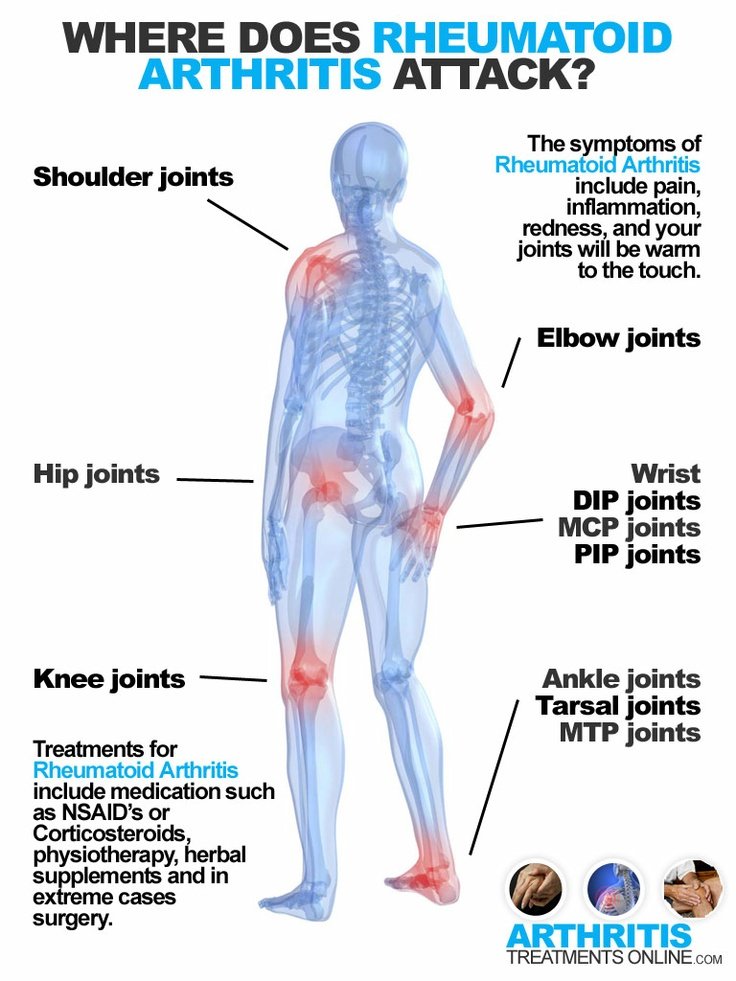
Knee And Hip Exercises For Osteoarthritis
If you have osteoarthritis in your hips or knees, exercising may be the last thing you feel like doing. Symptoms like pain and stiffness in your joints can make it tough to work out.
But moving is important for hip and knee OA. It causes your joints to compress and release, bringing blood flow, nutrients, and oxygen into the cartilage. âThis can help prolong the function and longevity of your joints,â says Eric Robertson, DPT, a physical therapist and associate professor of clinical physical therapy at the University of Southern California.
Physical activity can also help you feel better. âAlong with boosting your overall health, exercise can improve your OA symptomsâ like pain, stiffness, fatigue, and even depression, says Leigh F. Callahan, PhD, associate director of the University of North Carolina Thurston Arthritis Research Center. One study found that people with knee OA who worked out regularly lowered their pain by 12% compared to those who didnât.
Ready to lace up your sneakers? No single workout is best. But some moves are better for hip and knee OA. Experts recommend doing a mix of the following three exercises. But first, remember to check in with your doctor before you start any new physical activity.
