How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Managed
You can manage rheumatoid arthritis by taking medicines as prescribed to treat pain and joint inflammation. You can also help reduce symptoms by exercising and maintaining a healthy weight. Aim to do 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This can be at one time or broken up into shorter sessions.
You may also need to make changes at home to help you manage daily tasks like cleaning or gardening. An occupational therapist can help you make adjustments if pain or joint stiffness makes certain tasks hard to complete. They can recommend tools to reduce strain on your joints, such as long-handled dustpans so you dont need to bend over, or book holders to reduce the strain on your hands and wrists.
You might find that rheumatoid arthritis makes you frustrated and upset. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause poor sleep, which can also make you feel down. Discus your feelings with friends and family and explain to them what they can do to support you. This may help you feel better and reassured that help is available, if needed. If you are struggling with a low mood or not managing to sleep, your doctor will be able to support you and work with you to build a plan to help.
Research On Rheumatoid Arthritis
In the last decade, much research has been conducted to increase our understanding of the immune system and what makes it malfunction. There have also been new therapies developed to help treat the disease. Some of the topics of intense research include:
What are the genetic factors that predispose people to develop rheumatoid arthritis?
Some white blood cells, commonly known as T cells, are important in maintaining a healthy and properly functioning immune system. However, scientists have discovered a variationcalled single nucleotide polymorphism in a gene that controls T cells. When the SNP gene variation is present, T cells attempt to correct abnormalities in joints too quickly, causing the inflammation and tissue damage associated with RA. The discovery of SNP may help determine peoples risk for getting RA and might help explain why autoimmune diseases run in families.
At conception, twins have an identical set of genes. So why would only one twin develop RA?
Can Any Other Tests Show The Difference Between Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Yes. Depending on what your exam and X-rays show, your provider might order blood tests, too. Because RA is an inflammatory, autoimmune disease, there are certain things to look for in the blood. These include markers of inflammation and autoantibodies. They are not present in OA.
Additionally, if you have swelling in a large joint , your provider might need to remove some fluid and send it for testing. This can also give clues to whether its RA or OA.
Don’t Miss: Rash From Rheumatoid Arthritis
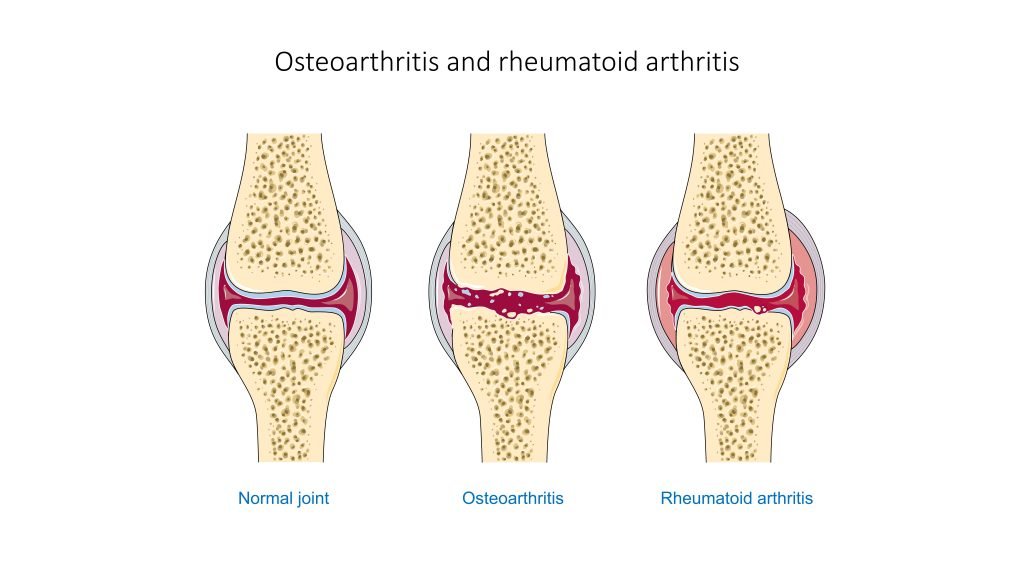
Difference Between Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are several different types of arthritis. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are two of the most common forms. Although the symptoms of these two types of arthritis can be similar, it’s very important to distinguish between them in order to determine the proper treatment.
