What Happens During Arthroplasty
You may have your surgery in an outpatient clinic or at a hospital. The technique your surgeon uses varies depending on the type of surgery and the joint you need replaced. Right before your procedure, you will receive anesthesia. This ensures you wont feel pain during arthroplasty.
Your surgeon makes incisions and removes the damaged joint. Then they replace it with an artificial joint. They use stitches, staples or surgical glue to close the incisions. Your provider wraps the joint in a bandage. You may also need a brace or sling.
Surgeons can do some joint replacement procedures using minimally invasive techniques. These techniques use fewer incisions and special tools. The recovery time for minimally invasive procedures can be less than it is for traditional procedures. Your surgeon will recommend the most appropriate procedure for you.
Types Of Arthritis That Affect The Knee
Osteoarthritis is characterized by cartilage degeneration and bony protrusions called osteophytes . In the knee, the most common sites of osteoarthritis include the tibia , femur , and patella .
The most common type of arthritis affecting the knee is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis occurs when a joints articular cartilage breaks down. In the knee, articular cartilage covers the top of the tibia , bottom of the femur , and back of the patella .
Not everyone with knee osteoarthritis will get knee pain. Pain may occur if the loss of healthy cartilage:
- Causes the bones of the joint to rub against one another.
- Compromises the joints biomechanics in some other way.
See Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Post-traumatic knee arthritisPost-traumatic arthritis is a type of osteoarthritis. It develops after a meniscus tear, ligament injury, or other trauma. The injury may heal but wear-and-tear on the articular cartilage can accelerate. Post-traumatic arthritis may not become symptomatic until years after the injury.
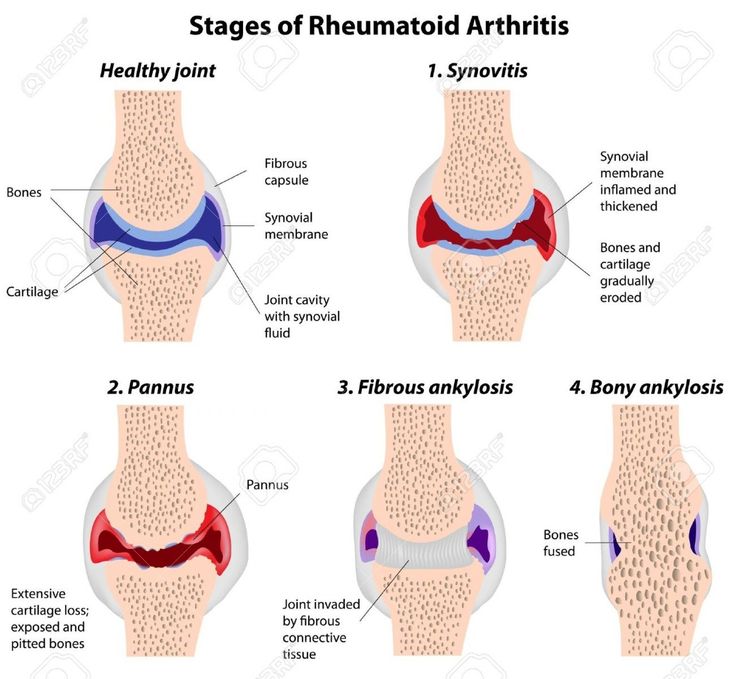
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that targets the synovial membrane surrounding many joints of the body. Some of the most common areas affected include the wrists, knees, and ankles.
Knee pain can be caused by an autoimmune disease called rheumatoid arthritis . RA causes joint inflammation that can make the knee feel swollen, stiff, warm, and painful. Over time, untreated RA can cause permanent knee joint damage.
See What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis ?
Complementary Medicine For Osteoarthritis
Taking supplements
In many cases, theres little research evidence to show that supplements and herbal remedies can improve arthritis or its symptoms, but many people feel they do benefit from them.
