Stretching Exercises For Knee Osteoarthritis
Stretching can help minimize the loss of flexibility in and around your knee. You want to make sure youre stretching your hamstrings, quads, calves and hip flexors to help address any stiffness you might feel, says Dr. Orlandi.
Examples include:
- Hamstring stretch. Stand in front of a chair or steps. Place your right foot on the chair or step, with your heel on the surface and toes pointed up. Slowly bend forward at the waist, keeping your back as straight as possible. You should feel the stretch in the back of your thigh. Hold for a few at least 10 seconds before returning to standing. Alternate feet and repeat 5-10 times.
- Quad stretch. While standing, bend your left leg back, bringing your heel toward your butt. Grab your foot with your left hand and hold. Try to bring your left thigh back until its even with your right thigh. Hold for at least 10 seconds. Alternate legs and repeat 5-10 times.
- Calf raises. Stand on a step with your heels hanging over the edge. Rise up on your toes and then slowly drop your heels down until theyre below the level of the step. Hold for at least 10 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
Give yoga a try, too, to keep your joints and muscles in tip-top shape.
Inflammatory Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis: Causes And Symptoms
Arthritis actually describes over 100 different conditions that affect joints and the surrounding tissue. They fall into two main categories: inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis .
Inflammatory arthritis is a systemic disease in which the mechanisms that normally protect your body attack your own joints and tissues instead. The most well-known example is rheumatoid arthritis its hallmark symptom is prolonged stiffness and achiness in the morning after waking up. RA also tends to be symmetrical, meaning you’ll have problems in the same joints on both sides of your body, like both wrists or both knees.
The second type of arthritis and the most common form is osteoarthritis. A degenerative disorder, it’s caused by trauma or age-related wear and tear on your joints over time. Osteoarthritis is most likely to affect weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hip, lower spine or big toe, but it can also cause pain and stiffness in your thumb or finger joints.
Cartilage Loss/joint Space Narrowing
Cartilage loss is one of the primary markers used in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis. People with knee osteoarthritis can experience close to double the amount of degradation compared to the level of cartilage loss in a healthy knee over the same period of time. This cartilage loss causes the space between bones in the knee joint to narrow and can lead to bone-on-bone contact in the knee, often causing severe pain and discomfort. The rate of cartilage loss varies widely among individuals so it is difficult to predict how quickly it will wear away for any one person. During everyday activities like walking, crouching, or getting up from a seated position the forces acting at the points of contact between the joints can be up to three times greater than body weight. During a squat, this number approached seven times body weight. When the bones no longer have the cushioning provided by cartilage this can cause intense pain during these activities.
Also Check: Is Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
Types Of Arthritis That Affect The Knee
Osteoarthritis is characterized by cartilage degeneration and bony protrusions called osteophytes . In the knee, the most common sites of osteoarthritis include the tibia , femur , and patella .
The most common type of arthritis affecting the knee is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis occurs when a joints articular cartilage breaks down. In the knee, articular cartilage covers the top of the tibia , bottom of the femur , and back of the patella .
Not everyone with knee osteoarthritis will get knee pain. Pain may occur if the loss of healthy cartilage:
- Causes the bones of the joint to rub against one another.
- Compromises the joints biomechanics in some other way.
See Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Post-traumatic knee arthritisPost-traumatic arthritis is a type of osteoarthritis. It develops after a meniscus tear, ligament injury, or other trauma. The injury may heal but wear-and-tear on the articular cartilage can accelerate. Post-traumatic arthritis may not become symptomatic until years after the injury.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that targets the synovial membrane surrounding many joints of the body. Some of the most common areas affected include the wrists, knees, and ankles.
Knee pain can be caused by an autoimmune disease called rheumatoid arthritis . RA causes joint inflammation that can make the knee feel swollen, stiff, warm, and painful. Over time, untreated RA can cause permanent knee joint damage.
See What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis ?
What Conditions Do Cortisone Shots In The Knee Work For

Corticosteroids are used to treat a variety of knee conditions such as tendonitis, bursitis, and osteoarthritis .1 The first thing to note is that they are not considered a permanent solution. Corticosteroids can provide short term relief from knee pain but over time the beneficial effects will wear off. Because of this, the utility of corticosteroid injections is very situational. Professional athletes will often get injections to make it through key games during their season. Someone planning a long multi-week vacation may receive an injection to maximize mobility during their leisure time. Regardless of the cause of your knee pain, you should weigh the pros and cons of cortisone injections before deciding on treatment.