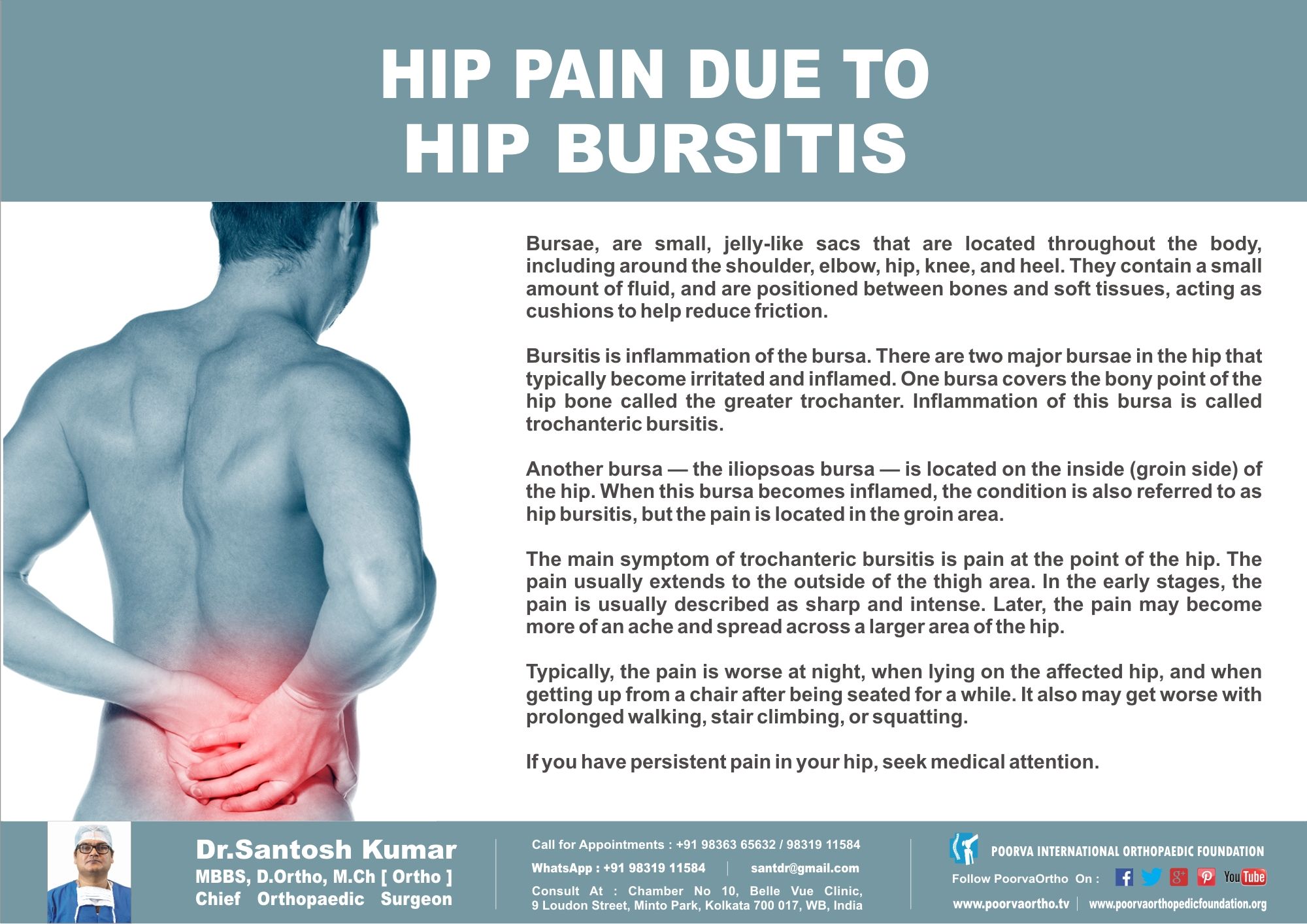
Start With Conservative Hip Pain Treatment
When youre first diagnosed with hip arthritis, Dr. Bauman says, You want to try conservative measures before even considering surgery. These include:
- Activity modification
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Advil, Aleve, and ibuprofen
- Injections into the hip joint
- Physical therapy
Dr. Bauman adds, Weight loss is oftentimes helpful in alleviating some of the pain of hip arthritis because any loss is weight thats not going through your joint when you go up and down stairs. While losing weight may slow some of the effects, it wont reverse damage caused by arthritis.
While theres no evidence that physical therapy limits the progression of arthritis or delays the need for surgery, physical therapy can help maintain strength in muscles that support the joint.
Dr. Ryan Bauman talks about conservative, nonsurgical treatment measures for hip pain.
Surgical treatment methods are only considered after all nonsurgical options have been tried without success.
When To See A Doctor
Most of the time you can treat your hip pain yourself with simple self-help treatments. If your pain is extremely bad or hasnt improved after two weeks of regularly taking painkillers, you should see your doctor.
You should see your doctor straight away if:
- youve had a fall or injured your hip
- the pain is getting worse
- youre having difficulty with daily activities, for example walking, going up stairs or leaning forwards when sitting
- you feel feverish or unwell, or youve been losing weight.
