Arthritis In The Heel And Ankle
Several types of arthritis, including OA, RA, AS, and PsA, can affect the heels and the ankles.
Symptoms of arthritis in the heel might include:
- Stiffness upon awakening in the morning
- Recurring pain in the heel
- Swelling of the heel
- Limited movement
- Skin changes, including rashes and growths
Inflammation at the heel from RA, AS, or PsA can lead to conditions that cause heel pain. This might include Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, or retrocalcaneal bursitis, a condition in which the bursa becomes inflamed, causing pain and swelling.
The ankle is not affected by arthritis as often as other joints, but it can be a source of severe pain and instability when it is affected. Additional symptoms of ankle arthritis include swelling and stiffness of the ankle and problems with mobility. Ankle arthritis will eventually affect gaitthe way a person walks.
How Arthritis In The Back Is Diagnosed
Diagnosing arthritis in the back begins with taking your medical history and doing a physical exam of your back and legs to assess your mobility/flexibility and make sure your nerves are working properly. The doctor will ask questions about:
- Where the pain is occurring
- How long the pain has lasted
- What the pain feels like/how severe it is
- What situations/activities make the pain feel better or worse
- How the pain is affecting/limiting your daily function
Imaging tests are usually needed to help confirm a diagnosis of arthritis. X-rays are typically the first imaging test ordered. They can joint damage/bone spurs, but cannot show damage to soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, or bulging discs. Other tests may be ordered to look for changes or damage that is not visible on X-rays. These may include MRI, CT, ultrasound, bone scans, or other tests as needed. The gold standard to diagnose arthritis in the back is actually an injection called a medial branch block, but its not often necessary, says Dr. Kirschner.
If your doctor suspects you could have a type of inflammatory arthritis, they may order blood tests to look for signs of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Other blood tests may look for genetic markers associated with axial spondyloarthritis, such as HLA-B27, or antibodies associated with rheumatoid arthritis .
Understanding Your Diagnosis And Treatment Plan
It’s not uncommon to hear people say “I have arthritis.” Generally speaking, they are correct, but more accurately, they have a specific type of arthritis. There are over 100 types of arthritis. Most of the 100 types are rare diseases. You can count on two hands the types you have probably heard of at all and on two fingers the ones most referred to and considered most common: .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Arthritis In The Back
What Is Inflammatory Arthritis
Inflammatory arthritis describes a group of diseases caused by an overactive immune system. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Affected joints may feel warm, swollen, and tender. But inflammatory arthritis can also affect other tissues in the body, including the lungs, heart, eyes, skin, and other organs. Left untreated, it can cause irreversible damage. Early treatment is the best way to relieve symptoms and limit the effects of inflammatory arthritis on the body.
While its not known what causes inflammatory arthritis in every patient, what is known is that the immune system does not know when to put on the brakes. Normally when we are exposed to bacteria, viruses, or fungi, the immune system produces white blood cells called lymphocytes as well as immune proteins to mount an attack against these invaders. Lymphocytes and immune proteins cause inflammation, which under typical circumstances is limited and resolves once the foreign substance is defeated.
But in someone with inflammatory arthritis, the immune response does not know when to stop. It turns on your body, attacking your own tissues instead of the foreign substance and causes continued inflammation. For this reason, inflammatory arthritis is known as an “autoimmune disease” auto meaning “self” and immune because the immune system loses its ability to distinguish self from foreign.