Below are a few of the supplements often used by people with osteoarthritis.
Glucosamine
Glucosamine is found naturally in the body in structures such as ligaments, tendons and cartilage. Supplements are usually produced from crab, lobster or prawn shells, although shellfish-free types are available. Theres some research to suggest it may have some benefit in painful osteoarthritis, especially of the knee.
Most trials have used a dose of 500 mg three times a day, and the evidence seems to suggest glucosamine sulphate may be more effective than glucosamine hydrochloride. It doesnt help the pain straight away so youll need to take it for a couple of months. If it hasnt helped after two months, then its unlikely that it will.
Chondroitin
Chondroitin exists naturally in our bodies and its thought that it helps give cartilage elasticity. The research evidence is limited to animal studies that suggest it might help to slow the breakdown of cartilage.
Dont expect to see any improvement for at least two months. And if your cartilage is badly damaged, its unlikely that youll benefit from chondroitin.
Fish oils
Complementary treatments
There are a number of different treatments available and they can generally be used alongside prescribed or over-the-counter medicines.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Arthritis In Toes
Cracking Or Popping Sounds
When you bend or straighten your knee, you may feel a grinding sensation or hear cracking or popping sounds. Doctors call this crepitus.
These symptoms can occur when youve lost some of the cartilage that helps with smooth range of motion. Both OA and RA can result in cartilage damage.
When cartilage is damaged, rough surfaces and bone spurs develop. As you move your joints, these irregular areas rub against each other.
Drug Slows Knee Osteoarthritis Progression
Nov. 12, 2012 A drug used outside the U.S. to treat osteoporosis may not only lessen the everyday pain associated with knee osteoarthritis, but may even slow down the progression of osteoarthritis, researchers say.
The drug is called strontium ranelate.
In a three-year study of more than 1,300 people with knee osteoarthritis, digital X-rays revealed substantially less loss of cartilage in the joint space in those who took strontium ranelate every day compared with people who took a placebo daily.
In people with osteoarthritis, the cartilage in a joint wears away in some areas. The function of cartilage is to reduce friction in the joints and serve as a shock absorber. The wearing away of cartilage leads to pain and other symptoms.
Nearly one in 100 people have evidence of knee osteoarthritis on an X-ray. And nearly 19% of women and 14% of men age 45 and older have joint pain, stiffness, and other symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, according to a large 2007 study.
Study head Jean-Yves Reginster, MD, PhD, presented the findings today at the American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting in Washington, D.C. He is president and chair of the department of public health sciences at the University of Liège in Belgium.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Arthritis In Your Hands
You May Like: Is Pineapple Good For Arthritis
What Is Total Knee Replacement
Total knee arthroplasty comprises a replacement of both the end of the femur bone and a replacement of the top part of the tibia . The procedure also involves placing a plastic spacer between where the cartilage used to be between the femur and the tibia.
In total knee arthroplasty surgery, a surgeon will remove the damaged cartilage and bone, and insert new state-of-the-art metal or plastic joint components to restore normal functioning of the knee.
From 1999 to 2008, total knee replacement procedures in the U.S. more than doubled for the population at large and tripled for people between the ages of 45 to 64. By 2012, surgery for end-stage knee osteoarthritis was performed on almost 660,000 Americans every year.
Risk Factors For Knee Pain
Anyone with knees can have knee pain, but there are some risk factors that increase your chances. Carrying extra weight is a primary risk factor, as is having a job that places lots of stress on the knees. Professional athletes and enthusiastic amateurs alike are all at risk of knee pain due to wear-and-tear and injury also.
Other risk factors include:
- Lack of flexibility or strength in supporting muscles
You May Like: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Hereditary
Risk Factors For Knee Arthritis
- Age. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative, wear and tear condition. The older you are, the more likely you are to have worn-down knee joint cartilage.
- Heredity. Slight joint defects or double-jointedness and genetic defects may contribute to osteoarthritis in the knee.