At the University of Michigan Health System, our experienced rheumatologists will do appropriate tests to determine which type of arthritis you have. Then we will develop an effective treatment plan and will explain your options.
Osteoarthritis occurs when the smooth cartilage joint surface wears out. Osteoarthritis usually begins in an isolated joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system malfunctions and attacks the body instead of intruders. In this case, it attacks the synovial membrane that encases and protects the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis often targets several joints at one time. The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- the symmetrical nature of the disease ,
- fever
Joint Pain: Where It Hurts Most
RA It can affect the entire body or just specific joints, most commonly the hands, wrists, fingers, elbows, knees, feet, and hips. Sometimes what is noticed first is the stiffness in the morning. The synovium, or the lining of the joint, is most affected.
OA It affects only a particular joint, and the pain doesn’t go away without physical or medical therapy. The joint cartilage is what is worn away.
As OA progresses it can result in bony growths or spurs that can further compromise joints . Sometimes you can have joints that make noise that can be painful . It is also possible to get some radiating pain .
Also Check: Can You Get Rid Of Arthritis
Joint Pain & Tenderness
Typically, joint pain is felt during times when the disease is active and the inflammation is irritating the joint, ultimately causing the pain .
Conversely, pain can also be felt when the disease isnt active because of past damage that has been done to the joints in the body. This is similar to pain from old sports injuries in the elbows, knees, and other joints.
In addition to outright pain, RA patients may also notice that their joints feel tender to the touch. This occurs when the inflammation in the joint tissue has affected the nerves within the joint capsule. In this case, any pressure placed on the jointseven slight compression during sleepcan elicit immediate pain.
Pain and tenderness may be felt if arthritic disease has settled into the bones in the cervical spine the vertebrae in the neck area of the spinal cord, or more specifically in the atlanto-axial joint .
It is the pain associated with RA that sends many patients in search of effective treatment options. Fortunately, there are quite a fewmany of which include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs providing RA patients some much-needed pain relief.
Risk Factors For Osteoarthritis
There are certain factors that may increase your risk for osteoarthritis. Some are modifiable and others are not. Risk factors include:
- Family members with the condition, particularly a parent or sibling
- An occupation that involves repetitive actions, like kneeling, climbing, or heavy lifting
- Having another condition that affects joint health, such as other types of arthritis
- Being at least 50 years old
- Overweight or obesity
If you have osteoarthritis in one part of your body, you have an increased risk of developing it in other parts of the body.
You May Like: Does Ra Cause Back Pain
Significance Of The Study
-
Rheumatoid arthritis not only affects the joints but can also affect internal organs, thus causing permanent disability in many instances. Currently, there is no cure for this autoimmune disease, rather, symptoms are addressed on an individual basis. Here, we succinctly summarize the classic and current treatment options available for the management of patients suffering from this complex disease.
Summary Of Hip Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis of the hip is common and can result in severe hip joint pain and disability. as a result of this condition, several hundred thousand people each year in the U.S. undergo total hip replacement.
- Most people with osteoarthritis of the hip can be managed without surgery.
- The cause of osteoarthritis of the hip is not known but some risk factors include obesity, severe hip trauma, and acquired conditions in adulthood, such as osteonecrosis and genetics.
- There are many other kinds of arthritis that can affect the hip. It is important to make sure that the correct diagnosis is made as some of these other conditions are treated very differently.
- The diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the hip is usually very straightforward and is made in almost all cases by a physician taking a thorough history, performing a physical examination, and getting x-rays with the patient standing up.
- Patients usually seek care for the typical symptoms of hip arthritis, including pain located in the groin thigh or buttock. The pain associated with osteoarthritis of the hip is generally worse with weight bearing or twisting. Stiffness and leg-length inequality are other symptoms.
You May Like: Rheumatoid Arthritis Longterm Effects
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated
There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. But there are treatment options your doctor can prescribe to help manage your pain and stop further damage to your joints. Your doctor may recommend a combination of medicines, including:
- Pain relief medicines, such as paracetamol.