Learn more about other treatments for knee arthritis
Recommended Reading: Is Banana Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
You Arent Exercising Which Is Bad For Your Knees
It may seem counterintuitive to exercise if you have joint pain, but the Arthritis Foundation tells people to be active. The knee joint loves motion, says Brian Halpern, MD, a sports medicine physician with the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City and author of The Knee Crisis Handbook. The challenge is to find the best types of activities for you. Dr. Halpern recommends bicycling, swimming, and elliptical trainers, as well as strengthening exercises that help muscles support the knee joint.
Skipping Stretching Is Bad
Regular stretching improves flexibility and eases joint pain. If you do not warm up or stretch before work outs, now is the time to start. It will strengthen muscles and tendons, lubricate joints, and boost your ability to have normal range-of-motion. Ultimately, strong muscles support joint stability, so stretching is a good way to maintain your joint health. Warm up before exercise by doing dynamic or active stretching. This involves doing movements that are similar to those used in the activity or sport that you will be doing. Active stretching boosts blood flow, increases muscle temperature, and gets muscles ready for activity.
Also Check: Are Eggs Bad For Psoriatic Arthritis
Visit A Physical Therapist
Physical therapists work with your doctor to design specific exercises for knee rehabilitation. Many of these will focus on lengthening and strengthening the supporting muscles of the upper and lower legs, such as quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves.
Even one visit to learn the proper form for knee arthritis exercises can help support your recovery.
What Other Alternatives Are There
Other Pharmacological Treatments: There are other types of injections for the knee joint such as hyaluronic acid and Platelet Rich Plasma that could provide a similar benefit. Various prescription and over the counter oral anti-inflammatorydrugs can also provide quick relief from pain. However, many of them come with a high risk of adverse side-effects.
Non-Drug Treatments: If you are worried about the risk of negative side effects associated with injections and oral pain killers conservative treatmentmay be for you. The focus here is to avoid/delay surgery, get you off painkilling drugs and improve the health of your knee joint.
Offloader Knee Braces: If you have knee osteoarthritis and want to preserve what cartilage you have left, offloader knee braces could be the right fit for you. These knee braces actively reduce the pressure between the bones in your knee joint significantly reducing pain.
Read Also: Is Eating Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis
How To Practice Squatting
Squatting can help build leg and hip strength, leading to more stable joints. Over time, your range of motion will increase.
As long as youre able to practice with minimal knee joint discomfort, its safe to include squats in your exercise routine.
People with arthritis may find the most benefit in wall squats, since squatting against the wall can help reduce your risk of putting unnecessary or incorrect pressure on your knees.
To do a basic squat:
Keep the knee over the ankle and not over the ball of the foot, Bell cautions.
If you begin to experience intense pain at any point more than your typical knee pain you should stop the practice for the day.
Be sure to give the move another try during your next practice. Youll find that your pain threshold increases as you build up muscle strength.
Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
Knee OA is a very common source of pain that can limit your mobility.
Causes of Knee OA
The cause of OA is unknown. These risk factors make it more likely you will develop knee OA:
- Age: OA can occur at any time of life, but it is most common in older adults.
- Sex: Women are more likely to have knee OA than men.
- Obesity: Being overweight adds stress to your knees. Fat cells also make proteins that can cause inflammation in and around your joints.
- Injuries: Any knee injury, even old ones, can lead to knee OA.
- Repeated stress: Frequent stress on your knee from your job or playing sports can increase risk for OA.
- Genetics: You can inherit a tendency to develop OA.
- Bone deformities: If you have crooked bones or joints, you are at higher risk.
- Some metabolic diseases: Diabetes and hemochromatosis, a condition in which your blood has too much iron, have been linked to OA
Symptoms of knee OA develop slowly and worsen over time.
- Pain: Movement causes pain. Sometimes your knee will ache while sitting still.
- Stiffness: Your knees may be stiff first thing in the morning or after sitting for a long time.
- Loss of motion: Over time, you may lose the ability to bend and straighten your knee all the way.
- Creaking and grating : You may hear crackling noises or feel a grating sensation.
- Instability: Your knee may give out or buckle, or feel like it could.
- Locking: The knee may lock or stick.
- Swelling: Your knee may get puffy all around or on one side.