Have You Had The Following Laboratory Tests Performed To Assess The Arthritis
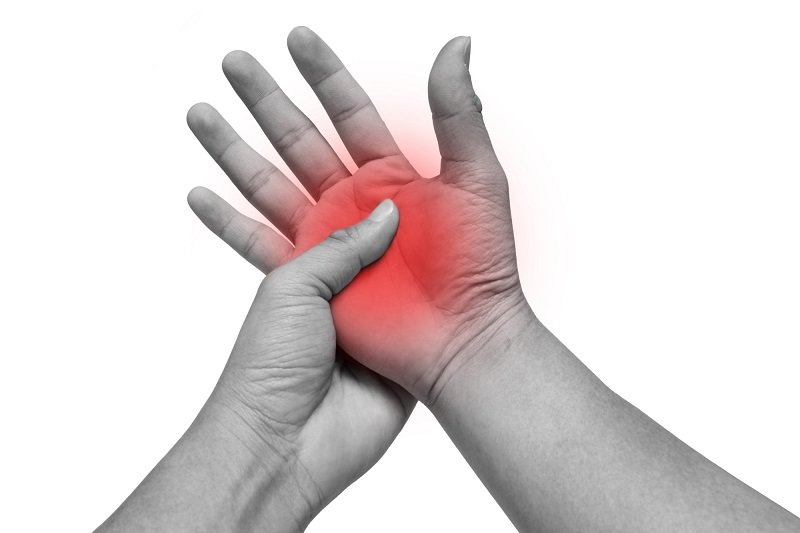
- Rheumatoid Factor . Is it positive or negative?
- Anti-citrullinated protein antibody . Is it positive or negative?
- Are the markers of inflammation, ESR and/or CRP in the blood elevated?
The classification criteria used worldwide to help in classifying an arthritis as RA is the 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria.
I present this here to help you screen for rheumatoid & to help determine the likelihood of having RA.
You May Like: How To Treat Arthritis In Lumbar Spine
What Are The Risk Factors For Arthritis
Some factors make you more likely to develop arthritis, including:
- Age: The risk of arthritis increases as you get older.
- Lifestyle: Smoking or a lack of exercise can increase your risk of arthritis.
- Sex: Most types of arthritis are more common in women.
- Weight: Obesity puts extra strain on your joints, which can lead to arthritis.
Sign #7 Change In Knee Shape
One way to know if you have arthritis in the knee is if the shape of the knee changes. You may have seen people with knock-knees, where it looks almost like a ball is growing off the inside of the knee. There are other such deformities that are a result of swelling and/or bone growths in the knee that cause it to become misshapen. The good news is that this is generally osteoarthritis and can be treated with removal of the growth and medication to reduce calcium growth and deposits on the knee bones.
Don’t Miss: Is Walking Good For Hip Arthritis
How Does Arthritis Feel
Arthritis usually causes stiffness pain and fatigue. The severity varies from person to person and even from day to day. In some people only a few joints are affected and the impact may be small. In other people the entire body system may be affected.
The joints of the body are the site of much of the action in arthritis. Many types of arthritis show signs of joint inflammation: swelling, stiffness, tenderness, redness or warmth. These joint symptoms may be accompanied by weight loss, fever or weakness.
When these symptoms last for more than two weeks, inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis may be the cause. Joint inflammation may also be caused by infection which can lead to septic arthritis. Degenerative joint disease is the most common type of arthritis joint inflammation is not a prominent feature of this condition. While normal joints can support a vast amount of use, mechanical abnormalities of a joint make it susceptible to degeneration.
It is healthy for you to keep active and move your joints. If you do not move a joint regularly, the muscles around it weaken and/or become tight. The joint can stiffen or even freeze. When you do try to move the joint and muscles hurt because they have been still for so long.
Arthritis can make it hard to do the movements you rely on every day for work or taking care of your family.
Tips On Easing Arthritis Pain
You can lessen your arthritic pain by adopting a few good habits. For example:
- Change posture often to lessen stiffness in your muscles and joints.
- Move the painful joint as often as possible.
- Always squat down before picking up something off the ground.
- When not sitting, always stand straight so as to properly align the neck, spinal column, hips and knees.
- Perform body stretches once or twice daily.
- Choose and wear proper footwear with shock-absorbing soles.
To help ease arthritis pain, the first choice of pain medication is acetaminophen. An effective pain reliever for this type of pain, it has the advantage of being very safe and has few secondary effects.
