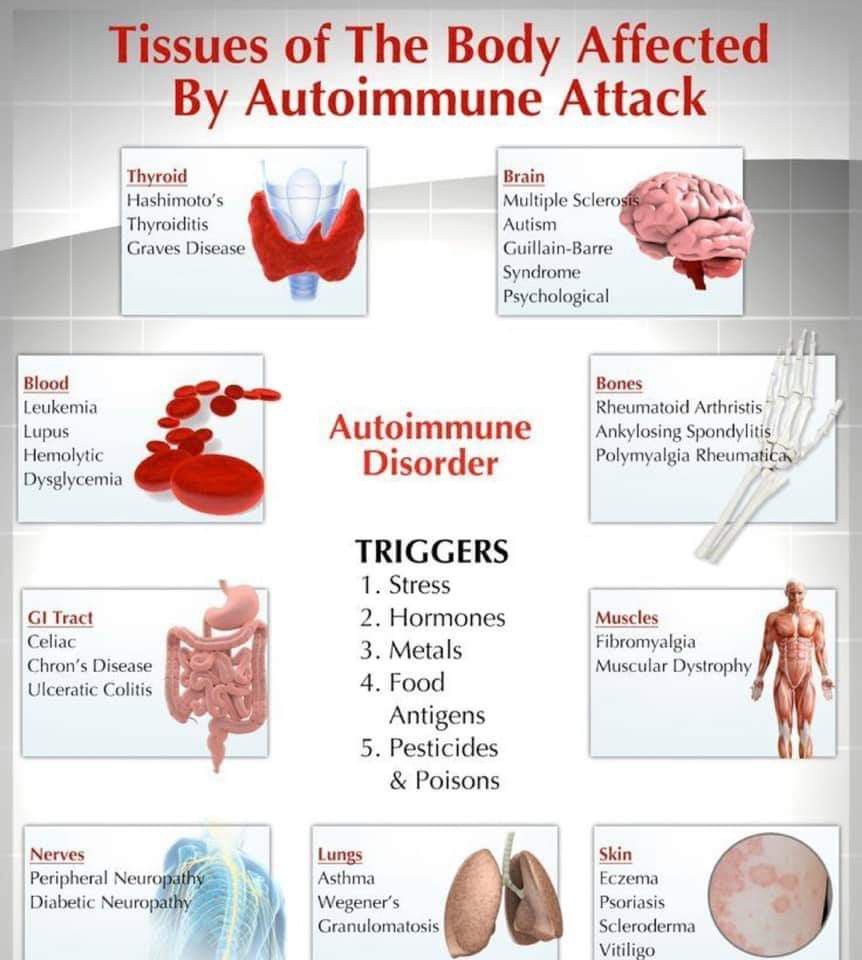
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means your immune system attacks the cells that line your joints by mistake, making the joints swollen, stiff and painful.
Over time, this can damage the joints, cartilage and nearby bone.
It’s not clear what triggers this problem with the immune system, although you’re at an increased risk if:
- you are a woman
Find out more about the causes of rheumatoid arthritis.
Foods To Eat On The Anti
A diet that may lower inflammation for rheumatoid arthritis should include certain foods such as:
- Wild-caught cold-water fish 2-3 times a week
- Healthy oils
- Avocados
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Fresh berries
- Red grapes and citrus fruits
- Whole grains
- Olives
- Vegetables
- Green Matcha tea and other types of green tea
- Spices
- Seeds
- Natural sweeteners
- Legumes and lentils
- Foods high in probiotics and prebiotics
- Spices
Keep in mind that there is no single food that can promote health. Eating a variety of bright-colored fruits and vegetables and fresh, whole foods is the best eating plan for the anti-inflammatory diet.
You May Like: Remedy For Arthritis In Lower Back
When Was Ra Finally Separated From The Arthritis Of Ibd
Luis Fernandez-Herlihy, an influential practitioner from the Lahey Clinic in Boston, summarised in 1959 his opinion describing the range of articular manifestations in patients with UC. He employed the following five categories: rheumatoid spondylitis, RA, erythema nodosum, arthralgias and acute toxic arthritis. Among these, acute toxic arthritis had the closest relationship with colitis he noted that this category became clinically evident only with the exacerbation of colitis and relieved on colitis remission without any residual deformity. He then postulated it is possible that acute toxic arthritis constitutes a milder, earlier, or perhaps an atypical form of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Questions And Information For Your Rheumatologist
Whether you are planning an initial visit to a rheumatologist for an evaluation or are going to see your long-established healthcare provider, to make the most of a visit to the doctors office, consider the following:
- Bring in a full list of the medications you are taking as well as any vitamins or supplements .