- Excess weight. Being overweight or obese puts additional stress on the knees over time.
- Injury. Severe injury or repeated injury to the knee can lead to osteoarthritis years later.
- Overuse. Jobs and sports that require physically repetitive motions that place stress on the knee can increase risk for developing osteoarthritis.
- Gender. Postmenopausal women are more likely to have osteoarthritis than men.
- Autoimmune triggers. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unknown, triggers of autoimmune diseases are still an area of active investigation.
- Developmental abnormalities. Deformities such as knock knee and bowleg place higher than normal stress on certain parts of the knee joint and can wear away cartilage in those areas.
- Other health conditions. People with diabetes, high cholesterol, hemochromatosis and vitamin D deficiency are more likely to have osteoarthritis.
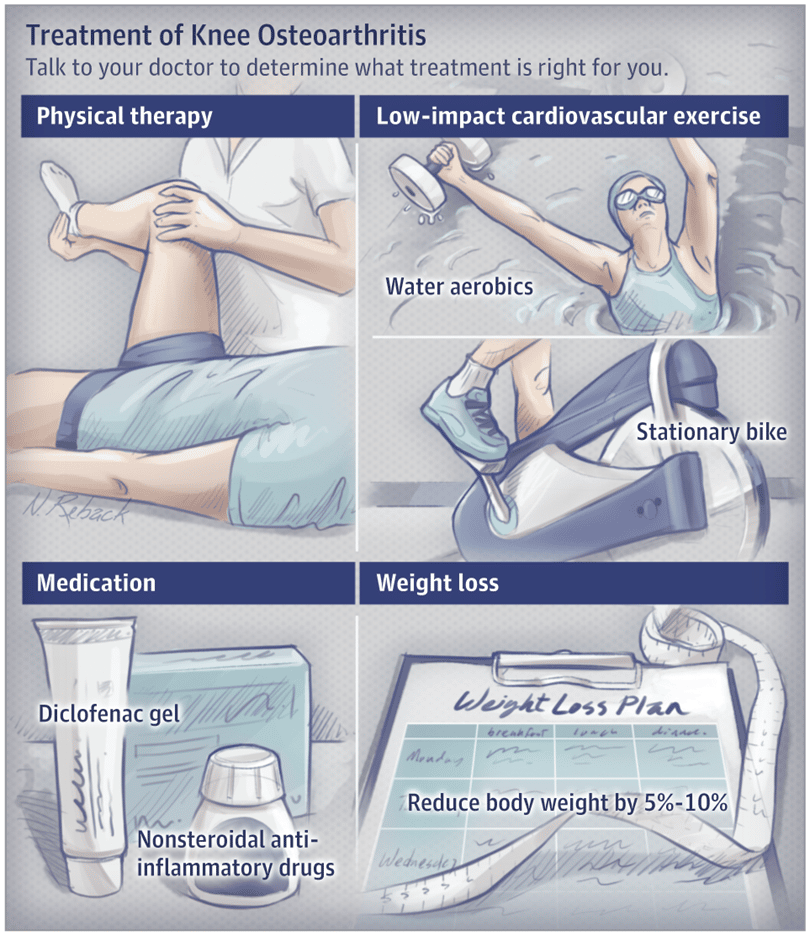
Home Remedies And Medical Options
Options include:
Experts say that people who play an active role in managing their OA, for example, are likely to see a more positive outcome. You can do so by learning about arthritis, becoming aware of what makes symptoms better or worse, and making decisions with your doctor.
Discover exercises to strengthen the knee muscles.
Recommended Reading: What To Give Cats For Arthritis
Visit A Physical Therapist
Physical therapists work with your doctor to design specific exercises for knee rehabilitation. Many of these will focus on lengthening and strengthening the supporting muscles of the upper and lower legs, such as quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves.
Even one visit to learn the proper form for knee arthritis exercises can help support your recovery.