Your doctor will check for:
You May Like: Are Bananas Good For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Causes Of Fatigue In Arthritis
Inflammation, pain, inactivity and lifestyle factors can cause extreme tiredness when living with arthritis.
Everyone gets worn out from time to time. But exhaustion that disrupts your daily life and doesnt get better after a good nights sleep has its own medical term: fatigue. Fatigue significantly affects the quality of life for people with many forms of arthritis-related diseases, includingrheumatoid arthritis,psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthritis, lupus, fibromyalgia andosteoarthritis. Your lack of energy may be caused by your inflammatory disease and other health conditions you have, as well asmedications side effectsand lifestyle habits.
Exercising At Home Or Work
The best knee exercises may be the ones you can do at home or even during a break at the office. Theyre easy, effective, and convenient, and dont require any special equipment. Do them slowly and gradually increase the number of repetitions as your muscles get stronger.
Afterward, be sure to do a few gentle stretching exercises to help prevent your muscles from tightening up. Consider exercising your knees every other day to give sore muscles a rest.
Recommended Reading: What Helps Lower Back Arthritis
Do I Have Arthritis In My Knee
Dr. Ekaterina Urch, orthopedic surgeon and knee specialist, covers the symptoms, causes, and best treatment options for knee arthritis.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is the result of inflammation in one or more of your joints. This inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in various joints within the body and can even lead people to replacing their joints because the arthritis has interfered with their every-day activity level. This can be particularly true with arthritis felt in the knee, one of the more common areas where arthritis can occur. Depending on how bad the pain is, it can interfere with the activities people enjoy and can keep them from pursuing an active life.
What are the different types of arthritis?
Not all types of arthritis are created equal. In fact, there are more than 100 different forms of arthritis. However, the two more common types of arthritis include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, which is known as a degenerative wear-and-tear type of arthritis, is commonly found in the knee. It is rare for osteoarthritis to be found in younger people. It is more commonly found in people 50 years of age and older.
Why is osteoarthritis causing you so much pain?
Rheumatoid arthritis
Posttraumatic arthritis
Symptoms of knee arthritis:
Other symptoms of knee arthritis:
Nonsurgical treatment for knee arthritis:
Other nonsurgical options to help ease arthritis pain:
What Is Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most commonly diagnosed type of joint arthritis disease, which can affect hands, knees and hips. Knee arthritis is known to affect joint functionality causing knee pain and even leading to disability as it progresses. There are different stages of knee osteoarthritis , with 0 assigned to a normal, healthy knee right up to the advanced stage 4, that is severe OA.
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention has found that the number of people suffering from knee pain disorder is gradually rising, with approximately 1 in 2 people likely to develop symptomatic knee OA in their lifetime leading to significant impact on health, workplace productivity and economic costs.
OA pain is easily identifiable through diagnostics and common symptoms. Some people who suffer from immense osteoarthritis knee pain may only show mild changes on x-ray, so it is extremely important to concentrate on the symptoms, rather than just the x-rays. Here is a look at the stages of osteoarthritis of the knee ranging from normal, minor, mild, moderate and severe stages, with appropriate treatment plans.