- If you are already taking medication, prepare notes about any reactions or side effects that you feel may be related to the drugs that you are taking.
- Be ready to report any physical or emotional changes that you are experiencing, whether or not they are strictly related to your inflammatory arthritis, and
- Bring in reports or copies of any blood tests or imaging tests (X-rays, ultrasounds, MRIs of joints that were done to better understand your arthritis.
- Bring a list of any questions you have about any aspect of your care.
- If it is your first visit, be ready to provide a list of all health conditions, prior surgeries and any allergies.
Some people also find it helpful to bring a loved one, friend or caregiver along on a doctors appointment, in order to have a second “set of ears” for any new information or instructions given. On occasion, close family members cannot fully understand the impact inflammatory arthritis has and it may be helpful for them to join you on a visit to your rheumatologist.
Also Check: Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
What Is The Difference Between Rheumatoid Arthritis And Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis both cause joint pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion, but the two diseases are distinct in their root cause and treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition where a persons own immune system attacks their joints, causing inflammation. Rheumatoid arthritis typically affects many joints simultaneously, especially in the hands, wrists, and feet, and is treated with medications to suppress the immune response.
Osteoarthritis is not an autoimmune disease, and although the exact causes are not known, multiple risk factors have been identified. In a healthy joint, cartilage provides cushioning and a smooth joint surface for motion. In an osteoarthritic joint, as cartilage is irreversibly destroyed and bone abnormalities develop, movement becomes painful and more difficult.
What Theories Are Proposed To Explain The Pathogenesis Of Ibd
Multiple theories have been promulgated to account for the underlying pathogenesis of IBD-arthritis. Ernest Fletcher in 1951 noted the long hospitalisation periods taking place in patients with UC and hypothesised the probable cause of arthritis as follows: it is uncertain whether this complication is due to the long confinement to bed or the main disease. Steinberg and Storey proposed the spread of a toxic agent through the intestinal wall to the pelvic veins and then subsequently to the vertebral veins. These veins, called Batsons plexus, were initially suggested as having the capacity to permit the spread of metastasis from pelvic tumours, particularly the prostate, through the veins to the spine. A similar and parallel explanation for the development of spinal disease to result from infections in the various organs from the pelvis was described by Romanus studying the genitourinary tract association with spondylitis and later put forth as a possible explanation for the spread of an infection in the colon to the spine. The latter theory was questioned by Zvaifler and Martel in 1960 when they observed that the spondylitis antedated the colitis by many years in a number of their patients.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Lower Back Arthritis
Gout Statistics And Facts
- 8.3 million people in the United States have gout .*
- Among people who have gout attacks, 90% have kidneys that dont remove enough uric acid from their urine while 10% make too much uric acid in their system.
- 90% of gout attacks start in a single joint. Most often, it is the bunion joint of the big toe.
- 90% of gout patients have one or more of the following conditions , which make it more difficult to manage gout: kidney dysfunction, coronary heart disease, obesity, high cholesterol and/or triglycerides, diabetes mellitus.**
*Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Arthritis Rheum. 2011.**Comorbidities of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Am J Med. 2012.
Osteoarthritis An Inflammatory Disease: Potential Implication For The Selection Of New Therapeutic Targets
Corresponding Author
Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Corresponding Author
Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Osteoarthritis is a well-known disease that is part of the aging process and also one of the most common diseases among mammals. Although this musculoskeletal disorder has been described in mammals of many ages, having been reported in Egyptian mummies and in dinosaurs, its exact etiology is far from being fully understood. With the graying of the world population, it is of the utmost importance to find out more about the pathogenesis of the disease and thus allow the discovery of new treatments to stop or prevent its progression.
A number of risk factors have lately been identified . Mechanical factors, among others, are likely to play a very important role in the initiation of the disease process. Endogenous factors such as type II collagen mutation or dysplastic conditions are also known to be involved in initiating the OA process .
Recommended Reading: Bananas And Arthritis
What Are The Risk Factors For Arthritis
Some factors make you more likely to develop arthritis, including:
- Age: The risk of arthritis increases as you get older.
- Lifestyle: Smoking or a lack of exercise can increase your risk of arthritis.
- Sex: Most types of arthritis are more common in women.
- Weight: Obesity puts extra strain on your joints, which can lead to arthritis.