How To Help Arthritis In Knees
If you are experiencing severe knee arthritis that is impacting your quality of life, its important to talk to your doctor first. They can help diagnose any underlying causes and design a treatment plan to improve your daily life.
For mild to moderate pain, here are our tips for how to help arthritis in the knees. As always, talk with your doctor before starting a new treatment.
Read Also: What Medicine Can You Take For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Getting Tested For Arthritis
Arthritis testing is ordered by a doctor or specialist if indicated by a patients signs or symptoms. For testing that requires a sample of a patients blood, the sample can be drawn in a doctors office or other medical setting.
A sample of synovial fluid is obtained through a procedure called a joint aspiration or arthrocentesis. During a joint aspiration, a doctor applies local anesthesia to the affected joint before using a needle to withdraw a sample of synovial fluid for analysis. An ultrasound may be performed during a joint aspiration to help the doctor obtain the sample.
Urine samples and oral swabs may be collected by a doctor or by the patient using a doctors instructions. In some cases, a 24-hour urine sample may be required, which involves the collection of all a patients urine over a 24-hour period.
What Tests Are Done To Diagnose Post
After a physical exam, you might need at least one of a few imaging tests:
- X-rays: An X-ray will confirm show how damaged the bones in your joint are.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging : Your provider might use an MRI to get a complete picture of the damage to your joint and the area around it. This will show them your bones and the tissue around them.
- CT scan: If you need surgery, your provider or surgeon needs to know exactly how damaged your joint is. A CT scan will give them a more detailed picture of your bones and the surrounding tissue than an X-ray.
Recommended Reading: Is Knee Brace Good For Arthritis
Talk To Your Doctor About Knee Joint Injections
Knee joint injections should only be explored when more conservative treatments for knee pain have proven ineffective. Before the procedure, your doctor will inject a numbing agent to reduce pain, followed by a corticosteroid to decrease inflammation. They may also discuss options like PRP injections.
While injections may work to decrease pain, knee joint injections do not treat any underlying knee pain causes or halt progressive joint deterioration. Still, when combined with a healthy diet, regular exercise, physical therapy, and other lifestyle changes, they can provide profound relief. Learn more about this option in the following video.
What Is A Knee Osteotomy
A knee osteotomy is an operation that surgeons use to treat the pain and instability that can occur when there is damage or arthritis in part of the knee joint. Doctors may recommend an osteotomy instead of a knee replacement when only one area of the knee has damage.
During this knee surgery, a surgeon repositions the bones in the tibia or femur to realign the knee. This new positioning shifts your body weight from the damaged part of your knee to a healthy part.
A knee osteotomy can help slow deterioration of cartilage in the knee and may delay your need for knee replacement surgery for many years. Osteotomy of the knee has been used for decades to improve pain and function.
You May Like: What Different Types Of Arthritis Are There
Also Check: Can You Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis Naturally
Arthritis Runs In Your Family
Does your family skip the annual Thanksgiving touch-football tradition because everyone would need to ice their knees afterward? Youre more likely to suffer arthritis symptoms if your parents, grandparents, or siblings have the condition, according to the Cleveland Clinic. And recent research from the UK identified nine genes for osteoarthritis, which suggests that genes may explain at least part of the reason this link exists. And help yourself stay active with these stretches for arthritis that you can do without leaving your chair.
Donât Miss: How To Pop Your Knee
Other Pain Relief Treatments
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
A TENS machine sends electrical pulses to your nerve endings through pads placed on your skin. It produces a tingling sensation and is thought to relieve pain by altering pain signals sent to the brain. The research evidence on the effectiveness of TENS is mixed, but some people do find it helpful. A physiotherapist will be able to advise on the types of TENS machine available and how to use them. Or they may be able to loan you one to try before you buy.