You May Like: Finger Arthritis Relief
What Tests Are There
X-rays
X-rays are often the best way of finding out whats wrong with your hip as they show the condition of the bones. They may also show problems in your pelvis which could explain your pain. Theyre not as useful for looking at the soft tissues around the joint.
CT scans
A CT scan can often be very helpful to work out if the hip joint has an unusual shape. CT scans use x-rays to show sections or slices of the hip, which a computer then puts together to form a 3D image of the hip.
There are conditions where the socket of the hip can be very shallow, and a CT scan can show this.
MRI scans
MRI scans use radio waves to build a picture to show whats happening to the soft tissue, such as the muscles and tendons, inside your hip. Theyre particularly helpful for diagnosing the painful condition avascular necrosis, which reduces the flow of blood to the ends of bone, causing them to collapse .
Blood tests
If your doctor thinks your pain is caused by an infection or rheumatoid arthritis, blood tests can often help.
Stage 4 Hip Osteoarthritis
Since osteoarthritis is a progressive illness, eventually you may experience Stage 4 osteoarthritis in one or both hips. At this point, the cartilage would have become so thin and brittle and the synovial fluid so diminished that you experience pain and stiffness most of the time, even when youre not moving. Sometimes the pain can be very severe and can make it difficult for you to complete even the simplest of tasks, and can keep you awake at night too.
Hopefully by this stage you have been seeing an orthopedic surgeon, because your quality of life can greatly improve with the help of the right physician. They can review your options with you, which may include surgery to replace some or all of the arthritic hip. The surgical procedures available today are very successful, with faster and easier recoveries than ever before, and you can be left with a hip free of arthritis and free of pain.
Read Also: Arthritis In Fingers Prevention
Basics Of Hip Arthritis
Many kinds of arthritis can affect the hip joint. The most common type of hip arthritis is osteoarthritis, which some people call “degenerative joint disease.”
Osteoarthritis occurs when the joint surface cartilage becomes worn away leaving the raw bone beneath exposed. The cartilage normally serves as a pad or a bearing in the joint. Under normal conditions, the cartilage bearing is slicker than a hockey puck on ice. When the bearing wears away, the result is a roughed joint surface that causes the pain and stiffness that people associate with osteoarthritis .
Osteoarthritis of the hip is a serious condition. Osteoarthritis is the most common of the more than 100 kinds of arthritis and the hip joint is the second most commonly affected large joint in the body.
Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease that can takes months to years to appear. While it is not curable, it most certainly is treatable using activity modifications, medications, and/or injections. If those interventions dont work, hip replacement surgery often will relieve the pain associated with hip arthritis.
Osteoarthritis of the hip results in pain, stiffness, and joint deformity. The symptoms of osteoarthritis can affect ones ability to walk, work, and enjoy life.
For most patients who have mild arthritis, pain can be managed with ice, rest, activity modifications, pills, or joint injections.
Risk Factors For Hip Arthritis
- Age. The older you are, the more likely you have worn out the cartilage in your hip joint.
- Excess weight. Being overweight or obese puts additional stress on the hips.
- Injury. Severe injury, such as a hip fracture or labral tears, can cause arthritis years later.
- Overuse. Jobs and sports that require physically repetitive motions that place stress on the hip can increase risk for developing osteoarthritis.
- Gender. Women who are postmenopausal are more likely to develop hip osteoarthritis than men. Rheumatoid arthritis affects women more than men.
- Structural or developmental abnormalities. Irregularly shaped bones forming the hip joint, such as with hip dysplasia and impingement, can lead to abnormal stress on the cartilage.
- Autoimmune triggers. While the causes of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis remain unknown, triggers of autoimmune diseases are an area of active investigation. For example, infection is believed to be one of the triggers for psoriasis.
- Genetics. Certain autoimmune conditions that lead to hip arthritis may run in the family.
- Other health conditions. People with diabetes, high cholesterol, hemochromatosis and vitamin D deficiency are more likely to develop osteoarthritis.
Also Check: Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Worse At Night
How Is Osteoarthritis Of The Spine Diagnosed
The best way to confirm a diagnosis of osteoarthritis is by X-ray. The doctor will take a medical history and perform a physical exam to see if the person has pain, tenderness, loss of motion involving the neck or lower back, or if symptoms are suggestive, signs of nerve involvement such as weakness, reflex changes, or loss of sensation.
The doctor may order certain tests to aid in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the spine. These tests include:
- X-rays to look for bone damage, bone spurs, and loss of cartilage or disc however, X-rays are not able to show early damage to cartilage.
- Blood tests to exclude other diseases
- Magnetic resonance imaging to show possible damage to discs or narrowing of areas where spinal nerves exit
Exercise And Physical Therapy
Exercise is essential for reducing the risk of osteoarthritis and slowing its progress. Exercise not only helps you manage your weight, but it also improves strength, flexibility, and mobility.
Low-impact exercises are less likely to put strain on a damaged joint. Experts strongly recommend tai chi for people with hip osteoarthritis.
Other options include:
Regular stretching can help relieve stiff, achy, or painful joints. Here are some tips to help you stretch safely:
- Start by asking a physical therapist for suggestions and guidance.
- Do all stretches gently and build up flexibility slowly.
- Stop if you feel pain.
- Increase intensity slowly.
If you dont feel pain after the first few days of an activity, gradually spend more time on it. At first, you may find it hard to stretch very far, but your flexibility will increase over time, as you practice.
Here are a few possible stretches:
Forward fold
Start with your feet shoulder-width apart or sit in a chair. Slowly lean forward, keeping your upper body relaxed. You should feel the stretch in your hips and lower back.
Knee pull
Lie on your back. Pull your bent knee up toward your chest until you feel a stretch. If your body allows it, use your other leg to deepen the stretch.
Extended leg balance
This is the same exercise as the knee pull, but you start from a standing position. Place one hand along the wall for support.
Cobra
Here are some other stretches you can ask your healthcare provider about:
- standing hip flexors
Don’t Miss: Are Eggs Bad For Psoriatic Arthritis
How To Know If You Have Hip Arthritis
Having problems with one particular routine task is a common giveaway that hip arthritis is affecting your life: putting on your socks and shoes. You need an adequate range of motion in your hips to put your foot up on your opposing leg to put on your shoes and socks. People with hip arthritis tend to lose the range of motion in the hips. Problems putting on your socks and shoes are not always associated with pain but rather just becomes more difficult to do.
You can also tell how long you have been affected by hip arthritis by looking back at how long you have been having problems putting on your socks and shoes. Hip arthritis can onset rapidly and deteriorate the range of motion in the hips quickly. A patient can go from seeing no signs to needing a hip replacement in less than 24 months.
While that is a common symptom, there are many others that a person could be experiencing. Regardless of the type of arthritis, other signs of hip arthritis can include:
- Pain in the groin or thigh that radiates to your knee, outer thigh or buttocks.
- Pain that is worse in the morning or after sitting for a while.
- Flare ups after vigorous activity.
- Limping or pain that causes difficulty walking.
- Sticking or locking of the hip joint.
- Difficulty getting out of a car.
- Pain when leaning over.
- Grinding noises during movement.
- Increased pain in rainy weather.
Do Drugs The Right Way
Take your medication just as your doctor prescribes. Call your doctor first if youre tempted to stop because you feel its not working or believe its causing side effects. It can take weeks or even months for a medication’s full benefits to become apparent, and some side effects ease over time. Stopping medication abruptly may not only cause you to miss out on its benefits in some cases, but it can also be downright dangerous.
You May Like: What Arthritis Mean
Eating Right Nourishes Joints
Eating a healthy diet is good for your joints, because it helps build strong bones and muscles.
For your bones, make sure you get enough calcium every day. You can do this by eating foods such as milk, yogurt, broccoli, kale, figs, and fortified foods like soy or almond milk. If those foods don’t tempt your taste buds, ask your doctor if calciumsupplements are right for you.
For your muscles, you need to get enough protein. Exactly how much you need depends on your age, sex, and how active you are. Most Americans get enough protein. Good sources include lean meats, seafood, beans, legumes, soy products, and nuts. Go for a variety.
You also need vitamin D to keep your bones and joints in good health. Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium from the foods you eat. Dairy products. many cereals, soy milk, and almond milk are fortified with vitamin D. You can ask your doctor about the proper amount of vitamin D and ways you can get it.
Oranges may also give your joints a healthy boost. Some studies suggest that vitamin C and other antioxidants can help keep your joints healthy.
Show Sources
Whos Most At Risk Of Osteoarthritis
Thats hard to say, says orthopedic surgeon Ryan Bauman, MD. But, he adds, Its a very common problem that affects many people. And specifically with hip arthritis, theres not a direct correlation that patients who are overweight or obese are at an increased risk compared to someone of normal weight. Arthritis can run in families, and trauma or previous hip injuries can increase risk of arthritis later in life.
Dr. Ryan Bauman explains who may be at risk of developing arthritis.
Click play to watch the video or read video transcript.
Who is at risk for osteoarthritis?
It’s difficult to know who is actually at risk for arthritis, it’s a very common problem that affects many people and specifically with hip arthritis there’s not a direct correlation that patients that are overweight or obese are at an increased risk compared to someone of normal weight. Oftentimes arthritis runs in families, such that people that have relatives that have had arthritis are oftentimes at risk. Additionally things like trauma or previous hip injuries such as labral tears or other injuries to your hip in your adolescence or teenage years can put you at risk for arthritis later in life.
Read Also: What Is The Best Painkiller For Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Is Dry Needling
Dry needling is an effective and efficient technique for the treatment of muscular pain and myofascial dysfunction. Dry needling or intramuscular stimulation is a technique that Dr Chan Gunn developed. Dry needling is a beneficial method to relax overactive muscles.
In simple terms, the treatment involves the needling of a muscle’s trigger points without injecting any substance. Western anatomical and neurophysiological principles are the basis of dry needling. It should not be confused with the Traditional Chinese Medicine technique of acupuncture. However, since both dry needling and acupuncture utilise the same filament needles, the confusion is understandable.
In his IMS approach, Dr Chan Gunn and Dr Fischer, in his segmental approach to Dry Needling, strongly advocate the importance of clearing trigger points in both peripheral and spinal areas.
Dry needling trained health practitioners use dry needling daily for the treatment of muscular pain and dysfunction.
Know Your Limits For Your Joints’ Sake
Certain exercises and activities might just be too tough for your joints to handle at first. Go slow. Modify exercises that cause joint pain. Ask a trainer, physical therapist, or coach to help you with modifications. You will likely feel some muscle pain after working out for a few days, especially the second and third day. Listen to your body, and learn the difference between “threatening pain” and good muscle-building pain.
You May Like: Is Peanut Butter Bad For Arthritis
What You Need To Know
- There are several types of hip arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and post-traumatic arthritis.
- The causes of hip arthritis vary depending on the type. The most common cause is age-related wear and tear in the hip joint.
- Symptoms of hip arthritis may include pain in or near the hip joint, stiffness, audible clicking sounds when moving the hip, and weakness.
- While hip arthritis is usually a chronic condition, there are treatments to help ease the symptoms and reduce further damage. If your quality of life suffers, surgery such as hip replacement can provide long-term relief.
Treatment Options For Ra In The Hip
Theres no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but treatment is available to reduce inflammation and stop the progression of the disease.
The goal of treatment is to help you achieve remission, which is a period when symptoms disappear. Your treatment will depend on the nature and severity of your symptoms.
Also Check: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Affect Your Back
Why Should You Stretch
A British Medical Journal study found that pre-event stretching does not reduce the overall risk of injury. However, stretching reduces the risk of specific damage . These soft tissue injuries are common in both elite and recreational sportspeople. It seems reasonable and common sense that stretching may not prevent you from suffering a broken bone or a joint dislocation, but it could reduce your chance of a soft tissue injury.
The other main finding was that stretching reduces the risk of experiencing soreness, making exercising more enjoyable!
While sustained stretches in isolation may not be the answer, other studies have shown that warming up does reduce your injury rate. While there is no “absolutely proven”method of warming up yet, the preferred options appear to be a graduated progression to prepare you for your sport. In simple terms, warm-up steadily from gentle exercises that increase in intensity and speed as you progress through your warm-up period.
It makes common sense for you to warm things up slowly to start and then prepare with replicate skills to what you will require shortly on the field, at the end of your warm-up.
For more specific warm-up and injury prevention advice particular to your sport or work, please ask your physiotherapist to prescribe a warm-up and warm-down routine specific to you and your sport or physical activity.