What Causes Arthritis
Different types of arthritis have different causes. For instance, gout is the result of too much uric acid in your body. But for other types of arthritis, the exact cause is unknown. You may develop arthritis if you:
- Have a family history of arthritis.
- Have a job or play a sport that puts repeated stress on your joints.
- Have certain autoimmune diseases or viral infections.
Recommended Reading: Is Eating Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
How Is Ra Treated
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs biological response modifiers are medications that are an effective second-line treatment. In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
Definitions And Clinical Manifestations
Arthropathy associated with IBD can involve both peripheral and axial joints. IBD associated arthropathy is considered a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy . Spondyloarthropathies , Psoriatic Arthritis, Reactive Arthritis, and Undifferentiated SpA), are characterized by axial and peripheral joint disease with inflammatory features and classically a negative rheumatoid factor. Spondyloarthropathies share a common genetic predisposition, including HLA-B27 association. Extraarticular manifestations such as skin manifestations, dactylitis, enthesopathy, and eye disease can also be seen. IBD-associated arthritis is more akin to AS than to the other subtypes of SpA in that it is more likely to be symmetric and continuous, whereas reactive arthritis or psoriatic arthritis can be asymmetric or have non-continuous lesions within the spine. The European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group criteria are most commonly used for classification of SpA .
Other musculoskeletal manifestations in IBD include enthesitis , dactylitis , and arthralgia . Complications of IBD and its treatment such as septic arthritis or osteonecrosis should also be considered in the differential of joint pain occurring in the IBD patient, particularly in the setting of mono or oligoarticular arthritis.
Also Check: Is Tomato Bad For Arthritis
Role Of Inflammation In Disease Progression: What Is The Evidence
The question is whether synovitis in OA is an innocent bystander or truly participates in the structural changes of the disease. Moreover, is synovial inflammation only relevant during the flare of the disease or is it an ongoing process that permanently contributes to the progression of the disease after it is established? From all observations, there are at least 2 major questions that could be raised regarding synovial inflammation and OA. First, what evidence do we have that inflammation is associated with disease progression? Second, what are the inflammatory factors that could possibly be involved in the genesis of OA structural changes?
The main observations that suggest an association between inflammation and the progression of structural changes in OA are derived from clinical studies . A number of those studies have lately demonstrated an interesting possible association between synovitis, OA inflammation, and progression of structural changes. There are a number of biologic markers that are believed to be associated with OA synovial inflammation, such as cartilage oligomeric protein , the serum level of C-reactive protein , and hyaluronic acid . It is generally believed that high disease activity suggests a rapid progression of the disease.
These data strongly suggest, from both the biologic and clinical sides, an association between joint inflammation and the progression of structural changes in OA.
What Causes Inflammation And What Are Its Effects
Inflammation occurs when substances from the body’s white blood cells are released into the blood or affected tissues to protect your body from foreign invaders. This release of chemicals increases the blood flow to the area of injury or infection, and may result in redness and warmth. Some of the chemicals cause a leak of fluid into the tissues, resulting in swelling. This protective process may stimulate nerves and cause pain.
The increased number of cells and inflammatory substances within the joint cause irritation, swelling of the joint lining, and eventual wearing down of cartilage .
Also Check: How To Relieve Arthritis Pain In Lower Back
How They Are Relatedand How They Differ
The terms polyarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis are often used interchangeably. While they are related, they don’t mean the same thing. RA is a disease, while the other two are ways of describing a particular case of arthritis .
Verywell / Hugo Lin
How Is Ra Diagnosed
RA is diagnosed by reviewing symptoms, conducting a physical examination, and doing X-rays and lab tests. Its best to diagnose RA earlywithin 6 months of the onset of symptomsso that people with the disease can begin treatment to slow or stop disease progression . Diagnosis and effective treatments, particularly treatment to suppress or control inflammation, can help reduce the damaging effects of RA.
Don’t Miss: Is Banana Good For Arthritis
Extracellular Matrix Derived Damage
ECM breakdown is ubiquitous at sites of inflammation, including the OA joint . An early observation by Homandberg and colleagues suggested that ECM breakdown products could promote inflammation and cartilage loss . Even before the resurgence of interest in the innate immune system and the wide appreciation of PRRs, it was observed that fragments derived from the breakdown of fibronectin, when injected into knees of adolescent rabbits, resulted in cartilage damage as evidenced by loss of proteoglycans . Further studies demonstrated that fibronectin fragments induced the production of proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor and IL-1, as well as matrix metalloproteinases MMP1 and MMP3, mediators now known to be implicated in chondrolysis . The observations of Homandberg support a model in which damage resulting in ECM breakdown produces DAMPs capable of inciting local inflammatory responses resulting in further chondrolysis and release of additional ECM breakdown products. Notably, several additional ECM breakdown products have been implicated as DAMPs in mediating joint damage, including tenascin C and hyaluronic acid .