- Omega-3 supplements. This is a type of fat naturally found in foods such as certain fish that you can take as a food supplement to help with pain and stiffness.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or cyclo-oxygenase-2 selective inhibitors. These are pain relief medicines that your doctor might prescribe when paracetamol and supplements do not relieve your pain and stiffness.
- Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs , such as methotrexate. These are a group of medicines that reduce your symptoms and the damage to your joints, including medicines known as biologic DMARDS .
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisolone. These are medicines that can help manage your pain and stiffness during flare ups. Corticosteroids are available as tablets, or it might be injected by your doctor into a joint to reduce pain.
Other complementary treatments such as massage, acupuncture or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation can help reduce your pain. But they will not reduce the damage to your joints and should not replace your prescribed medications.
Tripterygium wilfordii is a Chinese herb that is not recommended to treat rheumatoid arthritis as it can have dangerous side effects.
The Pain Of These Two Conditions Affects More Than Just The Joints
As an autoimmune disease, rheumatoid arthritis has side effects beyond joint pain. To start, the same underlying inflammation that damages the joints can affect organs and systems throughout the body, causing an increased risk of heart disease, lung disease, and more.
Certain medications used to treat rheumatoid arthritis can affect kidney and liver function. RA and the medications that treat it also make me immunocompromised, which makes fighting infections more difficult.
The pain and mobility limitations of OA also take a toll on people. OA can cause sleep issues, for example, and social limitations. OA can force people to give up their favorite activities or need to stop working. And while OA doesnt necessarily cause these conditions, there are a number of co-occurring health problems that are common in OA patients and could affect how it is able to be treated, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes.
Read Also: Psoriatic Arthritis Hives
Risk Factors For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Like osteoarthritis, there are several factors that can increase your risk of RA, including:
- Age Although RA can develop at any age, the likelihood increases with age. The onset of RA is highest for people in their sixties. When it starts between the ages of 60 and 65, its called elderly-onset RA or late-onset RA. Women and men get elderly-onset RA at nearly the same rate.
- Gender Women are two to three times more likely to develop RA than men. About 75% of RA patients are women.
- Smoking and exposure to smoke Studies have shown that cigarette smoking not only increases the risk of developing RA, but can also make the disease worse. Children whose mothers smoked have double the risk of developing RA as adults.
- Obesity
- Being obese can increase the risk of developing RA. Being overweight can also make the medication less effective.
Another potential risk factor for women is a history of live births. Women who have never given birth may be at a greater risk of developing RA than women who have given birth. It has also been found that women who have breastfed their infants have a decreased risk of developing RA. While the reason for these associations is unclear, researchers believe there are long-lasting hormonal changes associated with pregnancy and breastfeeding that can affect the risk of RA.
Stop Thinking You Can’t Exercise
Many people who have arthritis are afraid if they’re active they’ll have more pain and so they just don’t get any exercise. This may be one of the biggest misconceptions about arthritis.
At the same time, it’s an ironic idea because inactivity actually makes pain and disability from arthritis worse over time, while regular exercise keeps joints moving and prevents stiffness, strengthens the muscles around the joints, and improves mobility.
So if you’ve been sedentary out of fear you’ll make your arthritis worse, talk to your healthcare provider to make sure it’s OK to exercise. Then start slowly with gentle, joint-friendly movements. It’s fine to respect your arthritis pain, but you don’t have to let it stop you.
Don’t Miss: Ease Arthritis Pain In Hands
What Is Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease in the world. In the United States alone, it affects one in seven adults, which equates to 32.5 million people. However, there are also many hidden cases, as most people have not had their joint pain diagnosed. This is because many people who live with joint pain believe that the symptoms accompanying osteoarthritissuch as stiff and painful jointsare a natural part of growing older. OA can affect all the joints in the body and is a lifelong disease that currently has no cure. However, there are high quality treatments available that can ease the symptoms.
Affected Joints In Ra
RA usually begins in the smaller joints. Youre likely to have pain, stiffness, and swelling in the finger joints. As RA progresses, symptoms can develop in larger joints such as knees, shoulders, and ankles.
RA is a symmetrical disease. That means youll experience symptoms on both sides of your body at the same time.
Also Check: Best Treatment For Arthritis In Fingers
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a less common inflammatory joint condition that affects multiple joints in the body. It is an autoimmune disease, which means that the bodys own immune system attacks the joint for reasons that are not fully understood. As RA is a systemic disease that affects multiple joints, it generally provides more symptoms than OA. These symptoms can take the form of generalized pain, more pronounced stiffness, and tiredness. Just like OA, RA is a chronic disease that cannot be cured. However, there are modern medications available that can slow down the disease before the joints become permanently damaged.
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Contribute To Dry Eyes
Q) I’ve suffered from dry eyes for a long time. I suffer from rheumatoid arthritis and had a hip replacement in 2000. I’ve tried all the remedies the NHS has to offer and have been on sulfasalazine and methotrexate for three years. Does rheumatoid arthritis contribute to dry eyes? Can you suggest a cure or anything to relieve the symptoms?
Gordon, Shetland – 2010
A) Dry eyes are a recognised feature of rheumatoid arthritis. The rheumatoid process can cause damage to the cells that produce the moisture for the eyes and mouth. This is called Sjögrens syndrome . At its most severe, this condition can lead to damage of the surface of the eye and visual impairment, so it’s important to seek help. Mostly, lubricant eye drops are used, but sometimes surgical solutions are necessary. These include putting a plug in the duct that drains the tears away. Lubricants can also be used for the mouth and a tablet called pilocarpine may help both eyes and mouth.
This answer was provided by Dr Philip Helliwell in 2010, and was correct at the time of publication.
You May Like: How To Stop Arthritis In Fingers From Getting Worse
What Are The Complications Of Ra
Rheumatoid arthritis has many physical and social consequences and can lower quality of life. It can cause pain, disability, and premature death.
- Premature heart disease. People with RA are also at a higher risk for developing other chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. To prevent people with RA from developing heart disease, treatment of RA also focuses on reducing heart disease risk factors. For example, doctors will advise patients with RA to stop smoking and lose weight.
- Obesity. People with RA who are obese have an increased risk of developing heart disease risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Being obese also increases risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. Finally, people with RA who are obese experience fewer benefits from their medical treatment compared with those with RA who are not obese.
- Employment. RA can make work difficult. Adults with RA are less likely to be employed than those who do not have RA. As the disease gets worse, many people with RA find they cannot do as much as they used to. Work loss among people with RA is highest among people whose jobs are physically demanding. Work loss is lower among those in jobs with few physical demands, or in jobs where they have influence over the job pace and activities.
What To Do If You Suspect You Have Osteoarthritis Or Rheumatoid Arthritis
If you suspect that you are affected by osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, you should visit your primary care physician or a rheumatologist. OA and RA are clinical diagnoses that are made by a doctor or physiotherapist. A clinical diagnosis means that the diagnosis is mainly made based on the patients typical medical history. Blood tests and X-rays are typically only used to confirm the diagnosis.
Read Also: Arthritis Remedies Hands
Osteoarthritis And Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
No matter which form of arthritis you have, it can cause pain, swelling, stiffness, loss of motion, and deformity . Once the arthritis becomes advanced, it can erode the joint cartilage enough to let bone rub against bone. This rubbing is usually painful because, unlike cartilage, bone contains nerves.
- Pain in the joint: Localized pain is the chief symptom of both OA and RA. In the early stages, the pain might be occasional, yet worsens with activity. Pain level can varydays or weeks of no pain followed by periods of continual discomfort.
- Loss of mobility: As arthritis advances, the mobility in the affected joint diminishes.
- Noisy joints: As cartilage is lost from the ends of your bones, the movement of bone against bone, or sliding of ligaments along bone, is no longer smooth and can cause clicking, grinding, or popping noises.
- Swelling around the joint: The irritation of bone rubbing against bone, or the inflammation of the joint lining and surrounding tissue due to a faulty immune response, can cause the joint to swell and become red and tender to the touch.
- Reduced strength: Because people with painful arthritis often limit their activity, the muscles, ligaments, and tendons around a joint dont get sufficient exercise, and muscle strength decreases.