Read Also: Are Tomatoes Bad For Arthritis Sufferers
What Is Knee Arthritis
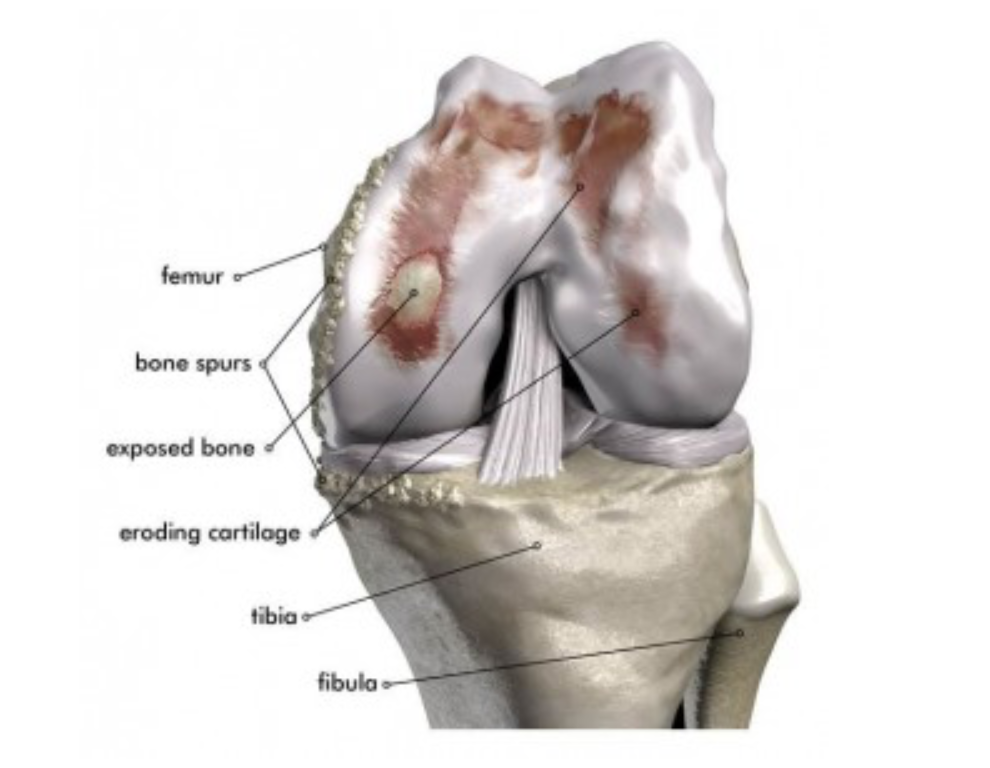
Knee arthritis is inflammation and deterioration of knee joint cartilage. Cartilage is the slippery coating on the ends of bones that serves as a cushion and allows the knee to smoothly bend and straighten. Knee cartilage coats the end of the thighbone , top of the shinbone and the backside of the kneecap . When cartilage wears away, the space between the bones narrows. In advanced arthritis, bone rubs on bone and bone spurs may form.
Damage to the joint cartilage over time may result in the development or worsening of deformities of the knee, including knock knees and bowleg.
How Is Oa Treated
There is no cure for OA, so doctors usually treat OA symptoms with a combination of therapies, which may include the following:
- Increasing physical activity
- Medications, including over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription drugs
- Supportive devices such as crutches or canes
- Surgery
In addition to these treatments, people can gain confidence in managing their OA with self-management strategies. These strategies help reduce pain and disability so people with osteoarthritis can pursue the activities that are important to them. These five simple and effective arthritis management strategies can help.
Physical Activity for Arthritis
Some people are concerned that physical activity will make their arthritis worse, but joint-friendly physical activity can actually improve arthritis pain, function, and quality of life.
Don’t Miss: Are Bananas Bad For Arthritis
Change In Synovial Fluid
Synovial fluid is the natural lubricant that fills the joint. It allows for smooth movements, keeps the joints separated, and acts as a filter for the joint allowing the passage of nutrients while keeping out harmful substances. In cases of severe knee osteoarthritis, the synovial fluid becomes more watery and less effective as a lubricant for the joint. This causes more friction and overall wear and tear and is one of the main contributors to the cartilage loss discussed above.
How Is Arthritis Of The Knee Treated
Healthcare providers can’t cure knee arthritis. But they have some tips that might reduce the severity of your symptoms and possibly stop the arthritis from getting worse, including:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise using low-impact activities instead of high-impact activities . Aim for about 150 minutes of exercise per week.
- Wear shock-absorbing inserts in your shoes.
- Apply heat or ice to the area.
- Wear a knee sleeve or brace.
- Physical therapy exercises that help with flexibility, strength and motion.
- Use a cane.
Most people have stage 4 arthritis when they get surgery.
You May Like: Bee Pollen For Arthritis
How To Practice Deep Lunging
For people with knee osteoarthritis, lunging poses the same benefits and risks as deep squatting.
Lunges are a great way to improve your overall leg and hip strength, but they may cause unnecessary pain when practiced incorrectly.
The trick, Bell says, is to make sure your knee doesnt extend past your ankle.
You may also find it helpful to practice lunges while holding on to the back of a chair or table for added support.
To do a basic lunge:
During your practice, its important that you take note of any changes in pain or discomfort. If you begin experiencing more pain than usual, you should stop lunging for the day and move on to another form of exercise.
Running can increase your overall wellness and help control weight. This can reduce the amount of stress on your knees and lessen the overall effect of osteoarthritis.
However, some caveats do apply:
No one with arthritis should start running, she says flatly.
To minimize symptoms: