Focusing On Negativity And Pessimism
Simply put, it takes a positive attitude, rather than a negative or pessimistic one, to achieve positive results. It is logical that you need a positive approach to stay on track with your treatment regimen, exercise routine, diet, and more. You must believe in the goal. In a study published in December 2018 in The Clinical Journal of Pain, researchers found that optimism and mental resilience were associated with less pain severity in people with or at risk forknee osteoarthritis.
RELATED: Catastrophizing About Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Can Make It Worse
Living With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong disease. When its treated, it may go away for a little while, but it usually comes back. Its important to see your doctor as soon as symptoms begin. The earlier you start treatment, the better your outcome. Some of the damage from RA is irreversible, so finding the disease and treating it early is very important.
If left untreated, RA can cause other health problems. Your hands may become bent or twisted. Other joints can become deformed. Inflammation will affect your cartilage and bones. Lung and heart problems also can occur. Talk to your doctor if you notice any new symptoms or problems.
What Is A Joint And How Does It Work
A joint is where two or more bones meet, such as in the fingers, knees, and shoulders. Joints hold bones in place and allow them to move freely within limits.
Most of the joints in our body are surrounded by a strong capsule. The capsule is filled with a thick fluid that helps to lubricate the joint. These capsules hold our bones in place. They do this with the help of ligaments. These are a bit like very strong elastic bands.
The ends of the bones within a joint are lined with cartilage. This is a smooth but tough layer of tissue that allows bones to glide over one another as you move.
If we want to move a bone, our brain gives a signal to the muscle, which then pulls a tendon, and this is attached to the bone. Muscles therefore have an important role in supporting a joint.
Don’t Miss: How To Help Arthritis In Hip
Who Should Diagnose And Treat Ra
A doctor or a team of doctors who specialize in care of RA patients should diagnose and treat RA. This is especially important because the signs and symptoms of RA are not specific and can look like signs and symptoms of other inflammatory joint diseases. Doctors who specialize in arthritis are called rheumatologists, and they can make the correct diagnosis. To find a provider near you, visit the database of rheumatologistsexternal icon on the American College of Rheumatology website.
Ra Progression: What Are The Signs Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Progression
If you suspect you have rheumatoid arthritis or have been recently diagnosed with RA, you will likely have lots of questions and be feeling uncertain about what this disease means for your future. What is the normal RA progression? Will my symptoms get worse? How can I manage the disease? Do I have to have a surgery?
These are all frequent questions asked by RA sufferers. The reality though is that each patient will experience a unique progression of this disease. RA progression depends on multiple unpredictable variables. Because it is still unclear exactly what triggers RA, it can be nearly impossible to predict an exact outcome.
Below is some general information about what to expect as well as the different stages of RA including the advanced condition known as progressive rheumatoid arthritis.
You May Like: What Do Doctors Prescribe For Arthritis Pain
Symptoms Of Progressive Rheumatoid Arthritis
Here are some general warning signs and symptoms that you may have developed progressive rheumatoid arthritis:
The active state of the disease is becoming more frequent Flare-ups are occurring regularly and lasting for longer periods of time Your pain and swelling are becoming more intense, spreading throughout other areas of your body Your diagnosis occurred early on, and so the disease has had a long time to develop You are beginning to develop rheumatoid nodules that you didnt have before Your blood tests show high levels of Rheumatoid Factor or anti-CCP
If you suspect that your rheumatoid arthritis has become progressive, consult your rheumatologist to determine the changes in your condition and discuss potential adjustments to your treatment plan.
Are There Any Complications
Osteoarthritis can develop over just a year or two, but more often its a slow process over many years that only causes fairly small changes in just part of the knee.
But in some cases, the cartilage can become so thin that it no longer covers the ends of the bones. This causes them to rub against each other and eventually wear away.
The loss of cartilage, the wearing of the bones, and the bony spurs can change the shape of the joint. This forces the bones out of their normal positions, making your knee feel unstable and painful.
Some people with osteoarthritis find a lump appears at the back of their knee. This is called a Bakers cyst or popliteal cyst.
A Bakers cyst is fluid-filled swelling at the back of the knee that happens when part of the joint lining bulges through a small tear in the joint capsule. This can then cause joint fluid to be trapped in the bulge.
It can happen on its own, but is more likely in a knee thats already affected by arthritis. A Bakers cyst doesnt always cause pain, but sometimes they can burst so the fluid leaks down into your calf, causing sharp pain, swelling and redness in the calf.
Osteoarthritis in the knee might change the way you walk or carry your weight, and this could cause you to develop the condition in other joints, such as your hips.
You May Like: Can Arthroscopic Surgery Help Knee Arthritis
The Treatment Of Early Ra
The time frames within which the effects of therapy have been studied in most trials of early intervention in RA have been somewhat arbitrarily defined and have been based on the principle of the earlier the better .
Most trials of early therapy have chosen a maximum symptom duration of 2 years. Therapeutic approaches studied to date have included intra-articular and systemic steroid, DMARD monotherapy, DMARD combination therapy and anti-TNF- therapy these approaches in each case were compared with less aggressive approaches to treatment.
Those studies that have shown benefit from early combination therapy have used steroids, albeit in different regimens.12,31,33 Steroids certainly allow a more rapid control of synovitis than conventional DMARDs, explaining their incorporation in step-down regimes. The use of steroid in the medium to long-term, however, remains controversial. Several studies suggest that oral steroids reduce the risk of development of erosions in patients with early RA39,40 and there is a clear biological rationale for this.41 However, data from the WOSERACT study does not support this clinical benefit.42
Therefore, even with potent regimens it appears unlikely that permanent drug-free remission can be induced in patients with established RA once symptoms have been present for more than 3 months.
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition, which means it is caused by the bodys immune system attacking itself. However, it is not yet known what triggers this.
Normally, your immune system makes antibodies that attack bacteria and viruses, helping fight infection. But if you have rheumatoid arthritis, your immune system mistakenly sends antibodies to the lining of your joints, where they attack the tissue surrounding the joint.
This causes the thin layer of cells covering your joints to become sore and inflamed.
This inflammation in turn causes chemicals to be released that thicken the synovium and damage nearby:
- National Rheumatoid Arthritis Society : Possible causes and risk factors
You May Like: What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis Flare Ups
Signs And Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis In Joints
RA inflammation in joints can usually be both observed and felt . Inflammation is usually worse in the morning, lasting for an hour or more after getting out of bed. It may get better with light to moderate activity but still persist throughout the day.
RA inflammation can cause a joint to be:
- Red in appearance
- Spongy or boggy when pressed
Joint involvement is usually symmetrical. For example, both the right and left wrists may be painful, stiff, and swollen.
Joint conditions directly related to RA inflammation include:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome, which can sometimes be caused by RA inflammation in the wrist.
- Tenosynovitis, particularly in the hand. Tenosynovitis is inflammation of the delicate synovial lining that surrounds a tendon. At least one study suggests that tenosynovitis of fingers flexor tendons is a strong predictor of rheumatoid arthritis.2Eshed I, Feist E, Althoff CE, et al. Tenosynovitis of the flexor tendons of the hand detected by MRI: an early indicator of rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatology 48 : 887-891 first published online May 27, 2009 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep136
- Rheumatoid nodules may form under the skin near joints. These nodules are firm bumps that range in size from pea-size to walnut-size and are mostly seen on or near elbows or fingers. Rheumatoid nodules are less likely to appear when RA is treated.
Symptoms can appear suddenly or gradually.
Difference In Life Expectancy Between Men And Women
Women are almost three times more likely to develop RA as men are. Symptoms seen in women are also typically more severe. To add insult to injury, the disease course for women can also be more progressive and can potentially involve more systemic complications.
Predicting a life expectancy for male patients with RA is difficult. While men typically dont experience the same severity of symptoms as women do, men already have a baseline higher risk of cardiovascular disease than women. When you add the diagnosis of RA, their risk for developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes increases even more than for women .
Recommended Reading: Does Hemp Oil Help Arthritis
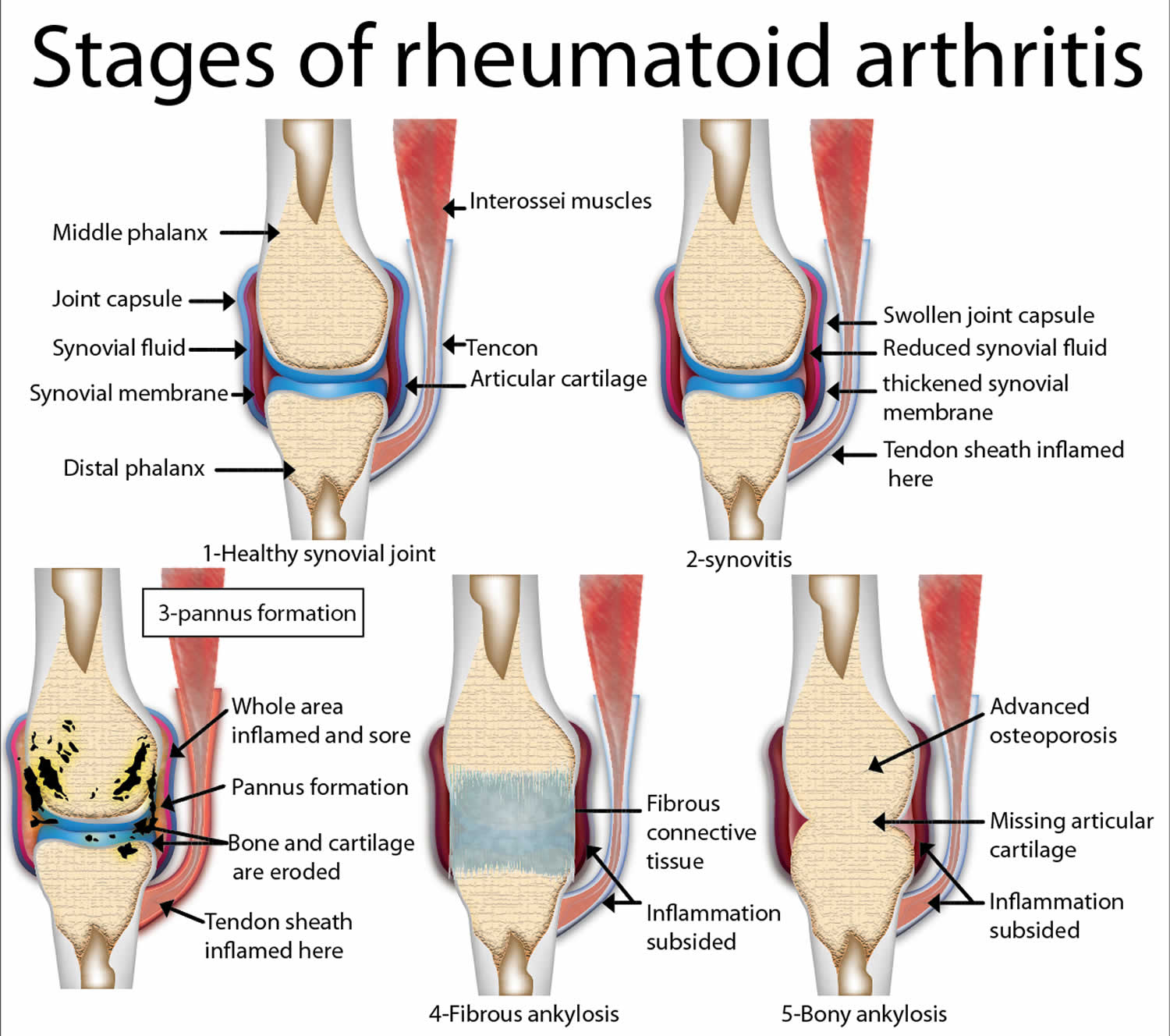
What Are The Four Stages Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stage 1: In early stage rheumatoid arthritis, the tissue around your joint is inflamed. You may have some pain and stiffness. If your provider ordered X-rays, they wouldnt see destructive changes in your bones.
- Stage 2: The inflammation has begun to damage the cartilage in your joints. You might notice stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
- Stage 3: The inflammation is so severe that it damages your bones. Youll have more pain, stiffness and even less range of motion than in stage 2, and you may start to see physical changes.
- Stage 4: In this stage, the inflammation stops but your joints keep getting worse. Youll have severe pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of mobility.
Get Foot Pain Relief With Arthritis
Need some foot pain relief? If you are older than 60, you may find yourself saying Oh, my aching feet! often. According to the Arthritis Foundation, close to half of people in their sixties and seventies suffer from arthritis foot pain. In fact, the damage starts even sooner: Beginning in your forties, your feet begin to show wear and tear, explains Dennis Frisch, a doctor of podiatric medicine in Boca Raton, Florida.
Arthritis is inflammation in or around the joints that results in swelling, pain, and stiffness. It can generally be divided in two categories:
- Osteoarthritis and other wear-and-tear types of arthritis
- Inflammatory arthritis
Osteoarthritis, the most common kind of arthritis, affects millions of people worldwide. This type of arthritis occurs over time and by overuse. The cartilage between the bones at your pivotal joints wears away. As a result, your bones grind against each other, causing pain and swelling. Very often osteoarthritis also causes degeneration of the cartilage at the base of your big toe, resulting in big toe joint pain. Bony spurs then develop at the joint there, followed by pain in the big toe and decreased motion of the joint.
Arthritis in the feet causes pain and a loss of strength, flexibility, or exercise ability. For millions of people with arthritis in the feet, simple daily tasks such as walking out to get the mail can be painful. Eventually, walking may become nearly impossible.
Recommended Reading: Is Tylenol Arthritis Good For Headaches
Joint Pain And Arthritis
Chronic pain caused by arthritis affects millions of people in the United States every year. About one in four adults with arthritis15 million peoplereport experiencing severe joint pain related to arthritis.1Additionally, nearly half of adults with arthritis have persistent pain.2
Children with arthritis have pain as well. There is limited information about pain in children in the general population.
Learn about statistics on arthritis-related severe joint pain in the United States, and recommended pain management strategies that can help people with arthritis control their pain.
Defining Pain
Severe joint pain: When an individual rates his or her pain as 7 or higher out of 10 on a scale of 0 to 10 .
Persistent pain: When an individual reports having pain on most or all days in the past 3 months.
Use Heat Or Cold Safely
- Use either heat or cold for only 15-20 minutes at a time. Let your skin return to its normal temperature before using another application.
- Always put a towel between your skin and any type of pack.
- Always follow the advice of your physical therapist or doctor carefully when using these methods especially heat.
- Check your skin before and after using heat or cold.
- Use milder temperatures for a childs skin because it is more sensitive than an adults skin.
Dont:
You May Like: What Medication For Arthritis Pain
Also Check: What Foods Not To Eat With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Interactions With Ra Medications
Another reason to limit or avoid drinking alcohol if you have RA is that alcohol interacts with some medications for RA. This means that if you drink alcohol and take those medications at the same time, you risk damaging your liver and experiencing unpleasant and sometimes dangerous side effects.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, which means that your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake, causing inflammation in the affected parts of the body.
RA mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees. In a joint with RA, the lining of the joint becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. This tissue damage can cause long-lasting or chronic pain, unsteadiness , and deformity .
RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes.
Also Check: What’s The Best Thing For Arthritis
Surgical Options For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Surgery is sometimes needed to fix damaged joints. The exact surgery you need will depend on the joint thats damaged and on the extent of the damage. Surgical options include:
- Arthroscopy and synovectomy. An arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that can be used to perform a synovectomy. A synovectomy is done to remove the inflamed lining of a joint.
- Tendon repair.Surgery can help fix tendons around your joints that are torn or loose.
- Joint replacement. A joint replacement removes the entire damaged joint and replaces it with an artificial joint.
Some people report that dietary changes help reduce their RA symptoms. This generally involves following an anti-inflammatory diet and avoiding foods high in sugar, artificial ingredients, and carbohydrates.
An anti-inflammatory diet includes foods such as:
that omega-3 fish oil supplements and turmeric are linked to a reduction in RA symptoms.
Talk with your doctor before you begin any supplements to make sure they wont negatively interact with your current prescriptions.
Key Facts On Rheumatoid Arthritis
- RA is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in the joints.
- RA causes inflammation, pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility.
- People usually experience the symptoms of RA in multiple joints on both sides of the body symmetrically.
- The symptoms tend to occur in cycles, so people have flare-ups that alternate with periods of remission.
- Over time, RA can lead to permanent joint damage.
RA is a chronic condition for which there is currently no cure. However, treatment can slow down the progression of the disease. It can also help reduce pain, make symptoms manageable, and prevent joint damage.
In this article, we look at RA in more detail, including the stages of progression and the factors that can influence it. We also discuss the outlook for people with RA and provide tips on how to improve the quality of life with this condition.
It is difficult to predict the exact effect that RA will have on a persons life expectancy because the course of the disease differs significantly among individuals.
However, one 2015 study showed that people with RA might have a 54% higher risk of mortality compared with people who do not have the condition.
Nevertheless, with the right treatment, many people can live past the age of 80 or even 90 years while experiencing relatively mild symptoms and only minor limitations on day-to-day life.
Recommended Reading: What Should You Eat If You Have Arthritis
Capturing Patients With Very Early Synovitis
Until relatively recently patients with RA were seen by rheumatologists many months after the onset of their symptoms. In the 1980s the median delay from symptom onset to referral to secondary care was over 20 months in a teaching hospital in Glasgow, UK.13 Over the last 20 years there has been a dramatic reduction in this delay between 199497 the median time from symptom onset to GP referral was 4 months and from GP referral to hospital clinic appointment was 1 month.13 Nevertheless, most patients with RA are still seen in rheumatology clinics more than 3 months after the onset of symptoms. Using a variety of strategies, early arthritis clinics have facilitated access of patients with early synovitis to rheumatological care. In Austria, for example, a nationwide public information campaign encouraged patients with symptoms and signs of inflammatory arthritis to contact their primary care provider.72 In Birmingham, UK, and Leiden, Holland, approaches have focused more on the primary care providers, who have been targeted with regular letters highlighting the importance of early referral, and on workshops focusing on the recognition of early synovitis. In addition, the primary care teams have been provided with a rapid-access system through which patients are evaluated by a rheumatologist within 12 weeks of referral.73,74