Hyaluronic acid injections
Hyaluronic acid, or hyaluronan, is a lubricant and shock absorber thats found naturally in the fluid in your joints. Injections of hyaluronic acid have sometimes been used as a treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee. The treatment isnt currently available on the NHS because research evidence on its long-term effectiveness is mixed. The treatment is, however, available privately.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Reduce Arthritis Inflammation
Who Should Get Testing
Anyone with concerns about arthritis should talk to their doctor about whether or not arthritis testing is appropriate. Arthritis testing may be recommended for patients experiencing symptoms of arthritis in one or multiple joints. In patients with symptoms in a single joint, indications for urgent arthritis testing include:
- Joint pain, swelling, warmth, or stiffness
- Skin changes near the joint, including broken, red, warm, or tender skin
- Past diagnosis of a severe bleeding disorder
- Past diagnosis or current symptoms of a sexually transmitted disease
In patients with symptoms affecting multiple joints, indications for seeking prompt medical care, including arthritis testing, include:
- Joint changes, including swelling, warmth, and redness
- Skin changes, including rashes, spots, or blotches
- Sores, especially in the mouth, nose, or near the genitals
- Chest or abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath or severe cough
- Fever, sweats, weight loss, or chills
- Eye changes, including redness or pain
Arthritis testing is also performed in patients who have been diagnosed with certain types of arthritis in order to plan treatment, as well as monitor treatment progress and disease progression. In these cases, arthritis testing can aid doctors in managing the disease as effectively as possible.
Exercise: Rx For Overcoming Osteoarthritis
Exercising may be the last thing you want to do when your joints are stiff and achy. But exercise is a crucial part of osteoarthritis treatment in order to ease pain and stay active.
Osteoarthritis is a chronic and progressive disease characterized by loss of the cartilage that covers and protects the ends of the bones where they meet at a joint. Without this protective coating, bone rubs against bone, causing irritation and inflammation. The result is pain and stiffness in the joint and often pain in the muscles and ligaments that surround it.
Osteoarthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. Nearly equal numbers of women and men have the condition, but women tend to develop symptoms after age 55, about 10 years later than men do. It most often affects the hips, knees, spine, and hands.
Because most people diagnosed with osteoarthritis are older about half of those over 65 have it to some degree its long been considered a normal part of aging that reflects a lifetime of wear and tear on cartilage. But experts now know that many factors besides age are involved. Osteoarthritis risk can be inherited. An injury or disease may also kick off the deterioration. The rate of progression depends on genetics, biomechanical forces, and biological and chemical processes, all of which vary from person to person.
You May Like: What Helps Arthritis Hip Pain
What Are The Stages Of Arthritis Of The Knee
There are five stages of osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis that affects your knees:
- Stage 0 . If youre at stage 0, your knees are healthy. You dont have arthritis of the knee.
- Stage 1 . Stage 1 means that youve got some wear and tear in your knee joint. You probably wont notice pain.
- Stage 2 . The mild stage is when you might start to feel pain and stiffness, but theres still enough cartilage to keep the bones from actually touching.
- Stage 3 . If youre at the moderate stage, youll have more pain, especially when running, walking, squatting, and kneeling. Youll likely notice it after long periods of rest . You’re probably in a great deal of pain because the cartilage has narrowed even further and there are many bone spurs.
- Stage 4 . Severe osteoarthritis means that the cartilage is almost gone. Your knee is stiff, painful and possibly immobile. You might need surgery.
How Is Knee Arthritis Diagnosed
Your doctor may use some of the following diagnostic tests and procedures to determine if you have knee arthritis:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Blood tests for genetic markers or RA antibodies
- X-rays to determine cartilage loss in the knee
- Joint aspiration: drawing out and testing the synovial fluid inside the knee joint
Cartilage cannot be seen on X-ray, but narrowing of the joint space between the bones indicates lost cartilage. X-rays show bone spurs and cysts, which can be caused by osteoarthritis. Other tests such as MRI or CT scans are rarely needed for diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: What Food To Eat When You Have Arthritis