In some cases, you can use anti-inflammatory medication, many of which are sold over-the-counter. These products are not for everyone, and may cause undesirable effects. Always ask your pharmacist for advice before using them.
You May Like: Rheumatoid Arthritis Better With Movement
Recommended Reading: Is Cheese Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Knowing If You Have Arthritis Of The Knee
Should I See A Doctor
Its common to have aches and pains in your muscles and joints from time to time. This may especially be true if you take part in unusual or strenuous physical activities.
So, how can you tell the difference between the early signs of arthritis and normal pain and stiffness? And, how do you know when you should see a doctor about your symptoms?
If you have swelling or stiffness that you cant explain and that doesn’t go away in a few days, or if it becomes painful to touch your joints, you should see a doctor. The earlier you get a diagnosis and start the right type of treatment, the better the outcome will be.
Here are some other things to think about that might help you decide whether you need to see a doctor:
Read Also: How Do You Know If You Have Arthritis
What Is Arthritis Pain
When your pain comes from a body joint like the knees, ankles or fingers, it is called arthritis pain. There are many types of arthritis , but the most common type is known as arthrosis. This is a degenerative disease of the joints that results in the cartilage wearing down. It normally develops as we grow older, and causes a pain that returns often.
If you suffer from arthrosis, you may find:
- that this pain appears following a period of inactivity
- a tenderness when you touch the joint
- joint stiffness
- discomfort during fluctuations in temperature.
Other types of arthritis, as with rheumatoid polyarthritis, also cause inflammation in addition to pain.
Arthritis Treatment: Occupational Therapy

Protecting your joints is an important part of arthritis treatment. With the help of an occupational therapist, you can learn easier ways to do your normal activities. An occupational therapist can teach you how to:
- Avoid positions that strain your joints
- Use your strongest joints and muscles while sparing weaker ones
- Provide braces or supports to protect certain joints
- Use grab bars in the bath
- Use modified doorknobs, canes, or walkers
- Use devices to help you with tasks such as opening jars or pulling up socks and zippers
Read Also: Is Heat Good For Arthritis In The Knee
It’s Easy To Get The Care You Need
See a Premier Physician Network provider near you.
Both cause stiff, painful joints. Both are types of arthritis. Other than that,rheumatoid arthritis andosteoarthritis share little in common.
Their differences begin with what causes them. Osteoarthritis is more commonly occurs later in life, after years of mechanical wear and tear on the cartilage which lines and cushions your joints. Rheumatoid arthritis, which can occur at most any age, is anautoimmune disease. That is, your body’s immune system attacks your joints.
Dr. Michael Raab explains the differences of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Click play to watch the video or read video transcript.
What is arthritis?
Here are other important things to know about the key differences between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Pain Or Muscle Pain: How To Tell The Difference
As a Good Samaritan, you helped your neighbour who was moving his couch up to the third floor. The result: your back is throbbing with pain.
Most active people sometimes come up against a few obstacles that can temporarily affect their ability to move and require taking pain medication. A wrong move, a fall or an injury are a few events that can be a source of muscle pain or inflammation. When these events occur, it seems a lot of us line up to read the dizzying selection of product packages on display in the analgesics and anti-inflammatory section at the pharmacy. Faced with such a wide choice of products, it is normal to get confused, especially when we are not exactly certain just what kind of pain is bothering us.
You May Like: How To Reduce Arthritis Pain In Back
Risk Factors For Knee Arthritis
- Age. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative, wear and tear condition. The older you are, the more likely you are to have worn-down knee joint cartilage.
- Heredity. Slight joint defects or double-jointedness and genetic defects may contribute to osteoarthritis in the knee.
- Excess weight. Being overweight or obese puts additional stress on the knees over time.
- Injury. Severe injury or repeated injury to the knee can lead to osteoarthritis years later.
- Overuse. Jobs and sports that require physically repetitive motions that place stress on the knee can increase risk for developing osteoarthritis.
- Gender. Postmenopausal women are more likely to have osteoarthritis than men.
- Autoimmune triggers. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unknown, triggers of autoimmune diseases are still an area of active investigation.
- Developmental abnormalities. Deformities such as knock knee and bowleg place higher than normal stress on certain parts of the knee joint and can wear away cartilage in those areas.
- Other health conditions. People with diabetes, high cholesterol, hemochromatosis and vitamin D deficiency are more likely to have osteoarthritis.
Difference Between Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are several different types of arthritis. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are two of the most common forms. Although the symptoms of these two types of arthritis can be similar, it’s very important to distinguish between them in order to determine the proper treatment.
At the University of Michigan Health System, our experienced rheumatologists will do appropriate tests to determine which type of arthritis you have. Then we will develop an effective treatment plan and will explain your options.
Osteoarthritis occurs when the smooth cartilage joint surface wears out. Osteoarthritis usually begins in an isolated joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system malfunctions and attacks the body instead of intruders. In this case, it attacks the synovial membrane that encases and protects the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis often targets several joints at one time. The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- the symmetrical nature of the disease ,
- fever
Also Check: How Dangerous Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Can Imaging Exams Detect Arthritis
Imaging exams can help your healthcare provider get a clear picture of your bones, joints and soft tissues. An X-ray, MRI or ultrasound can reveal:
- Bone fractures or dislocations that may be causing you joint pain.
- Cartilage breakdown around your joints.
- Muscle, ligament or tendon injuries near your joints.
- Soft tissue inflammation.
What Happens When Someone Has Jia
People with JIA may have pain and stiffness that can change from day to day or from morning to afternoon. These symptoms can come and go. When the condition becomes more active and the symptoms worsen, it’s known as a “flare” or a “flare-up.”
JIA often causes only minor problems, but in some cases it can cause serious joint damage or limit growth. Although JIA mostly affects the joints and surrounding tissues, it can also affect other organs, like the eyes, liver, heart, and lungs.
JIA is a condition, meaning it can last for months and years. Sometimes the symptoms just go away with treatment, which is known as remission. Remission may last for months, years, or a person’s lifetime. In fact, many teens with JIA eventually enter full remission with little or no permanent joint damage.
Page two
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Arthritis In Your Back
Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis also causes pain and swelling in the joints. Usually, the small joints of the fingers and toes are affected first. The most common symptom is stiffness, and it takes a long time to get the joints moving, especially in the morning.
The disease is symmetrical, meaning that if your left index finger is swollen and painful, youll usually have the same symptoms in the right index finger.
Rheumatoid arthritis can be systemic, meaning it can also affect the whole body.
Other non-joint symptoms can include:
- shortness of breath
Initial Ra Signs: What Are The First Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis

Jump to:RA StatisticsRA CausesSigns and SymptomsLiving with RA
You just hit your early 30s. You notice that it is harder to get up every morning than it was even five years ago. Theres a general feeling of stiffness over your entire body that you can never quite escape. You initially wrote it off as just an unfortunate part of the aging process , but now youre starting to think there may be something more serious going on.
Youve also started losing weight, but not because you are dieting nor exercising. You originally thought it was because of you have no appetite or real interest in food, but even when you DO eat it seems to have no effect on your weight. All of this has contributed to a sense of depression something that youve never had to deal with previously. Unfortunately, there IS something serious going on. These are just a few of the major early signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis .
RA is a long-term autoimmune disorder that typically affects a persons joints. What usually begins as a warm feeling or swollen hands can quickly turn into pain that just wont go away. Internally, the disease can also manifest itself as a low red blood cell count, inflammation of the lungs or even inflammation of the heart.
A crucial part of seeking appropriate medical treatment as quickly as possible involves knowing what to look for and what to be concerned about. Most importantly, it is essential to know when things are getting serious.
Also Check: Is Red Meat Bad For Arthritis