Osteoarthritis And Immune Response
The inflammation observed in OA is believed to involve innate immune response prior to a mild degree of adaptive immunity . During tissue damage, a group of endogenous molecules, called damage-associated molecular pattern , signals the immune cells to induce a protective response against the tissue, causing tissue repair. However, a prolonged signaling of DAMP to immune cells leads to an exacerbated cytokine release, which can be destructive to the tissue .
Innate immune cells activated by DAMP include macrophages and mast cells, which have shown to present a key role in the pathogenesis of OA. Mast cells are considered regulators of vascular permeability, and they may play a crucial role in OA joint inflammation as they facilitate leukocyte infiltration .
Proteins from complement system have been found to play a role in OA, especially in early stages, as they were upregulated in both synovial membrane and fluid . Additionally, the deposition of the membrane attack complex is correlated with the presence of inflammation on histology of synovial membrane, and it was present in chondrocytes in late OA . MAC can lead to chondrocyte destruction as it stimulates catabolic events through the increase of leukocytes and, consequently, the production of MMP . Also in the studies with experimental knockout models for C5 and C6, the joint damages were attenuated .
Don’t Miss: Are Eggs Bad For Psoriatic Arthritis
Foods That Increase Inflammation
Just as healthy foods are part of the anti-inflammatory diet, some foods must be avoided because they are thought to promote inflammation in the body. Foods to avoid on the anti-inflammatory diet include:
You May Also Like
- Refined sugars
- Fried, fatty foods
- Sweetened and diet soda
- Red meat
- Lunchmeat other processed meat with nitrates
- Refined oils
- An overabundance of omega 6 fatty acids
- Alcohol
- Processed and snack foods
- Ice cream, candy, and cakes
- Foods containing added sugar and salt
You may also find it beneficial to limit the intake of several other foods, such as:
4 Massages That Are Perfect For Achy Joints
Secondhand Smoke Raises Odds for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Kids
Quiz: Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Is Your Hand Pain Arthritis, Carpal Tunnel or Something Else?
Could You Be at Risk For Rheumatoid Arthritis?
What Are The Risk Factors For Ra
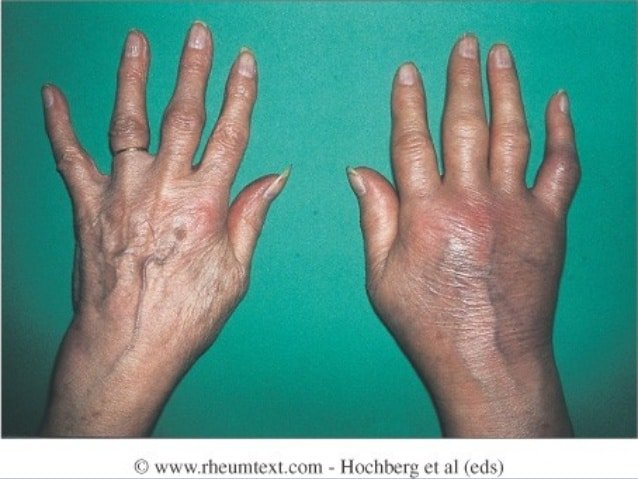
Researchers have studied a number of genetic and environmental factors to determine if they change persons risk of developing RA.
Characteristics that increase risk
- Age. RA can begin at any age, but the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest among adults in their sixties.
- Sex. New cases of RA are typically two-to-three times higher in women than men.
- Genetics/inherited traits. People born with specific genes are more likely to develop RA. These genes, called HLA class II genotypes, can also make your arthritis worse. The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese.
- Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a persons risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse.
- History of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at greater risk of developing RA.
- Early Life Exposures. Some early life exposures may increase risk of developing RA in adulthood. For example, one study found that children whose mothers smoked had double the risk of developing RA as adults. Children of lower income parents are at increased risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity. Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Studies examining the role of obesity also found that the more overweight a person was, the higher his or her risk of developing RA became.
Characteristics that can decrease risk
Recommended Reading: Is Banana Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis